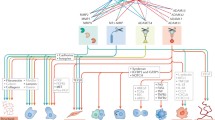
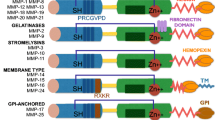
Abstract
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a family of metalloendopeptidases that induce remodelling of extracellular matrix (ECM) and differentially cleave many soluble mediators that regulate cell physiology. Due to their matrix-degrading capabilities and elevated expression levels in both neoplastic and host cells in human cancer, MMPs have acquired considerable attention as targets for anti-cancer therapy. This chapter summarizes two decades of research examining MMP biochemistry and biology utilizing in vitro cell-based and biochemical analyses, more recent examination of their functional significance in de novo mouse models of human cancer development and results from human clinical trials where MMP inhibitors were evaluated for efficacy as anti-cancer therapeutics.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knudson, A.G.J., 1977, Genetic predisposition to cancer. In Origins of Human Cancer, J.D.W. H.H. Hiatt, J.A. Wiunsted eds, Vol. 4:45–52. Cold Spring Harbor Lab, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Fearon, E. R., and Vogelstein, B., 1990, A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell, 61:759–767.
Knudson, A. G., 2001, Two genetic hits (more or less) to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 1:157–162.
Hanahan, D., and Weinberg, R. A., 2000, The hallmarks of cancer. Cell, 100:57–70.
Bissell, M. J., and Radisky, D., 2001, Putting tumours in context. Nat Rev Cancer, 1:46–54.
Coussens, L. M., and Werb, Z., 2002, Inflammation and cancer. Nature, 420:860–867.
Hahn, W. C., and Weinberg, R. A., 2002, Modelling the molecular circuitry of cancer, Nat Rev Cancer, 2:331–341.
Bergers, G., and Benjamin, L. E., 2003, Angiogenesis: Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer, 3:401–410.
Hussain, S. P., Hofseth, L. J., and Harris, C. C., 2003, Radical causes of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 3:275–286.
Fidler, I. J., 2003, Timeline: The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the 'seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer, 3:453–458.
Nagase, H., and Woessner, J. F., 1999, Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem, 274:21491–21494.
Bergers, G., Brekken, R., McMahon, G., Vu, T. H., Itoh, T., Tamaki, K., Tanzawa, K., Thorpe, P., Itohara, S., Werb, Z., and Hanahan, D., 2000, Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol, 2:737–744.
McQuibban, G. A., Gong, J. H., Tam, E. M., McCulloch, C. A., Clark-Lewis, I., and Overall, C. M., 2000, Inflammation dampened by gelatinase A cleavage of monocyte chemoattractant protein-3. Science, 289:1202–1206.
Powell, W. C., Fingleton, B., Wilson, C. L., Boothby, M., and Matrisian, L. M., 1999, The metalloproteinase matrilysin proteolytically generates active soluble Fas ligand and potentiates epithelial cell apoptosis. Curr Biol, 9:1441–7.
Manes, S., Llorente, M., Lacalle, R. A., Gomez-Mouton, C., Kremer, L., Mira, E., and Martinez, A. C., 1999, The matrix metalloproteinase-9 regulates the insulin-like growth factor-triggered autocrine response in DU-145 carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem, 274:6935–6945.
Sternlicht, M. D., and Bergers, G., 2000, Matrix metalloproteinases as emerging targets in anticancer therapy: status and prospects. Emerg Theurpeut Targets, 4:609–633.
Egeblad, M., and Werb, Z., 2002, New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer, 2:161–174.
Wilson, C. L., Heppner, K. J., Labosky, P. A., Hogan, B. L., and Matrisian, L. M., 1997, Intestinal tumorigenesis is suppressed in mice lacking the metalloproteinase matrilysin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94:1402–7.
Sternlicht, M. D., Lochter, A., Sympson, C. J., Huey, B., Rougier, J. P., Gray, J. W., Pinkel, D., Bissell, M. J., and Werb, Z., 1999, The stromal proteinase MMP3/stromelysin-1 promotes mammary carcinogenesis. Cell, 98:137–146.
Coussens, L. M., Tinkle, C. L., Hanahan, D., and Werb, Z., 2000, MMP-9 supplied by bone marrow-derived cells contributes to skin carcinogenesis. Cell, 103:481–490.
Coussens, L. M., Shapiro, S. D., Soloway, P. D., and Werb, Z., 2001, Models for gain-of-function and loss-of-function of MMPs. Transgenic and gene targeted mice. Methods Mol Biol, 151:149–179.
Rawlings, N. D., and Barrett, A. J., 1995, Evolutionary families of metallopeptidases. Methods Enzymol, 248:183–228.
Stocker, W., Grams, F., Baumann, U., Reinemer, P., Gomis-Ruth, F. X., McKay, D. B., and Bode, W., 1995, The metzincins—topological and sequential relations between the astacins, adamalysins, serralysins, and matrixins (collagenases) define a superfamily of zinc-peptidases. Protein Sci, 4:823–40.
Sternlicht, M.D., and Werb, Z., 1999, ECM Proteinases. In Guidebook to the Extracellular Matrix, Kries, T., and Vale, R., eds, 503–562. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK.
Overall, C. M., 2002, Molecular determinants of metalloproteinase substrate specificity: matrix metalloproteinase substrate binding domains, modules, and exosites. Mol Biotechnol, 22:51–86.
Puente, X. S., Sanchez, L. M., Overall, C. M., and Lopez-Otin, C., 2003, Human and mouse proteases: a comparative genomic approach. Nat Rev Genet, 4:544–558.
Lopez-Otin, C., and Overall, C. M., 2002, Protease degradomics: a new challenge for proteomics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 3:509–519.
Woessner, J. F., and Nagase, H., 2000, Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK.
Hirose, T., Patterson, C., Pourmotabbed, T., Mainardi, C. L., and Hasty, K. A., 1993, Structure-function relationship of human neutrophil collagenase: identification of regions responsible for substrate specificity and general proteinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90:2569–2573.
Li, J., Brick, P., O'Hare, M. C., Skarzynski, T., Lloyd, L. F., Curry, V. A., Clark, I. M., Bigg, H. F., Hazleman, B. L., Cawston, T. E., and et al., 1995, Structure of full-length porcine synovial collagenase reveals a C-terminal domain containing a calcium-linked, four-bladed beta-propeller. Structure, 3:541–9.
Murphy, G., Nguyen, Q., Cockett, M. I., Atkinson, S. J., Allan, J. A., Knight, C. G., Willenbrock, F., and Docherty, A. J., 1994, Assessment of the role of the fibronectin-like domain of gelatinase A by analysis of a deletion mutant. J Biol Chem, 269:6632–6.
Banyai, L., Tordai, H., and Patthy, L., 1994, The gelatin-binding site of human 72 kDa type IV collagenase (gelatinase A). Biochem J, 298(Pt 2):403–407.
Itoh, Y., Kajita, M., Kinoh, H., Mori, H., Okada, A., and Seiki, M., 1999, Membrane type 4 matrix metalloproteinase (MT4-MMP, MMP-17) is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteinase. J Biol Chem, 274:34260–34266.
