Abstract
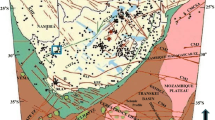
Based on lots of field investigations and comprehensive interpretations of seismic profiles with outcrop cross-sections, this paper shows that the foreland belts surrounding the Southwest Tarim Foreland Basin have the regularity of segmentation along the strike of foreland belts. There are many thin-skinned thrusting systems thrusting from mountains to the basin and the arcuate back-thrusting systems to the mountains distributed at intervals in the front of West Kunlun-Pamir and Southern Tianshan. Between thrusting and back-thrusting systems, the strike-slip faults developed. The northeast uplifts and depressions of Southwest Tarim Basin correspond with the segmentation of foreland basin. The thin-skinned thrusting system is formed in the case that the thickness of sedimentary covers is less than 10 km in depth where the basement is an uplift belt in general. The back-thrusting systems and triangle zones are formed in the case that the thickness of sedimentary covers is larger than 8 km in depth where the basement is a depression zone. The main mechanics of segmentation of foreland basin are the difference of mountain uplift and deformation rate along the longitude of the mountains, the huge sedimentary rocks in different depression centers, the uplift belts and depression zones in the basement rocks, and multi-displaced weak layers in the foreland basin. The segmentation of Southwest Tarim Foreland Basin is due to the intra-plate deformation of re-orogenies of West Kunlun-Pamir and Southwest Tianshan and the co-related deformation between mountains and basement of basin since Neocene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berberian, M., Master, ‘Blind’ thrust faults hidden under the Zagros folds: active basement tectonics and surface morphotectonics, Tectonophysics, 1995, 241: 193–224.[DOI]
Brusset, S., Souquet, P., Deramond, J. et al., Partition between collision and subduction accretionary prisms along an inherited transcurrent fault zone: New insights on the Taiwan fold and thrust belt, Tectonics, 1999, 18(3): 546–558.
Canerot Joseph y, Qu Guosheng, The Jurassic basin in the south-west of Tarim, Xinjiang (China), Himalayan cycle evolution and comparison with the north-east of the Tethys, Cuadernos de Geologia Iberica, 1998, 24: 311–331.
Hildebrand, P. R., Searle, M. P., Shakirullah, Van Heijst, H. J., Geological evolution of the Hindu Kush, NW Frontier Pakistan: active margin to continent-continent collision zone, Tectonics of the Nanga Parbat syntaxis and the western Himalaya, Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Pub. (eds. Asif Khan, M., Treloar, P. J., Searle, M. P. et al.), 2000, 170: 277–294.
Jadoon, I. A. K., Lawrence R. D., Lillie, R. J., Balanced and retrodeformed geological cross-section from the frontal Sulaiman Lobe, Pakistan: Duplex development in thick strata along the western margin of the Indian Plate, Thrust Tectonics (ed. McClay, K. R.), Chapman and Hall, 1992, 343–56.
Jadoon, I. A. K., Frisch, W., Hinterland-vergent tectonic wedge below the Riwat thrust, Himalayan foreland, Pakistan: Implications for hydrocarbon exploration, AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(3): 438–448.
Jaswal, T. M., Lillie, R. J., Lawrence, R. D., Structure and Evolution of the Northern Potwar deformed zone, Pakistan, AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(2): 308–328.
Jamison, W. R., Mechanical models of triangle zone evolution, Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 1996, 44(2): 180–152.
Pavlis, T., Das, S., The Pamir-Hindu Kush Seismic zone as a strain marker for flow in the upper mantle, Tectonics, 2000, 19: 103–115. [DOI] Segmentations of foreland belts and their tectonic mechanism in Southwest Tarim Basin 1597
Qu Guosheng, Canerot, J., Comparative studies of Cenozoic and Mesozoic tectonics and evolution between west Kunlun-Pamir (China) and Pyrenees (France), Proc. 30th Int’l Geol. Congr., 1997, 6: 133–140.
