Abstract
Context
Land use changes and intensification have been amongst the major causes of the on-going biodiversity decline in Europe. A better understanding and description of how different levels of land use intensity affect biodiversity can support the planning and evaluation of policy measures.
Objectives
Our study investigates how land use-related landscape characteristics affect bird diversity, considering different spatial scales and species groups with characteristic habitat use.
Methods
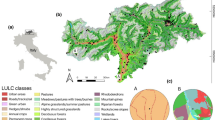
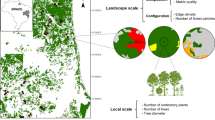
We used breeding bird census data from 2693 observation points along 206 transects and applied a random effects hurdle model to describe the influence of the landscape characteristics altitude, forest proportion, patch density, land cover diversity, and land use intensity on avian species richness.
Results
Land use intensity and related landscape characteristics formed an important explanatory variable for bird richness. Increasing land use intensity was accompanied by a decrease in bird species richness. While forest bird richness decreased with a decreasing amount of forest cover, farmland species richness increased. This led to a bird diversity peak in extensively used semi-open landscapes. The influence of land cover diversity on species richness was small. Increasing patch density had positive effects on forest birds, but affected farm birds negatively. The strongest correlation between land use-based indicators and bird diversity was determined using spatial indicators at a close range around observation points (100–500 m radius).
Conclusions
Our results assist interpretation of the Pan-European Common Bird Indices and emphasize the importance of using multifaceted and thoroughly selected indicators in the context of biodiversity monitoring and decision-making support.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1981) Likelihood of a model and information criteria. J Econom 16:3–14
Atauri JA, de Lucio JV (2001) The role of landscape structure in species richness distribution of birds, amphibians, reptiles and lepidopterans in Mediterranean landscapes. Landscape Ecol 16:147–159
Bar-Massada A, Wood EM, Pidgeon AM, Radeloff VC (2012) Complex effects of scale on the relationships of landscape pattern versus avian species richness and community structure in a woodland savanna mosaic. Ecography 35:393–411
Batary P, Baldi A, Kleijn D, Tscharntke T (2011) Landscape-moderated biodiversity effects of agri-environmental management: a meta-analysis. Proc R Soc B 278:1894–1902
Baudron F, Giller KE (2014) Agriculture and nature: trouble and strife? Biol Conserv 170:232–245
Benton TG, Vickery JA, Wilson JD (2003) Farmland biodiversity: is habitat heterogeneity the key? Trends Ecol Evol 18:182–188
Bibby C, Burgess N, Hill D, Mustoe S (2000) Bird census techniques. Academic Press, London
Böhning-Gaese K (1997) Determinants of avian species richness at different spatial scales. J Biogeogr 24:49–60
Bolker BM (2008) Ecological models and data in R. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Butler SJ, Brooks D, Feber RE, Storkey J, Vickery JA, Norris K (2009) A cross-taxonomic index for quantifying the health of farmland biodiversity. J Appl Ecol 46(6):1154–1162
Concepción ED, Díaz M, Baquero R (2008) Effects of landscape complexity on the ecological effectiveness of agri-environment schemes. Landscape Ecol 23:135–148
Concepción ED, Díaz M, Kleijn D, Báldi A, Batáry P, Clough Y, Gabriel D, Herzog F, Holzschuh A, Knop E, Marshall EJP, Tscharntke T, Verhulst J (2012) Interactive effects of landscape context constrain the effectiveness of local agri-environmental management. J Appl Ecol 49:695–705