Pei, D., Kang, T., and Qi, H., 2000, Cysteine array matrix metalloproteinase (CA-MMP)/MMP-23 is a type II transmembrane matrix metalloproteinase regulated by a single cleavage for both secretion and activation. J Biol Chem, 275:33988–97.
Seidah, N. G., and Chretien, M., 1997, Eukaryotic protein processing: endoproteolysis of precursor proteins. Curr Opin Biotechnol, 8:602–607.
Nagase, H., 1997, Activation mechanisms of matrix metalloproteinases. Biol Chem, 378:151–160.
Lafleur, M. A., Handsley, M. M., and Edwards, D. R., 2003, Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in angiogenesis. Expert Rev Mol Med, 5:1–39.
Esteve, P. O., Chicoine, E., Robledo, O., Aoudjit, F., Descoteaux, A., Potworowski, E. F., and St Pierre, Y., 2002, Protein kinase C-zeta regulates transcription of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene induced by IL-1 and TNF-alpha in glioma cells via NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem, 277:35150–35155.
Troussard, A. A., Costello, P., Yoganathan, T. N., Kumagai, S., Roskelley, C. D., and Dedhar, S., 2000, The integrin linked kinase (ILK) induces an invasive phenotype via AP-1 transcription factor-dependent upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9). Oncogene, 19:5444–5452.
Fini, M.E., Cook, J.R., Mohan, R., and Brinckerhoff, C.E., 1998, Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. In Matrix Metalloproteinases, Parks, W.C., and Mecham, R.P., eds, 299–356. Academic Press, New York.
Hou, G., Vogel, W. F., and Bendeck, M. P., 2002, Tyrosine kinase activity of discoidin domain receptor 1 is necessary for smooth muscle cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase expression. Circ Res, 90:1147–1149.
Olaso, E., Labrador, J. P., Wang, L., Ikeda, K., Eng, F. J., Klein, R., Lovett, D. H., Lin, H. C., and Friedman, S. L., 2002, Discoidin domain receptor 2 regulates fibroblast proliferation and migration through the extracellular matrix in association with transcriptional activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2. J Biol Chem, 277:3606–3613.
Arnott, C. H., Scott, K. A., Moore, R. J., Hewer, A., Phillips, D. H., Parker, P., Balkwill, F. R., and Owens, D. M., 2002, Tumour necrosis factor-alpha mediates tumour promotion via a PKC alpha-and AP-1-dependent pathway. Oncogene, 21:4728–4738.
Ventura, J. J., Kennedy, N. J., Lamb, J. A., Flavell, R. A., and Davis, R. J., 2003, c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase is essential for the regulation of AP-1 by tumor necrosis factor. Mol Cell Biol, 23:2871–2882.
Gilbert, S. J., Duance, V. C., and Mason, D. J., 2004, Does protein kinase R mediate TNF-alpha-and ceramide-induced increases in expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinases in articular cartilage by a novel mechanism?. Arthritis Res Ther, 6:R46–R55.
Chen, N., Nomura, M., She, Q. B., Ma, W. Y., Bode, A. M., Wang, L., Flavell, R. A., and Dong, Z., 2001, Suppression of skin tumorigenesis in c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase-2-deficient mice. Cancer Res, 61:3908–3912.
Vogel, W., Gish, G. D., Alves, F., and Pawson, T., 1997, The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases are activated by collagen. Mol Cell, 1:13–23.
Vogel, W., 1999, Discoidin domain receptors: structural relations and functional implications. Faseb J, 13Suppl:S77–82.
Johnson, J. D., Edman, J. C., and Rutter, W. J., 1993, A receptor tyrosine kinase found in breast carcinoma cells has an extracellular discoidin I-like domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90:10891.
Matsuyama, W., Wang, L., Farrar, W. L., Faure, M., and Yoshimura, T., 2004, Activation of discoidin domain receptor 1 isoform b with collagen up-regulates chemokine production in human macrophages: role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB. J Immunol, 172:2332–2340.
Kamohara, H., Yamashiro, S., Galligan, C., and Yoshimura, T., 2001, Discoidin domain receptor 1 isoform-a (DDR1alpha) promotes migration of leukocytes in three-dimensional collagen lattices. Faseb J, 15:2724–2726.
Alves, F., Vogel, W., Mossie, K., Millauer, B., Hofler, H., and Ullrich, A., 1995, Distinct structural characteristics of discoidin I subfamily receptor tyrosine kinases and complementary expression in human cancer. Oncogene, 10:609–618.
Barker, K. T., Martindale, J. E., Mitchell, P. J., Kamalati, T., Page, M. J., Phippard, D. J., Dale, T. C., Gusterson, B. A., and Crompton, M. R., 1995, Expression patterns of the novel receptor-like tyrosine kinase, DDR, in human breast tumours. Oncogene, 10:569–575.
Ye, S., 2000, Polymorphism in matrix metalloproteinase gene promoters: implication in regulation of gene expression and susceptibility of various diseases. Matrix Biol, 19:623–629.
Kanamori, Y., Matsushima, M., Minaguchi, T., Kobayashi, K., Sagae, S., Kudo, R., Terakawa, N., and Nakamura, Y., 1999, Correlation between expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene in ovarian cancers and an insertion/deletion polymorphism in its promoter region. Cancer Res, 59:4225–7.
Ghilardi, G., Biondi, M. L., Mangoni, J., Leviti, S., DeMonti, M., Guagnellini, E., and Scorza, R., 2001, Matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter polymorphism 1G/2G is correlated with colorectal cancer invasiveness. Clin Cancer Res, 7:2344–2346.
Van Wart, H. E., and Birkedal-Hansen, H., 1990, The cysteine switch: a principle of regulation of metalloproteinase activity with potential applicability to the entire matrix metalloproteinase gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 87:5578–82.
Springman, E. B., Angleton, E. L., Birkedal-Hansen, H., and Van Wart, H. E., 1990, Multiple modes of activation of latent human fibroblast collagenase: evidence for the role of a Cys73 active-site zinc complex in latency and a “cysteine switch” mechanism for activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 87:364–8.
Sternlicht, M. D., and Werb, Z., 2001, How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 17:463–516.
O'Connell, J. P., Willenbrock, F., Docherty, A. J., Eaton, D., and Murphy, G., 1994, Analysis of the role of the COOH-terminal domain in the activation, proteolytic activity, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase interactions of gelatinase B. J Biol Chem, 269:14967–73.
Pei, D., 1999, CA-MMP: a matrix metalloproteinase with a novel cysteine array, but without the classic cysteine switch. FEBS Lett, 457:262–70.
Fridman, R., Toth, M., Pena, D., and Mobashery, S., 1995, Activation of progelatinase B (MMP-9) by gelatinase A (MMP-2). Cancer Res, 55:2548–2555.
Knauper, V., Will, H., Lopez-Otin, C., Smith, B., Atkinson, S. J., Stanton, H., Hembry, R. M., and Murphy, G., 1996, Cellular mechanisms for human procollagenase-3 (MMP-13) activation. Evidence that MT1-MMP (MMP-14) and gelatinase a (MMP-2) are able to generate active enzyme. J Biol Chem, 271:17124–31.
