Abstract
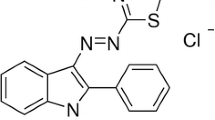
The heterogeneous catalytic degradation of a model azo dye, acid red 1 (AR1), initiated by zero valent iron nanoparticles (ZVINP), and its synergic effect with ultrasound (US) have been investigated in the present study. The treatment of AR1 using ZVINP at pH 3 showed maximum efficiency in terms of colour removal (53.0%) and mineralization (48.5% TOC reduction) after 25 min of reaction. However, the coupling of this system with US showed an enhanced efficiency against the decolourization and mineralization of AR1. More than 95% colour removal was achieved within 5 min in the case of US/ZVINP system. Around 55% TOC reduction suggests the conversion of the parent molecules in to aromatic transformed products, and it is further supported by LC-Q-TOF analysis. The remarkably higher efficiency in the coupled system is attributed to the synergic effect of ZVINPs and ultrasound. The highest degradation rates observed at highly acidic (pH 3) and alkaline pH (pH 9) suggests that different mechanisms are operating at both pH. The products identified gave some insight into the mechanism. The ZVINPs prepared in the present study was easily recoverable (and reusable) and hence may be considered as an effective replacement for the conventional Fenton’s reagent.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anjaneyulu Y, Sreedhara Chary N, Samuel Suman Raj D (2005) Decolourization of industrial effluents—available methods and emerging technologies—a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 4:245–273
Boyter HA (2007) Environmental legislations USA. In: Christie RM (ed) Environmental aspects of textile dyeing. Woodhead publishing in textiles, Cambridge
Chang M-C, Shu H-Y, Yu H-H, Sung Y-C (2006) Reductive decolourization and total organic carbon reduction of the diazo dye CI acid black 24 by zero-valent iron powder. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:1259–1266
Chen B, Wang X, Wang C, Jiang W, Li S (2011) Degradation of azo dye direct sky blue 5B by sonication combined with zero-valent iron. Ultrason Sonochem 18:1091–1096
Dai Y, Li F, Ge F, Zhu F, Wu L, Yang X (2006) Mechanism of the enhanced degradation of pentachlorophenol by ultrasound in the presence of elemental iron. J Hazard Mater 137:1424–1429
Destaillats H, Colussi AJ, Joseph JM, Hoffmann MR (2000) Synergistic effects of sonolysis combined with ozonolysis for the oxidation of azobenzene and methyl orange. J Phys Chem A 104:8930–8935
Dumitrache F, Morjan I, Alexandrescu R, Ciupina V, Prodan G, Voicu I, Fleaca C, Albu L, Savoiu M, Sandu I, Popovici E, Soare I (2005) Iron–Iron oxide core–shell nanoparticles synthesized by laser pyrolysis followed by superficial oxidation. Appl Surf Sci 247:25–31
Eren Z (2012) Ultrasound as a basic and auxiliary process for dye remediation: a review. J Environ Manag 104:127–141
Fan J, Guo Y, Wang J, Fan M (2009) Rapid decolorization of azo dye methyl orange in aqueous solution by nanoscale zerovalent iron particles. J Hazard Mater 166:904–910
Feitz AJ, Joo SH, Guan J, Sun Q, Sedlak DL, David Waite T (2005) Oxidative transformation of contaminants using colloidal zero-valent iron. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 265:88–94
Freyria FS, Bonelli B, Sethi R, Armandi M, Belluso E, Garrone E (2011) Reactions of acid orange 7 with iron nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. J Phys Chem C 115:24143–24152
García-Araya JF, Beltrán FJ, Aguinaco A (2010) Diclofenac removal from water by ozone and photolytic TiO2 catalysed processes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:798–804
Geng M, Thagard SM (2013) The effects of externally applied pressure on the ultrasonic degradation of rhodamine B. Ultrason Sonochem 20:618–625
Ghodbane H, Hamdaoui O (2009) Degradation of acid blue 25 in aqueous media using 1700 kHz ultrasonic irradiation: ultrasound/Fe(II) and ultrasound/H2O2 combinations. Ultrason Sonochem 16:593–598
Ghows N, Entezari MH (2013) Kinetic investigation on sono-degradation of reactive black 5 with core–shell nanocrystal. Ultrason Sonochem 20:386–394
Gomathi Devi L, Eraiah Rajashekhar K, Anantha Raju KS, Girish Kumar S (2011) Influence of various aromatic derivatives on the advanced photo Fenton degradation of Amaranth dye. Desalination 270:31–39
Güyer GT, Ince NH (2011) Degradation of diclofenac in water by homogeneous and heterogeneous sonolysis. Ultrason Sonochem 18:114–119
He Z, Lin L, Song S, Xia M, Xu L, Ying H, Chen J (2008) Mineralization of C.I. Reactive blue 19 by ozonation combined with sonolysis: performance optimization and degradation mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 62:376–381
Hung H-M, Ling FH, Hoffmann MR (2000) Kinetics and mechanism of the enhanced reductive degradation of nitrobenzene by elemental iron in the presence of ultrasound. Environ Sci Technol 34:1758–1763
Iida Y, Yasui K, Tuziuti T, Sivakumar M (2005) Sonochemistry and its dosimetry. Microchem J 80:159–164
Jiang J, Pang S-Y, Ma J (2008) Comment on “factors affecting the yield of oxidants from the reaction of nanoparticulate zero-valent iron and oxygen”. Environ Sci Technol 42:5377–5377
Li X-Q, Elliott DW, Zhang W-X (2006) Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for abatement of environmental pollutants: materials and engineering aspects. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 31:111–122
Lien H-L, Zhang W-X (2001) Nanoscale iron particles for complete reduction of chlorinated ethenes. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 191:97–105