Culman SW, Young-Mathews A, Hollander AD, Ferris H, Sanchez-Moreno S, O’Geen AT, Jackson LE (2010) Biodiversity is associated with indicators of soil ecosystem functions over a landscape gradient of agricultural intensification. Landscape Ecol 25:1333–1348
Cunningham RB, Lindenmayer DB (2005) Modeling count data of rare species: some statistical issues. Ecology 86:1135–1142
Desrochers RE, Kerr JT, Currie DJ (2011) How, and how much, natural cover loss increases species richness. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 20:857–867
Donald PF, Green RE, Heath MF (2001) Agricultural intensification and the collapse of Europe’s farmland bird populations. Proc R Soc B 268:25–29
Donald PF, Sanderson FJ, Burfield IJ, van Bommel FPJ (2006) Further evidence of continent-wide impacts of agricultural intensification on European farmland birds, 1990–2000. Agric Ecosyst Environ 116:189–196
Dullinger S, Essl F, Rabitsch W, Erb K, Gingrich S, Haberl H, Hülber K, Jarošík V, Krausmann F, Kühn I, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Hulme PE (2013) Europe’s other debt crisis caused by the long legacy of future extinctions. PNAS 110:7342–7347
European Environment Agency (EEA) (2007) CLC2006 technical guidelines. Technical report, Luxembourg
European Environment Agency (EEA) (2009) Progress towards the European 2010 biodiversity target. EEA Technical report 4. Office for Official Publication of the European Communities, Luxembourg
European Bird Census Council (2012) Report on the Pan-European common bird monitoring scheme. June 2012. http://www.ebcc.info. Accessed July 2014
Farina A (1997) Landscape structure and breeding bird distribution in a sub-Mediterranean agro-ecosystem. Landscape Ecol 12:365–378
Filippi-Codaccioni O, Devictor V, Bas Y, Julliard R (2010) Toward more concern for specialisation and less for species diversity in conserving farmland biodiversity. Biol Conserv 143:1493–1500
Frühauf J, Teufelbauer N (2006) Evaluierung des Einflusses von ÖPUL-Maßnahmen auf Vögel des Kulturlandes anhand von repräsentativen Monitoring-Daten: Zustand und Entwicklung: Studie von BirdLife Österreich für die ÖPUL-Halbzeit-Evaluierung (update) im Auftrag des BMLFUW, Wien
Frühauf J, Teufelbauer N (2008) Preparation of the Austrian Farmland bird index. Pilot study. Report on behalf of the Austrian Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management, Wien
Gonthier DJ, Ennis KK, Farinas S, Hsieh HY, Iverson AL, Batáry P, Rudolphi J, Tscharntke T, Cardinale BJ, Perfecto I (2014) Biodiversity conservation in agriculture requires a multi-scale approach. Proc R Soc B 281:20141358
Gotelli NJ, Colwell RK (2001) Quantifying biodiversity: procedures and pitfalls in the measurement and comparison of species richness. Ecol Lett 4:379–391
Gottschalk TK, Diekoetter T, Ekschmitt K, Weinmann B, Kuhlmann F, Purtauf T, Dauber J, Wolters V (2007) Impact of agricultural subsidies on biodiversity at the landscape level. Landscape Ecol 22:643–656
Gregory RD, van Strien A (2010) Wild bird indicators: using composite population trends of birds as measures of environmental health. Ornithol Sci 9:3–22
Gregory RD, van Strien A, Vorisek P, Meyling AWG, Noble DG, Foppen RPB, Gibbons DW (2005) Developing indicators for European birds. Phil Trans R Soc B 360:269–288
Haber W (2008) Biological diversity a concept going astray? GAIA—Ecol Perspect Sci Soc 17(Supplement 1):91–96
Huggett AJ (2005) The concept and utility of ‘ecological thresholds’ in biodiversity conservation. Biol Conserv 124:301–310
Kirchner M, Schmidt J, Kindermann G, Kulmer V, Mitter H, Prettenthaler F, Rüdisser J, Schauppenlehner T, Schönhart M, Strauss F, Tappeiner U, Tasser E, Schmid E (2015) Ecosystem services and economic development in Austrian agricultural landscapes—the impact of policy and climate change scenarios on trade-offs and synergies. Ecol Econ 109:161–174
Kleijn D, Rundlöf M, Scheper J, Smith HG, Tscharntke T (2011) Does conservation on farmland contribute to halting the biodiversity decline? Trends Ecol Evol 26:474–481