Itoh, Y., Takamura, A., Ito, N., Maru, Y., Sato, H., Suenaga, N., Aoki, T., and Seiki, M., 2001, Homophilic complex formation of MT1-MMP facilitates proMMP-2 activation on the cell surface and promotes tumor cell invasion. Embo J, 20:4782–4793.
Ramos-DeSimone, N., Hahn-Dantona, E., Sipley, J., Nagase, H., French, D. L., and Quigley, J. P., 1999, Activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) via a converging plasmin/stromelysin-1 cascade enhances tumor cell invasion. J Biol Chem, 274:13066–76.
Overall, C. M., and Sodek, J., 1990, Concanavalin A produces a matrix-degradative phenotype in human fibroblasts. Induction and endogenous activation of collagenase, 72-kDa gelatinase, and Pump-1 is accompanied by the suppression of the tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem, 265:21141–21151.
Strongin, A. Y., Collier, I., Bannikov, G., Marmer, B. L., Grant, G. A., and Goldberg, G. I., 1995, Mechanism of cell surface activation of 72-kDa type IV collagenase. Isolation of the activated form of the membrane metalloprotease. J Biol Chem, 270:5331–5338.
Fang, K. C., Raymond, W. W., Lazarus, S. C., and Caughey, G. H., 1996, Dog mastocytoma cells secrete a 92-kD gelatinase activated extracellularly by mast cell chymase. J Clin Invest 97:1589–1596.
Fang, K. C., Raymond, W. W., Blount, J. L., and Caughey, G. H., 1997, Dog mast cell alpha-chymase activates progelatinase B by cleaving the Phe88-Gln89 and Phe91-Glu92 bonds of the catalytic domain. J Biol Chem, 272:25628–25635.
Saarinen, J., Kalkkinen, N., Welgus, H. G., and Kovanen, P. T., 1994, Activation of human interstitial procollagenase through direct cleavage of the Leu83-Thr84 bond by mast cell chymase. J Biol Chem, 269:18134–18140.
Okada, Y., and Nakanishi, I., 1989, Activation of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) and matrix metalloproteinase 2 ('gelatinase') by human neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G. FEBS Lett, 249:353–356.
Rice, A., and Banda, M. J., 1995, Neutrophil elastase processing of gelatinase A is mediated by extracellular matrix. Biochemistry, 34:9249–56.
Ferry, G., Lonchampt, M., Pennel, L., de Nanteuil, G., Canet, E., and Tucker, G. C., 1997, Activation of MMP-9 by neutrophil elastase in an in vivo model of acute lung injury. FEBS Lett, 402:111–115.
Shamamian, P., Schwartz, J. D., Pocock, B. J., Monea, S., Whiting, D., Marcus, S. G., and Mignatti, P., 2001, Activation of progelatinase A (MMP-2) by neutrophil elastase, cathepsin G, and proteinase-3: a role for inflammatory cells in tumor invasion and angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol, 189:197–206.
Butler, G. S., Hutton, M., Wattam, B. A., Williamson, R. A., Knauper, V., Willenbrock, F., and Murphy, G., 1999, The specificity of TIMP-2 for matrix metalloproteinases can be modified by single amino acid mutations. J Biol Chem, 274:20391–20396.
Sato, H., Takino, T., Okada, Y., Cao, J., Shinagawa, A., Yamamoto, E., and Seiki, M., 1994, A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells. Nature, 370:61–5.
Zhao, H., Bernardo, M. M., Osenkowski, P., Sohail, A., Pei, D., Nagase, H., Kashiwagi, M., Soloway, P. D., DeClerck, Y. A., and Fridman, R., 2004, Differential Inhibition of Membrane Type 3 (MT3)-Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP) and MT1-MMP by Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase (TIMP)-2 and TIMP-3 Regulates Pro-MMP-2 Activation. J Biol Chem, 279:8592–8601.
Baker, A. H., Edwards, D. R., and Murphy, G., 2002, Metalloproteinase inhibitors: biological actions and therapeutic opportunities. J Cell Sci, 115:3719–3727.
Bein, K., and Simons, M., 2000, Thrombospondin type 1 repeats interact with matrix metalloproteinase 2. Regulation of metalloproteinase activity. J Biol Chem, 275:32167–32173.
Rodriguez-Manzaneque, J. C., Lane, T. F., Ortega, M. A., Hynes, R. O., Lawler, J., and Iruela-Arispe, M. L., 2001, Thrombospondin-1 suppresses spontaneous tumor growth and inhibits activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and mobilization of vascular endothelial growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98:12485–12490.
Rhee, J., and Coussens, L., 2002, RECKing MMP function: implications for cancer development. Trends in Cell Bio, 12:209–211.
Oh, J., Takahashi, R., Kondo, S., Mizoguchi, A., Adachi, E., Sasahara, R. M., Nishimura, S., Imamura, Y., Kitayama, H., Alexander, D. B., Ide, C., Horan, T. P., Arakawa, T., Yoshida, H., Nishikawa, S., Itoh, Y., Seiki, M., Itohara, S., Takahashi, C., and Noda, M., 2001, The Membrane-Anchored MMP Inhibitor RECK Is a Key Regulator of Extracellular Matrix Integrity and Angiogenesis. Cell, 107:789–800.
Brew, K., Dinakarpandian, D., and Nagase, H., 2000, Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: evolution, structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1477:267–283.
Amour, A., Slocombe, P. M., Webster, A., Butler, M., Knight, C. G., Smith, B. J., Stephens, P. E., Shelley, C., Hutton, M., Knauper, V., Docherty, A. J., and Murphy, G., 1998, TNF-alpha converting enzyme (TACE) is inhibited by TIMP-3. FEBS Lett, 435:39–44.
Liu, L., Rich, B. E., Inobe, J., Chen, W., and Weiner, H. L., 1997, A potential pathway of Th2 development during primary immune response. IL-10 pretreated dendritic cells can prime naive CD4+T cells to secrete IL-4. Adv Exp Med Biol, 417:375–81.
Yang, Z., Strickland, D. K., and Bornstein, P., 2001, Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase 2 levels are regulated by the low density lipoprotein-related scavenger receptor and thrombospondin 2. J Biol Chem, 276:8403–8408.
Sottrup-Jensen, L., Sand, O., Kristensen, L., and Fey, G. H., 1989, The alpha-macroglobulin bait region. Sequence diversity and localization of cleavage sites for proteinases in five mammalian alpha-macroglobulins. J Biol Chem, 264:15781–9.
Takahashi, C., Sheng, Z., Horan, T. P., Kitayama, H., Maki, M., Hitomi, K., Kitaura, Y., Sasahara, R. M., Horimoto, A., and al., e., 1998, Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and inhibition of tumor invasion by the membrane-anchored glycoprotein RECK. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA, 95:13221–13226.
Welm, B., Mott, J. D., and Werb, Z., 2002, Vasculogenesis is a wreck without Reck: Regulating matrix metalloproteinase activity during embryogenesis is critical for development. Curr Biol, 12:209–211.