Lifka J, Ondruschka B, Hofmann J (2003) The use of ultrasound for the degradation of pollutants in water: aquasonolysis—a review. Eng Life Sci 3:253–262
Lin Y-T, Weng C-H, Chen F-Y (2008) Effective removal of AB24 dye by nano/micro-size zero-valent iron. Sep Purif Technol 64:26–30
Mezyk SP, Neubauer TJ, Cooper WJ, Peller JR (2007) Free-radical-induced oxidative and reductive degradation of sulfa drugs in water: absolute kinetics and efficiencies of hydroxyl radical and hydrated electron reactions. J Phys Chem A 111:9019–9024
Minero C, Lucchiari M, Vione D, Maurino V (2005) Fe(III)-enhanced sonochemical degradation of methylene blue in aqueous solution. Environ Sci Technol 39:8936–8942
Mishra KP, Gogate PR (2011) Intensification of degradation of aqueous solutions of rhodamine B using sonochemical reactors at operating capacity of 7 L. J Environ Manag 92:1972–1977
Mylon SE, Sun Q, Waite TD (2010) Process optimization in use of zero valent iron nanoparticles for oxidative transformations. Chemosphere 81:127–131
Nam S, Tratnyek PG (2000) Reduction of azo dyes with zero-valent iron. Water Res 34:1837–1845
Pagga U, Brown D (1986) The degradation of dyestuffs: part II behaviour of dyestuffs in aerobic biodegradation tests. Chemosphere 15:479–491
Pang YL, Abdullah AZ, Bhatia S (2011) Review on sonochemical methods in the presence of catalysts and chemical additives for treatment of organic pollutants in wastewater. Desalination 277:1–14
Satapanajaru T, Chompuchan C, Suntornchot P, Pengthamkeerati P (2011) Enhancing decolorization of reactive black 5 and reactive red 198 during nano zerovalent iron treatment. Desalination 266:218–230
Shafia E, Esposito S, Armandi M, Bahadori E, Garrone E, Bonelli B (2016) Reactivity of bare and Fe-doped alumino-silicate nanotubes (imogolite) with H2O2 and the azo-dye acid orange 7. Catal Today 277:89–96
Shu H-Y, Chang M-C, Yu H-H, Chen W-H (2007) Reduction of an azo dye acid black 24 solution using synthesized nanoscale zerovalent iron particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 314:89–97
Shu H-Y, Chang M-C, Chang C-C (2009) Integration of nanosized zero-valent iron particles addition with UV/H2O2 process for purification of azo dye acid black 24 solution. J Hazard Mater 167:1178–1184
Sijumon VA, Aravind UK, Aravindakumar CT (2017) Degradation of Amaranth dye using zero valent iron nanoparticles: optimal conditions and mechanism. Environ Eng Sci 34(5):376–383
Singh K, Arora S (2011) Removal of synthetic textile dyes from wastewaters: a critical review on present treatment technologies. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 41:807–878
Spadaro JT, Gold MH, Renganathan V (1992) Degradation of azo dyes by the lignin-degrading fungus phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2397–2401
Sreekanth R, Prasanthkumar KP, Sunil Paul MM, Aravind UK, Aravindakumar CT (2013) Oxidation reactions of 1- and 2-naphthols: an experimental and theoretical study. J Phys Chem A 117:11261–11270
Stieber M, Putschew A, Jekel M (2011) Treatment of pharmaceuticals and diagnostic agents using zero-valent iron–kinetic studies and assessment of transformation products assay. Environ Sci Technol 45:4944–4950
Sun Y-P, Li X-Q, Cao J, Zhang W-X, Wang HP (2006a) Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 120:47–56
Sun Y-P, Li X-Q, Cao J, Zhang W-X, Wang HP (2006b) Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 120:47–56
Sunil Paul MM, Aravind UK, Pramod G, Aravindakumar CT (2013) Oxidative degradation of fensulfothion by hydroxyl radical in aqueous medium. Chemosphere 91:295–301
Tantak NP, Chaudhari S (2006) Degradation of azo dyes by sequential Fenton’s oxidation and aerobic biological treatment. J Hazard Mater 136:698–705
Thomas S, Sreekanth R, Sijumon VA, Aravind UK, Aravindakumar CT (2014) Oxidative degradation of acid red 1 in aqueous medium. Chem Eng J 244:473–482
Wang C-B, Zhang W-X (1997) Synthesizing nanoscale iron particles for rapid and complete dechlorination of TCE and PCBs. Environ Sci Technol 31:2154–2156
Wang JL, Xu LJ (2011) Advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: formation of hydroxyl radical and application. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:251–325
Wasiewicz M, Chmielewski AG, Getoff N (2006) Radiation-induced degradation of aqueous 2,3-dihydroxynaphthalene. Radiat Phys Chem 75:201–209
Weng C-H, Lin Y-T, Chang C-K, Liu N (2013) Decolourization of direct blue 15 by Fenton/ultrasonic process using a zero-valent iron aggregate catalyst. Ultrason Sonochem 20:970–977
Zhang H, Duan L, Zhang Y, Wu F (2005) The use of ultrasound to enhance the decolorization of the C.I. Acid orange 7 by zero-valent iron. Dyes Pigments 65:39–43
Zhang W-X (2003) Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview. J Nanopart Res 5:323–332
Acknowledgements
Shoniya Thomas is thankful to the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India, for financial support. C.T. Aravindakumar is thankful to BRNS, Mumbai, KSCSTE, Thiruvanthapuram and DST (under Purse & FIST programme) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 6604 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, S., Abraham, S.V., Aravind, U.K. et al. Enhanced degradation of acid red 1 dye using a coupled system of zero valent iron nanoparticles and sonolysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 24533–24544 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0080-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0080-5