Koch AJ, Drever MC, Martin K (2011) The efficacy of common species as indicators: avian responses to disturbance in British Columbia, Canada. Biodivers Conserv 20:3555–3575
Krebs JR, Wilson JD, Bradbury RB, Siriwardena GM (1999) The second silent spring? Nature 400(6745):611–612
Loss SR, Ruiz MO, Brawn JD (2009) Relationships between avian diversity, neighborhood age, income, and environmental characteristics of an urban landscape. Biol Conserv 142:2578–2585
Martin TG, Wintle BA, Rhodes JR, Kuhnert PM, Field SA, Low-Choy SJ, Tyre AJ, Possingham HP (2005) Zero tolerance ecology: improving ecological inference by modelling the source of zero observations. Ecol Lett 8:1235–1246
McFadden D (1973) Conditional Logit analysis of qualitative choice behavior. In: Zarembka P (ed) Frontiers in econometrics. Academic Press, New York, pp 105–142
McGarigal K, Marks B (1995) FRAGSTATS: spatial pattern analysis program for quantifying landscape structure: U.S. Forest Service General Technical Report, Portland, OR
Nichols JD, Hines JE, Sauer JR, Fallon FW, Fallon JE, Heglund PJ (2000) A double-observer approach for estimating detection probability and abundance from point counts. Auk 117:393–408
Olson DM, Dinerstein E, Wikramanayake ED, Burgess ND, Powell GV, Underwood EC, D’Amico JA, Itoua I, Strand HE, Morrison JC, Loucks CJ, Allnutt TF, Ricketts TH, Kura Y, Lamoreux JF, Wettengel WW, Hedao P, Kassem KR (2001) Terrestrial ecoregions of the worlds: a new map of life on Earth. Bioscience 51:933–938
Pimentel D, Stachow U, Takacs DA, Brubaker HW, Dumas AR, Meaney JJ, O’Neil JAS, Onsi DE, Corzilius DB (1992) Conserving biological diversity in agricultural/forestry systems. Bioscience 42:354–362
Radford JQ, Bennett AF, Cheers GJ (2005) Landscape-level thresholds of habitat cover for woodland-dependent birds. Biol Conserv 124:317–337
Rüdisser J, Tasser E (2011) Landbedeckung Österreichs—Datenintegration und Modellierung. In: Strobl J, Blaschke T, Griesebner G (eds) Angewandte Geoinformatik 2011: Beiträge zum 23. AGIT-Symposium Salzburg, pp 579–588
Rüdisser J, Tasser E, Tappeiner U (2012) Distance to nature—a new biodiversity relevant environmental indicator set at the landscape level. Ecol Indic 15:208–216
Sala OE, Chapin FS, Armesto JJ, Berlow E, Bloomfield J, Dirzo R, Huber-Sanwald E, Huenneke LF, Jackson RB, Kinzig A, Leemans R, Lodge DM, Mooney HA, Oesterheld M, Poff NL, Sykes MT, Walker BH, Walker M, Wall DH (2000) Biodiversity—global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 287:1770–1774
Salek M, Svobodova J, Zasadil P (2010) Edge effect of low-traffic forest roads on bird communities in secondary production forests in central Europe. Landscape Ecol 25:1113–1124
Schindler S, von Wehrden H, Poirazidis K, Wrbka T, Kati V (2013) Multiscale performance of landscape metrics as indicators of species richness of plants, insects and vertebrates. Linking landscape structure and biodiversity. Ecol Indic 31:41–48
Schwarz G (1978) Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6:461–464
Skaug H, Fournier D, Nielsen A, Magnusson A, Bolker B (2013) Generalized linear mixed models using AD model builder: R package version 0.7.5
Tasser E, Sternbach E, Tappeiner U (2008) Biodiversity indicators for sustainability monitoring at municipality level: an example of implementation in an alpine region. Ecol Indic 8:204–223
Teufelbauer N (2010) Der Farmland Bird Index für Österreich—erste Ergebnisse zur Bestandsentwicklung häufiger Vogelarten des Kulturlandes: the Farmland Bird Index for Austria—first results of the changes in populations of common birds of farmed land. Egretta 51:35–50
Tscharntke T, Klein AM, Kruess A, Steffan-Dewenter I, Thies C (2005) Landscape perspectives on agricultural intensification and biodiversity—ecosystem service management. Ecol Lett 8:857–874