Stamenkovic, I., 2003, Extracellular matrix remodelling: the role of matrix metalloproteinases. J Pathol, 200:448–464.
Giannelli, G., Falk-Marzillier, J., Schiraldi, O., Stetler-Stevenson, W. G., and Quaranta, V., 1997, Induction of cell migration by matrix metalloprotease-2 cleavage of laminin-5. Science, 277:225–228.
Bosman, F. T., and Stamenkovic, I., 2003, Functional structure and composition of the extracellular matrix. J Pathol, 200:423–428.
Dumin, J. A., Dickeson, S. K., Stricker, T. P., Bhattacharyya-Pakrasi, M., Roby, J. D., Santoro, S. A., and Parks, W. C., 2001, Pro-collagenase-1 (matrix metalloproteinase-1) binds the alpha(2)beta(1) integrin upon release from keratinocytes migrating on type I collagen. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276:29368–29374.
Guo, H., Zucker, S., Gordon, M. K., Toole, B. P., and Biswas, C., 1997, Stimulation of matrix metalloproteinase production by recombinant extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer from transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem, 272:24–27.
Guo, H., Li, R., Zucker, S., and Toole, B. P., 2000, EMMPRIN (CD147), an inducer of matrix metalloproteinase synthesis, also binds interstitial collagenase to the tumor cell surface. Cancer Res, 60:888–891.
Brooks, P. C., Strömblad, S., Sanders, L. C., von Schalscha, T. L., Aimes, R. T., Stetler-Stevenson, W. G., Quigley, J. P., and Cheresh, D. A., 1996, Localization of matrix metalloproteinase MMP-2 to the surface of invasive cells by interaction with integrin alpha v beta 3. Cell, 85:683–693.
Yu, W. H., Woessner, J. F., Jr., McNeish, J. D., and Stamenkovic, I., 2002, CD44 anchors the assembly of matrilysin/MMP-7 with heparin-binding epidermal growth factor precursor and ErbB4 and regulates female reproductive organ remodeling. Genes Dev, 16:307–323.
Yu, Q., and Stamenkovic, I., 1999, Localization of matrix metalloproteinase 9 to the cell surface provides a mechanism for CD44-mediated tumor invasion. Genes Dev, 13:35–48.
Bourguignon, L. Y., Gunja-Smith, Z., Iida, N., Zhu, H. B., Young, L. J., Muller, W. J., and Cardiff, R. D., 1998, CD44v(3,8–10) is involved in cytoskeleton-mediated tumor cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-9) association in metastatic breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol, 176:206–215.
Fiore, E., Fusco, C., Romero, P., and Stamenkovic, I., 2002, Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9/gelatinase B) proteolytically cleaves ICAM-1 and participates in tumor cell resistance to natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Oncogene, 21:5213–5223.
Olson, M. W., Toth, M., Gervasi, D. C., Sado, Y., Ninomiya, Y., and Fridman, R., 1998, High affinity binding of latent matrix metalloproteinase-9 to the alpha2(IV) chain of collagen IV. J Biol Chem, 273:10672–81.
Yu, Q., and Stamenkovic, I., 2000, Cell surface-localized matrix metalloproteinase-9 proteolytically activates TGF-beta and promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis. Genes Dev, 14:163–176.
Ruiter, D., Bogenrieder, T., Elder, D., and Herlyn, M., 2002, Melanoma-stroma interactions: structural and functional aspects, Lancet Oncol, 3:35–43.
Martin, P., 1997, Wound healing—aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science, 276:75–81.
Uitto, J., and Kouba, D., 2000, Cytokine modulation of extracellular matrix gene expression: relevance to fibrotic skin diseases. J Dermatol Sci, 24Suppl 1:S60–S69.
van Kempen, L. C., Ruiter, D. J., van Muijen, G. N., and Coussens, L. M., 2003, The tumor microenvironment: a critical determinant of neoplastic evolution. Eur J Cell Biol, 82:539–548.
Gheree-Kermani, M., and Phan, M., 2001, Role of Cytokines and cytokine therapy in wound healing and fibrotic disease. Curr Pharm Des:1083–1103.
Bergers, G., and Coussens, L. M., 2000, Extrinsic regulators of epithelial tumor progression: metalloproteinases. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 10:120–127.
Engbring, J. A., and Kleinman, H. K., 2003, The basement membrane matrix in malignancy. J Pathol, 200:465–470.
Colorado, P. C., Torre, A., Kamphaus, G., Maeshima, Y., Hopfer, H., Takahashi, K., Volk, R., Zamborsky, E. D., Herman, S., Sarkar, P. K., Ericksen, M. B., Dhanabal, M., Simons, M., Post, M., Kufe, D. W., Weichselbaum, R. R., Sukhatme, V. P., and Kalluri, R., 2000, Anti-angiogenic cues from vascular basement membrane collagen. Cancer Res, 60:2520–2526.
McCawley, L. J., and Matrisian, L. M., 2001, Matrix metalloproteinases: they're not just for matrix anymore!. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 13:534–40.
O'Reilly, M. S., Boehm, T., Shing, Y., Fukai, N., Vasios, G., Lane, W. S., Flynn, E., Birkhead, J. R., Olsen, B. R., and Folkman, J., 1997, Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell, 88:277–285.
Kamphaus, G. D., Colorado, P. C., Panka, D. J., Hopfer, H., Ramchandran, R., Torre, A., Maeshima, Y., Mier, J. W., Sukhatme, V. P., and Kalluri, R., 2000, Canstatin, a novel matrix-derived inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. J Biol Chem, 275:1209–1215.
Maeshima, Y., Colorado, P. C., and Kalluri, R., 2000, Two RGD-independent αvβ3 integrin binding sites on tumstatin regulate distinct anti-tumor properties. J Biol Chem, 275:23745–50.
Petitclerc, E., Boutaud, A., Prestayko, A., Xu, J., Sado, Y., Ninomiya, Y., Sarras, M. P., Jr., Hudson, B. G., and Brooks, P. C., 2000, New functions for non-collagenous domains of human collagen type IV. Novel integrin ligands inhibiting angiogenesis and tumor growth in vivo. J Biol Chem, 275:8051–8061.
Ramchandran, R., Dhanabal, M., Volk, R., Waterman, M. J., Segal, M., Lu, H., Knebelmann, B., and Sukhatme, V. P., 1999, Antiangiogenic activity of restin, NC10 domain of human collagen XV: comparison to endostatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 255:735–739.
Hiraoka, N., Allen, E., Apel, I. J., Gyetko, M. R., and Weiss, S. J., 1998, Matrix metalloproteinases regulate neovascularization by acting as pericellular fibrinolysins. Cell, 95:365–377.
Cornelius, L. A., Nehring, L. C., Harding, E., Bolanowski, M., Welgus, H. G., Kobayashi, D. K., Pierce, R. A., and Shapiro, S. D., 1998, Matrix metalloproteinases generate angiostatin: effects on neovascularization. J Immunol, 161:6845–6852.
Hiller, O., Lichte, A., Oberpichler, A., Kocourek, A., and Tschesche, H., 2000, Matrix metalloproteinases collagenase-2, macrophage elastase, collagenase-3, and membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase impair clotting by degradation of fibrinogen and factor XII, J Biol Chem 275:33008–33013.