Jones, P. B., Triangle zone geometry, terminology and kinematics, Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 1996, 44(2): 139–152.
Pegler, G. and Das, S., An enhanced image of the Pamir-Hindu Kush seismic zone from relocated earthquake hypocenters, Geophys. J. Intl., 1998, 134: 573–595. [DOI]
Searle, M. P., Asif Khan, M., Fraster, J. E. et al., The tectonic evolution of the Kohistan-Karakoram collision belt along the Karakoram highway transect, north Pakistan, Tectonics, 1999, 18: 929–949. [DOI]
Searle, M., Hacker, B. R., Bilham, R., The Hindu Kush seismic zone as a paradigm for the creation of ultrahigh-pressure diamond and coesitebearing continental rocks, The Journal of Geology, 2001, 109: 143–153. [DOI]
Coward, P. J. T., Chambers, A. F., Izatt, C. N. et al., Thrust geometries, interferences and rotations in the Northern Himalaya, Thrust Tectonics (ed. K. R. McClay), Chapman and Hall, 1992.
Mashak, S., Kinematics of orocline and arc formation in the thin-skinned orogens, Tectonics, 1988, 7(1): 73–86.
Mitra, S., and V. S. Mount, Foreland basementinvolved structures, AAPG Bulletin, 1998, 82(1): 70–109.
He Dengfa, Li Desheng, Tectonic Evolution and Oil and Gas Concentration of Tarim Basin (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996.
He Dengfa, Lu Xiuxiang, Lin Yonghan, et al., Foreland Basin Analysis (in Chinese), Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1996.
He Dengfa, Zhao Wenzhi, Dynamic Evolvement and Oil System Cycle in Northwest China (in Chinese), Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1999.
Ding Daogui, Wang Daoxuan, Liu Weixin et al., West Kunlun Orogenic Belts and Basin (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996.
Dong Dazhong, Xiao Ancheng, The Characteristics of Petroleum Geology and Resource in Southwest Tarim Basin (in Chinese), Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1998.
Dong Yunpeng, Zhang Guowei, New research methods and developments of structure, tectonics and dynamics of orogenic belts and foreland basin, Development of Earth Science (in Chinese), 1997, 12(1): 1–6.
Hu Wangshui, Chen Yusui, Xiao Ancheng et al., The tectonic characteristics of faults zone and their controls for oil and gas in Southwest Tarim Depression, Xinjiang Petroleum Geology (in Chinese), 1997, 18(3): 201–207.
Wu Xiufang, Wang Xin, Yang Shufeng et al., Crustal shorten rate evaluated by the balanced geological cross-sections and magnetic stratigraphy– an example from Pamir-West Kunlun thrust belts, Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese), 2003, 10 (1): 52–58.
Xiao Ancheng, Yang Shufeng, Cheng Hanlin et al., Structural characteristics of thrust system in the front of the West Kunlun mountains, Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese), 2000, 7(Suppl.): 38–43.
Jia Chengzao, Wei Guoqi, Yao Huijun et al., Tectonic Evolution and Regional Structural Geology, Book Series on Petroleum in the Tarim Basin (in Chinese), Beijing: Petroleum Industry Publishing House, 1995.
Jia Chengzao eds., Tectonic Characteristics and Petroleum Tarim Basin China (in Chinese), Beijing: Petroleum Industry Publish House, 1997.
Jia Chengzao, He Dengfa, Lei Zhenyu, et al., Petroleum Exploration in Foreland Thrust Belts (in Chinese), Beijing: Petroleum Industry Publish House, 2000.
Qu Guosheng, Chen Jie, Chen Xinfa et al., Cause of moderate and strong earthquake swarm and earthquake tendency in Jiashi area Study on Seismic Risk Prediction (for 1999) (in Chinese) (ed. Institute of Geology), Beijing: Seismological Press, 1998, 158–168.