Tscharntke T, Tylianakis JM, Rand TA, Didham RK, Fahrig L, Batáry P, Bengtsson J, Clough Y, Crist TO, Dormann CF, Ewers RM, Fründ J, Holt RD, Holzschuh A, Klein AM, Kleijn D, Kremen C, Landis DA, Laurance W, Lindenmayer D, Scherber C, Sodhi N, Steffan-Dewenter I, Thies C, Van der Putten WH, Westphal C (2012) Landscape moderation of biodiversity patterns and processes—eight hypotheses. Biol Rev 87:661–685
UNESCO (United Nations Educational S, and Cultural Organization) (1996) Operational guidelines for the implementation of the world heritage convention. UNESCO, Paris. http://whc.unesco.org/archive/opguide05-annex3-en.pdf
Vackár D, ten Brink B, Loh J, Baillie JEM, Reyers B (2012) Review of multispecies indices for monitoring human impacts on biodiversity. Ecol Indic 17:58–67
Voříšek P, Klvaňová A, Wotton S, Gregory RD (eds) (2008) A best practice guide for wild bird monitoring schemes. Czech Republic, Třeboň
Walpole M, Almond REA, Besancon C, Butchart SHM, Campbell-Lendrum D, Carr GM, Collen B, Collette L, Davidson NC, Dulloo E, Fazel AM, Galloway JN, Gill M, Goverse T, Hockings M, Leaman DJ, Morgan DHW, Revenga C, Rickwood CJ, Schutyser F, Simons S, Stattersfield AJ, Tyrrell TD, Vie J, Zimsky M (2009) Tracking progress toward the 2010 biodiversity target and beyond. Science 325:1503–1504
Walz U, Syrbe R (2013) Linking landscape structure and biodiversity. Ecol Indic 31:1–5
Wehrden HV, Abson D, Beckmann M, Cord A, Klotz S, Seppelt R (2014) Realigning the land-sharing/land-sparing debate to match conservation needs: considering diversity scales and land-use history. Landscape Ecol 29:941–948
Whittingham MJ, Krebs JR, Swetnam RD, Vickery JA, Wilson JD, Freckleton RP (2007) Should conservation strategies consider spatial generality? Farmland birds show regional not national patterns of habitat association. Ecol Lett 10:25–35
Wilson JD, Evans AD, Grice PV (2010) Bird conservation and agriculture: a pivotal moment? Ibis 152:176–179
Wretenberg J, Part T, Berg A (2010) Changes in local species richness of farmland birds in relation to land-use changes and landscape structure. Biol Conserv 143:375–381
Wright HL, Lake IR, Dolman PM (2012) Agriculture—a key element for conservation in the developing world. Conserv Lett 5:11–19
Wu J (2010) Landscape of culture and culture of landscape: does landscape ecology need culture? Landscape Ecol 25:1147–1150
Zimmermann P, Tasser E, Leitinger G, Tappeiner U (2010) Effects of land-use and land-cover pattern on landscape-scale biodiversity in the European Alps. Agric Ecosyst Environ 139:13–22
Zuur FA, Ienon E, Walker N, Savelier AA, Smith GM (2009) Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Springer, New York
Acknowledgments
This article was funded by the Austrian Climate Research Fund project ‘CAFEE-Climate change in agriculture and forestry: an integrated assessment of mitigation and adaptation measures in Austria’ as well as the collaborative research programme proVISION of the Austrian Federal Ministry of Science under Research Contract 100394. Ulrike Tappeiner is a member of the research area ‘Alpine Space—Man and Environment’ at the University of Innsbruck. Special thanks go to all the volunteer observers of the Austrian Common Bird Monitoring Scheme and Mag. Ingeborg Fiala of the Austrian Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management (BMLFUW), who prompted this analysis. Finally, we wish to thank the editor Teresa Pinto-Correia and an anonymous reviewer for their very helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rüdisser, J., Walde, J., Tasser, E. et al. Biodiversity in cultural landscapes: influence of land use intensity on bird assemblages. Landscape Ecol 30, 1851–1863 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0215-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0215-3