Vaisanen, A., Kallioinen, M., Taskinen, P. J., and Turpeenniemi-Hujanen, T., 1998, Prognostic value of MMP-2 immunoreactive protein (72 kD type IV collagenase) in primary skin melanoma. J Pathol, 186:51–58.
McQuibban, G. A., Butler, G. S., Gong, J. H., Bendall, L., Power, C., Clark-Lewis, I., and Overall, C. M., 2001, Matrix metalloproteinase activity inactivates the CXC chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1. J Biol Chem, 276:43503–8.
McQuibban, G. A., Gong, J. H., Wong, J. P., Wallace, J. L., Clark-Lewis, I., and Overall, C. M., 2002, Matrix metalloproteinase processing of monocyte chemoattractant proteins generates CC chemokine receptor antagonists with anti-inflammatory properties in vivo. Blood, 100:1160–1167.
Sheu, B. C., Hsu, S. M., Ho, H. N., Lien, H. C., Huang, S. C., and Lin, R. H., 2001, A novel role of metalloproteinase in cancer-mediated immunosuppression. Cancer Res, 61:237–242.
Balbin, M., Fueyo, A., Tester, A. M., Pendas, A. M., Pitiot, A. S., Astudillo, A., Overall, C. M., Shapiro, S. D., and Lopez-Otin, C., 2003, Loss of collagenase-2 confers increased skin tumor susceptibility to male mice. Nat Genet, 35:252–257.
Coussens, L. M., and Werb, Z., 1996, Matrix metalloproteinases and the development of cancer. Chem Biol, 3:895–904.
Nelson, A. R., Fingleton, B., Rothenberg, M. L., and Matrisian, L. M., 2000, Matrix metalloproteinases: biologic activity and clinical implications, J Clin Oncol 18:1135–1149.
McCawley, L. J., and Matrisian, L. M., 2001, Tumor progression: defining the soil round the tumor seed. Curr Biol, 11:R25–R27.
Coussens, L. M., Fingleton, B., and Matrisian, L. M., 2002, Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: trials and tribulations. Science, 295:2387–2392.
Iwata, H., Kobayashi, S., Iwase, H., Masaoka, A., Fujimoto, N., and Okada, Y., 1996, Production of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human breast carcinomas, Jpn J Cancer Res 87:602–611.
Brummer, O., Athar, S., Riethdorf, L., Loning, T., and Herbst, H., 1999, Matrix-metalloproteinases 1, 2, and 3 and their tissue inhibitors 1 and 2 in benign and malignant breast lesions: an in situ hybridization study. Virchows Arch, 435:566–573.
Heppner, K. J., Matrisian, L. M., Jensen, R. A., and Rodgers, W. H., 1996, Expression of most matrix metalloproteinase family members in breast cancer represents a tumor-induced host response. Am J Pathol, 149:273–282.
Visscher, D. W., Hoyhtya, M., Ottosen, S. K., Liang, C. M., Sarkar, F. H., Crissman, J. D., and Fridman, R., 1994, Enhanced expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) in the stroma of breast carcinomas correlates with tumor recurrence. Int J Cancer, 59:339–344.
Lebeau, A., Nerlich, A. G., Sauer, U., Lichtinghagen, R., and Lohrs, U., 1999, Tissue distribution of major matrix metalloproteinases and their transcripts in human breast carcinomas. Anticancer Res, 19:4257–64.
Jones, J. L., Glynn, P., and Walker, R. A., 1999, Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9, their inhibitors, and the activator MT1-MMP in primary breast carcinomas. J Pathol, 189:161–168.
Remacle, A. G., Noel, A., Duggan, C., McDermott, E., O'Higgins, N., Foidart, J. M., and Duffy, M. J., 1998, Assay of matrix metalloproteinases types 1, 2, 3 and 9 in breast cancer. Br J Cancer, 77:926–31.
Scorilas, A., Karameris, A., Arnogiannaki, N., Ardavanis, A., Bassilopoulos, P., Trangas, T., and Talieri, M., 2001, Overexpression of matrix-metalloproteinase-9 in human breast cancer: a potential favourable indicator in node-negative patients. Br J Cancer, 84:1488–1496.
Ahmad, A., Hanby, A., Dublin, E., Poulsom, R., Smith, P., Barnes, D., Rubens, R., Anglard, P., and Hart, I., 1998, Stromelysin 3: an independent prognostic factor for relapse-free survival in node-positive breast cancer and demonstration of novel breast carcinoma cell expression. Am J Pathol, 152:721–728.
Nielsen, B. S., Rank, F., Lopez, J. M., Balbin, M., Vizoso, F., Lund, L. R., Dano, K., and Lopez-Otin, C., 2001, Collagenase-3 expression in breast myofibroblasts as a molecular marker of transition of ductal carcinoma in situ lesions to invasive ductal carcinomas. Cancer Res, 61:7091–7100.
Nielsen, B. S., Sehested, M., Kjeldsen, L., Borregaard, N., Rygaard, J., and Dano, K., 1997, Expression of matrix metalloprotease-9 in vascular pericytes in human breast cancer. Lab Invest, 77:345–55.
Nielsen, B. S., Timshel, S., Kjeldsen, L., Sehested, M., Pyke, C., Borregaard, N., and Dano, K., 1996, 92 kDa type IV collagenase (MMP-9) is expressed in neutrophils and macrophages but not in malignant epithelial cells in human colon cancer. Int J Cancer, 65:57–62.
Wright, J. H., McDonnell, S., Portella, G., Bowden, G. T., Balmain, A., and Matrisian, L. M., 1994, A switch from stromal to tumor cell expression of stromelysin-1 mRNA associated with the conversion of squamous to spindle carcinomas during mouse skin tumor progression. Mol Carcinog, 10:207–215.
Coussens, L. M., Raymond, W. W., Bergers, G., Laig-Webster, M., Behrendtsen, O., Werb, Z., Caughey, G. H., and Hanahan, D., 1999, Inflammatory mast cells up-regulate angiogenesis during squamous epithelial carcinogenesis. Genes Dev, 13:1382–1397.
Janeway, C. A., Travers, P., Walport, M., and Shlomchik, M., 2001, Immunobiology, 5th ed. Garland Publishing, New York and London.
Dranoff, G., 2002, Tumour immunology: Immune recognition and tumor protection. Curr Opin in Immunology, 14:161–164.
Dranoff, G., 2003, Coordinated tumor immunity. J Clin Invest, 111:1116–1118.
Oshikiri, T., Miyamoto, M., Shichinohe, T., Suzuoki, M., Hiraoka, K., Nakakubo, Y., Shinohara, T., Itoh, T., Kondo, S., and Katoh, H., 2003, Prognostic value of intratumoral CD8+ T lymphocyte in extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma as essential immune response. J Surg Oncol, 84:224–228.
Abe, M., Kondo, S., Hirano, S., Ambo, Y., Tanaka, E., Morikawa, T., Okushiba, S., and Katoh, H., 2003, Long-term survival after radical resection of advanced pancreatic cancer: a case report with special reference to CD8+ T-cell infiltration. Int J Gastrointest Cancer, 33:107–110.