Qu Guosheng, Cheng Jie, Xu Jiandong et al., Back-thrusting systems of Atushi-Bapanshuimo in Tarim Basin, Seismology and Geology (in Chinese), 2001, 23(1): 1–14.
Qu Guosheng, LI Yigang, Chen Jie et al., Geometry, kinematics and tectonic evolution of Kalpin thrust system, Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese), 2003, 10(Suppl.): 142–152.
Qu Guosheng, Canerot J., Wang Zongqi et al., Arc tectonics in orogenic belts, Geologica sinica (in Chinese), 1996, 31(4): 313–326.
Qu Guosheng, Chen Jie, Chen Xinan et al., Intra-plate deformation in the front of the West Kunlun– Pamir arcuate orogenic belt and the Southwest Tarim Foreland Basin, Geological Review (in Chinese), 1998, 44(4): 419–429.
Qu Guosheng, Xu Jiandong, Wang Yu et al., Structural analysis of Yigeziya arc thin-skinned thrusting system in the foreland belts of West Kunlun-Pamir, Acta Geoscientia Sinica (in Chinese), 1999, 20(57): 82–91.
Chen Jie, Qu Guosheng, Hu Jun, et al., Arcuate thrust tectonics and its contemporary seismicity in the eastern section of the external zone of the Pamir, Seismology and Geology (in Chinese), 1997, 19(4): 301–312.
Chen Jie, Yin Jinhui, Late Cenozoic deformation of the Kzaikeaeter Range, northeastern Pamirs, Quaternary Sciences (in Chinese), 1998, 18 (3): 286–291.
Chen Jie, Ding Guoyu, Burbank, D. W. et al., Late Cenozoic tectonics and seismicity in the southwestern Tianshan, China, Earthquake Research In China (in Chinese), 2001, 17(2): 34–155.
Cheng Shoude, Wang Yuanlong, The general characteristics of tectonic evolution of Xinjiang, Xinjiang Geology (in Chinese), 1998, 16(2): 97–107.
He Guoqi, Li Maosong, Liu Dequan et al., Paleozoic Crustal Evolution and Mineralogy in Xinjiang, China (in Chinese), Xing-jiang: Xinjiang People’s Publishing House, Hongkong: Hongkong Culture and Education Publishing House, 1994.
Jiang Chunfa, Yang Jingsui, Feng Binggui et al., Kunlun Opening and Closing Tectonics (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1992.
Pan Yusheng, Tectonic characters and evolution of West Kunlun Mountains, Scientia Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1990, 25(3): 224–231.
Pan Yusheng, Integrated Introduction on Scientific Researches of Kalakunlun-Kunlun Mountains (in Chinese), Beijing: Meterological Publishing House, 1992.
Pan Yusheng, Wang Yi, Ph. Matte et al., Tectonic evolution along the geotravers from Yecheng to Siquanhe, Acta Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1994, 68(4): 295–307.
Song Lixun, Formation, evolution and petroleum potential of Southwest Tarim Depression, Xinjiang Petroleum Geology (in Chinese), 1989, 10(1): 28–34.
Bureau of Geology and Mine, Xinjiang Autonomous Region, Geological Map of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (1–2000000) (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1985.
Bureau of Geology and Mine, Xinjiang Autonomous Region, Regional Geology of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993.
Liu Qiyuan, Chen Jiuhui, Li Shuncheng et al., Passive seismic experiment in Xinjiang Jiashi strong earthquake region and discussion on its seismic genesis, Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 2000, 43(3): 356–365.
Lu Xinbian, He Faqi, Zhao Hongsheng, Geophysical character – structures and evolvement in the southwest Tarim basin, Oil Exploration (in Chinese), 1997, 36(1): 43–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, G., Li, Y., Li, Y. et al. Segmentations of foreland belts and their tectonic mechanism in the Southwest Tarim Basin. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 48, 1585–1598 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1360/02yd0071
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/02yd0071