Wakabayashi, O., Yamazaki, K., Oizumi, S., Hommura, F., Kinoshita, I., Ogura, S., Dosaka-Akita, H., and Nishimura, M., 2003, CD4(+) T cells in cancer stroma, not CD8(+) T cells in cancer cell nests, are associated with favorable prognosis in human non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Sci, 94:1003–1009.
Nakakubo, Y., Miyamoto, M., Cho, Y., Hida, Y., Oshikiri, T., Suzuoki, M., Hiraoka, K., Itoh, T., Kondo, S., and Katoh, H., 2003, Clinical significance of immune cell infiltration within gallbladder cancer. Br J Cancer, 89:1736–1742.
Funada, Y., Noguchi, T., Kikuchi, R., Takeno, S., Uchida, Y., and Gabbert, H. E., 2003, Prognostic significance of CD8+ T cell and macrophage peritumoral infiltration in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep, 10:309–313.
Dunn, G. P., Bruce, A. T., Ikeda, H., Old, L. J., and Schreiber, R. D., 2002, Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat Immunol, 3:991–998.
Dudley, M. E., and Rosenberg, S. A., 2003, Adoptive-cell-transfer therapy for the treatment of patients with cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 3:666–675.
Balkwill, F., and Mantovani, A., 2001, Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow?. Lancet, 357:539–545.
Duncan, L. M., Richards, L. A., and Mihm, M. C., Jr., 1998, Increased mast cell density in invasive melanoma. J Cutan Pathol, 25:11–15.
Imada, A., Shijubo, N., Kojima, H., and Abe, S., 2000, Mast cells correlate with angiogenesis and poor outcome in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Eur Respir J, 15:1087–1093.
Takanami, I., Takeuchi, K., and Naruke, M., 2000, Mast cell density is associated with angiogenesis and poor prognosis in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer, 88:2686–2692.
Tomita, M., Matsuzaki, Y., and Onitsuka, T., 2000, Effect of mast cells on tumor angiogenesis in lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg, 69:1686–1690.
Toth-Jakatics, R., Jimi, S., Takebayashi, S., and Kawamoto, N., 2000, Cutaneous malignant melanoma: correlation between neovascularization and peritumor accumulation of mast cells overexpressing vascular endothelial growth factor. Hum Pathol, 31:955–960.
Shea, C. R., and Prieto, V. G., 1994, Mast cells in angiolipomas and hemangiomas of human skin: are they important for angiogenesis?. J Cutan Pathol, 21:247–251.
Benitez-Bribiesca, L., Wong, A., Utrera, D., and Castellanos, E., 2001, The role of mast cell tryptase in neoangiogenesis of premalignant and malignant lesions of the uterine cervix. J Histochem Cytochem, 49:1061–1062.
Ness, R. B., and Cottreau, C., 1999, Possible role of ovarian epithelial inflammation in ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst, 91:1459–67.
Weitzman, S. A., and Gordon, L. I., 1990, Inflammation and cancer: role of phagocyte-generated oxidants in carcinogenesis. Blood, 76:655–663.
Shacter, E., and Weitzman, S. A., 2002, Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology, 16:217–226.
Ernst, P. B., and Gold, B. D., 2000, The disease spectrum of Helicobacter pylori: the immunopathogenesis of gastroduodenal ulcer and gastric cancer. Annu Rev Microbiol, 54:615–640.
Engle, S. J., Ormsby, I., Pawlowski, S., Boivin, G. P., Croft, J., Balish, E., and Doetschman, T., 2002, Elimination of Colon Cancer in Germ-free Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1-deficient Mice. Cancer Res, 62:6362–6366.
Williams, C. S., Mann, M., and DuBois, R. N., 1999, The role of cyclooxygenases in inflammation, cancer, and development. Oncogene, 18:7908–7916.
Garcia-Rodriguez, L. A., and Huerta-Alvarez, C., 2001, Reduced risk of colorectal cancer among long-term users of aspirin and nonaspirin nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Epidemiology, 12:88–93.
Meier, C. R., Schmitz, S., and Jick, H., 2002, Association between acetaminophen or nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and risk of developing ovarian, breast, or colon cancer. Pharmacotherapy, 22:303–309.
Sharpe, C. R., Collet, J. P., McNutt, M., Belzile, E., Boivin, J. F., and Hanley, J. A., 2000, Nested case-control study of the effects of non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs on breast cancer risk and stage. Br J Cancer, 83:112–120.
Cotterchio, M., Kreiger, N., Sloan, M., and Steingart, A., 2001, Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 10:1213–1217.
Akre, K., Ekstrom, A. M., Signorello, L. B., Hansson, L. E., and Nyren, O., 2001, Aspirin and risk for gastric cancer: a population-based case-control study in Sweden. Br J Cancer, 84:965–968.
Bashkin, P., Razin, E., Eldor, A., and Vlodavsky, I., 1990, Degranulating mast cells secrete an endoglycosidase that degrades heparan sulfate in subendothelial extracellular matrix. Blood, 75:2204–2212.
Inuzuka, K., Ogata, Y., Nagase, H., and Shirouzu, K., 2000, Significance of coexpression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator, and matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) and 9 (gelatinase B) in colorectal carcinoma. J Surg Res, 93:211–218.
Stahle-Backdahl, M., Sudbeck, B. D., Eisen, A. Z., Welgus, H. G., and Parks, W. C., 1992, Expression of 92-kDa type IV collagenase mRNA by eosinophils associated with basal cell carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol, 99:497–503.
Zeng, Z. S., and Guillem, J. G., 1996, Colocalisation of matrix metalloproteinase-9-mRNA and protein in human colorectal cancer stromal cells. Br J Cancer, 74:1161–1167.
Coussens, L. M., Hanahan, D., and Arbeit, J., 1996, Genetic predisposition and parameters of malignant progression in K14-HPV16 transgenic mice. Am J Path, 149:1899–1917.
van Kempen, L. C. L., Rhee, J. S., Dehne, K., Lee, J., Edwards, D. R., and Coussens, L. M., 2002, Epithelial carcinogenesis: dynamic interplay between neoplastic cells and their microenvironment. Differentiation, 70:501–623.
Huang, S., Van Arsdall, M., Tedjarati, S., McCarty, M., Wu, W., Langley, R., and Fidler, I. J., 2002, Contributions of stromal metalloproteinase-9 to angiogenesis and growth of human ovarian carcinoma in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst, 94:1134–1142.
Hiratsuka, S., Nakamura, K., Iwai, S., Murakami, M., Itoh, T., Kijima, H., Shipley, J. M., Senior, R. M., and Shibuya, M., 2002, MMP9 induction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 is involved in lung-specific metastasis. Cancer Cell, 2:289–300.
van Kempen, L. C., and Coussens, L. M., 2002, MMP9 potentiates pulmonary metastasis formation. Cancer Cell, 2:251–252.
Biggs, J. R., and Kraft, A. S., 1995, Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase and cancer. J Mol Med, 73:509–614.
Lin, P., Buxton, J. A., Acheson, A., Radziejewski, C., Maisonpierre, P. C., Yancopoulos, G. D., Channon, K. M., Hale, L. P., Dewhirst, M. W., George, S. E., and Peters, K. G., 1998, Antiangiogenic gene therapy targeting the endothelium-specific receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 95:8829–8834.
Fong, T. A., Shawver, L. K., Sun, L., Tang, C., App, H., Powell, T. J., Kim, Y. H., Schreck, R., Wang, X., Risau, W., Ullrich, A., Hirth, K. P., and McMahon, G., 1999, SU5416 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase catalysis, tumor vascularization, and growth of multiple tumor types. Cancer Res, 59:99–106.
Noonberg, S. B., and Benz, C. C., 2000, Tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeted to the epidermal growth factor receptor subfamily: role as anticancer agents. Drugs, 59:753–67.
Attoub, S., Rivat, C., Rodrigues, S., Van Bocxlaer, S., Bedin, M., Bruyneel, E., Louvet, C., Kornprobst, M., Andre, T., Mareel, M., Mester, J., and Gespach, C., 2002, The c-kit Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor STI571 for Colorectal Cancer Therapy. Cancer Res, 62:4879–4883.
Somlyo, A. V., Phelps, C., Dipierro, C., Eto, M., Read, P., Barrett, M., Gibson, J. J., Burnitz, M. C., Myers, C., and Somlyo, A. P., 2003, Rho kinase and matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors cooperate to inhibit angiogenesis and growth of human prostate cancer xenotransplants. Faseb J, 17:223–234.
Bergers, G., Song, S., Meyer-Morse, N., Bergsland, E., and Hanahan, D., 2003, Benefits of targeting both pericytes and endothelial cells in the tumor vasculature with kinase inhibitors. J Clin Invest, 111:1287–1295.
Fowlkes, J. L., and Winkler, M. K., 2002, Exploring the interface between metallo-proteinase activity and growth factor and cytokine bioavailability. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 13:277–287.
Stamenkovic, I., 2000, Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol, 10:415–33.
Lynch, C. C., and Matrisian, L. M., 2002, Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor-host cell communication. Differentiation, 70:561–573.
D'Armiento, J., DiColandrea, T., Dalal, S. S., Okada, Y., Huang, M. T., Conney, A. H., and Chada, K., 1995, Collagenase expression in transgenic mouse skin causes hyperkeratosis and acanthosis and increases susceptibility to tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biol, 15:5732–5739.
Martin, D. C., Sanchez-Sweatman, O. H., Ho, A. T., Inderdeo, D. S., Tsao, M. S., and Khokha, R., 1999, Transgenic TIMP-1 inhibits simian virus 40 T antigen-induced hepatocarcinogenesis by impairment of hepatocellular proliferation and tumor angiogenesis. Lab Invest, 79:225–234.
Martin, D. C., Ruther, U., Sanchez-Sweatman, O. H., Orr, F. W., and Khokha, R., 1996, Inhibition of SV40 T antigen-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in TIMP-1 transgenic mice. Oncogene, 13:569–576.
Dong, J., Opresko, L. K., Dempsey, P. J., Lauffenburger, D. A., Coffey, R. J., and Wiley, H. S., 1999, Metalloprotease-mediated ligand release regulates autocrine signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 96:6235–6240.
Suzuki, M., Raab, G., Moses, M. A., Fernandez, C. A., and Klagsbrun, M., 1997, Matrix metalloproteinase-3 releases active heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor by cleavage at a specific juxtamembrane site. J Biol Chem, 272:31730–31737.
Arribas, J., Coodly, L., Vollmer, P., Kishimoto, T. K., Rose-John, S., and Massague, J., 1996, Diverse cell surface protein ectodomains are shed by a system sensitive to metalloprotease inhibitors. J Biol Chem, 271:11376–11382.
Werb, Z., 1997, ECM and cell surface proteolysis: regulating cellular ecology. Cell, 91:439–442.
Werb, Z., and Yan, Y., 1998, A cellular striptease act. Science, 282:1279–1280.
Yu, W. H., and Woessner, J. F., Jr., 2000, Heparan sulfate proteoglycans as extracellular docking molecules for matrilysin (matrix metalloproteinase 7). J Biol Chem, 275:4183–4191.
Kaya, G., Rodriguez, I., Jorcano, J. L., Vassalli, P., and Stamenkovic, I., 1997, Selective suppression of CD44 in keratinocytes of mice bearing an antisense CD44 transgene driven by a tissue-specific promoter disrupts hyaluronate metabolism in the skin and impairs keratinocyte proliferation. Genes Dev, 11:996–1007.
Gallea-Robache, S., Morand, V., Millet, S., Bruneau, J. M., Bhatnagar, N., Chouaib, S., and Roman-Roman, S., 1997, A metalloproteinase inhibitor blocks the shedding of soluble cytokine receptors and processing of transmembrane cytokine precursors in human monocytic cells. Cytokine, 9:340–346.
Lombard, M. A., Wallace, T. L., Kubicek, M. F., Petzold, G. L., Mitchell, M. A., Hendges, S. K., and Wilks, J. W., 1998, Synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-2, but not TIMP-1, inhibit shedding of tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptors in a human colon adenocarcinoma (Colo 205) cell line. Cancer Res, 58:4001–7.
McCusker, R. H., Busby, W. H., Dehoff, M. H., Camacho-Hubner, C., and Clemmons, D. R., 1991, Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding to cell monolayers is directly modulated by the addition of IGF-binding proteins. Endocrinology, 129:939–949.
Osborne, C. K., Coronado, E. B., Kitten, L. J., Arteaga, C. I., Fuqua, S. A., and Ramaharma, K., 1989, Insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II): a potential autocrine/paracrine growth factor for human breast cancer acting via the IGF-I receptor. Mol Endocrinol, 3:1701–1709.
Shimasaki, S., Shimonaka, M., Zhang, H. P., and Ling, N., 1991, Identification of five different insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) from adult rat serum and molecular cloning of a novel IGFBP-5 in rat and human. J Biol Chem, 266:10646–10653.
Fowlkes, J. L., Enghild, J. J., Suzuki, K., and Nagase, H., 1994, Matrix metalloproteinases degrade insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in dermal fibroblast cultures. J Biol Chem, 269:25742–25746.
Fowlkes, J. L., Serra, D. M., Nagase, H., and Thrailkill, K. M., 1999, MMPs are IGFBP-degrading proteinases: implications for cell proliferation and tissue growth. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 878:696–699.
Fowlkes, J. L., Serra, D. M., Bunn, R. C., Thrailkill, K. M., Enghild, J. J., and Nagase, H., 2003, Regulation of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I (Igf-I) Action by Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 (Mmp-3) Involves Selective Disruption of Igf-I/Igf-Binding Protein-3 (Igfbp-3) Complexes. Endocrinology.
Conover, C. A., Durham, S. K., Zapf, J., Masiarz, F. R., and Kiefer, M. C., 1995, Cleavage analysis of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-dependent IGF-binding protein-4 proteolysis and expression of protease-resistant IGF-binding protein-4 mutants. J Biol Chem, 270:4395–4400.
Manes, S., Mira, E., Barbacid, M. M., Cipres, A., Fernandez-Resa, P., Buesa, J. M., Merida, I., Aracil, M., Marquez, G., and Martinez, A. C., 1997, Identification of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 as a potential physiological substrate for human stromelysin-3. J Biol Chem, 272:25706–12.
Martin, D. C., Fowlkes, J.L., Babic, B., and Khokha, R., 1999, Insulin-like growth factor II signaling in neoplastic proliferation is blocked by transgenic expression of the metalloproteinase inhibitor TIMP-1. J Cell Biol, 146:881–892.
Tennant, M. K., Thrasher, J. B., Twomey, P. A., Drivdahl, R. H., Birnbaum, R. S., and Plymate, S. R., 1996, Protein and messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) for the type 1 insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor is decreased and IGF-II mRNA is increased in human prostate carcinoma compared to benign prostate epithelium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 81:3774–3782.
D'Errico, A., Grigioni, W. F., Fiorentino, M., Baccarini, P., Lamas, E., De Mitri, S., Gozzetti, G., Mancini, A. M., and Brechot, C., 1994, Expression of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) in human hepatocellular carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study. Pathol Int, 44:131–137.
Chan, J. M., Stampfer, M. J., Giovannucci, E., Gann, P. H., Ma, J., Wilkinson, P., Hennekens, C. H., and Pollak, M., 1998, Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Science, 279:563–566.
Hankinson, S. E., Willett, W. C., Colditz, G. A., Hunter, D. J., Michaud, D. S., Deroo, B., Rosner, B., Speizer, F. E., and Pollak, M., 1998, Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer. Lancet, 351:1393–1396.
Whitelock, J. M., Murdoch, A. D., Iozzo, R. V., and Underwood, P. A., 1996, The degradation of human endothelial cell-derived perlecan and release of bound basic fibroblast growth factor by stromelysin, collagenase, plasmin, and heparanases. J Biol Chem, 271:10079–10086.
Friedl, A., Chang, Z., Tierney, A., and Rapraeger, A. C., 1997, Differential binding of fibroblast growth factor-2 and-7 to basement membrane heparan sulfate: comparison of normal and abnormal human tissues. Am J Pathol, 150:1443–1455.
Levi, E., Fridman, R., Miao, H. Q., Ma, Y. S., Yayon, A., and Vlodavsky, I., 1996, Matrix metalloproteinase 2 releases active soluble ectodomain of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:7069–74.
Czubayko, F., Liaudet-Coopman, E. D., Aigner, A., Tuveson, A. T., Berchem, G. J., and Wellstein, A., 1997, A secreted FGF-binding protein can serve as the angiogenic switch in human cancer. Nat Med, 3:1137–1140.
Annes, J. P., Munger, J. S., and Rifkin, D. B., 2003, Making sense of latent TGFbeta activation. J Cell Sci, 116:217–224.
Massague, J., Blain, S. W., and Lo, R. S., 2000, TGFbeta signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell, 103:295–309.
Derynck, R., Akhurst, R. J., and Balmain, A., 2001, TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat Genet, 29:117–129.
Akhurst, R. J., 2002, TGF-beta antagonists: why suppress a tumor suppressor?. J Clin Invest, 109:1533–1536.
Moustakas, A., Pardali, K., Gaal, A., and Heldin, C. H., 2002, Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling in regulation of cell growth and differentiation. Immunol Lett, 82:85–91.
Markowitz, S. D., and Roberts, A. B., 1996, Tumor suppressor activity of the TGF-beta pathway in human cancers. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 7:93–102.
Alexandrow, M. G., and Moses, H. L., 1995, Transforming growth factor beta 1 inhibits mouse keratinocytes late in G1 independent of effects on gene transcription. Cancer Res, 55:3928–3932.
Taipale, J., Saharinen, J., and Keski-Oja, J., 1998, Extracellular matrix-associated transforming growth factor-beta: role in cancer cell growth and invasion. Adv Cancer Res, 75:87–134.
Miyazono, K., Ichijo, H., and Heldin, C. H., 1993, Transforming growth factor-beta: latent forms, binding proteins and receptors. Growth Factors, 8:11–22.
Munger, J. S., Harpel, J. G., Gleizes, P. E., Mazzieri, R., Nunes, I., and Rifkin, D. B., 1997, Latent transforming growth factor-beta: structural features and mechanisms of activation. Kidney Int, 51:1376–1382.
Oklu, R., and Hesketh, R., 2000, The latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein (LTBP) family. Biochem J, 352 Pt 3:601–610.
Imai, K., Hiramatsu, A., Fukushima, D., Pierschbacher, M. D., and Okada, Y., 1997, Degradation of decorin by matrix metalloproteinases: identification of the cleavage sites, kinetic analyses and transforming growth factor-beta1 release. Biochem J, 322:809–814.
Hildebrand, A., Romaris, M., Rasmussen, L. M., Heinegard, D., Twardzik, D. R., Border, W. A., and Ruoslahti, E., 1994, Interaction of the small interstitial proteoglycans biglycan, decorin and fibromodulin with transforming growth factor beta. Biochem J, 302(Pt 2):527–534.
Kresse, H., Hausser, H., Schonherr, E., and Bittner, K., 1994, Biosynthesis and interactions of small chondroitin/dermatan sulphate proteoglycans. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem, 32:259–264.
Velasco-Loyden, G., Arribas, J., and Lopez-Casillas, F., 2003, The shedding of betaglycan is regulated by pervanadate and mediated by MT1-MMP. J Biol Chem.
Damsky, C., 2002, Cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix adhesion receptors. Ann NY Acad Sci, 961:154–155.
Noe, V., Fingleton, B., Jacobs, K., Crawford, H. C., Vermeulen, S., Steelant, W., Bruyneel, E., Matrisian, L. M., and Mareel, M., 2001, Release of an invasion promoter E-cadherin fragment by matrilysin and stromelysin-1. J Cell Sci, 114:111–118.
Kajita, M., Itoh, Y., Chiba, T., Mori, H., Okada, A., Kinoh, H., and Seiki, M., 2001, Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves CD44 and promotes cell migration. J Cell Biol, 153:893–904.
Deryugina, E. I., Soroceanu, L., and Strongin, A. Y., 2002, Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase stimulates human glioma xenograft growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Res, 62:580–588.
Hynes, R. O., 2002, A reevaluation of integrins as regulators of angiogenesis. Nat Med, 8:918–921.
Hynes, R. O., 2002, Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell, 110:673–687.
Zamir, E., and Geiger, B., 2001, Molecular complexity and dynamics of cell-matrix adhesions. J Cell Sci, 114:3583–3590.
Kassis, J., Lauffenburger, D. A., Turner, T., and Wells, A., 2001, Tumor invasion as dysregulated cell motility. Semin Cancer Biol, 11:105–117.
Monsky, W. L., Kelly, T., Lin, C. Y., Yeh, Y., Stetler-Stevenson, W. G., Mueller, S. C., and Chen, W. T., 1993, Binding and localization of M(r) 72,000 matrix metalloproteinase at cell surface invadopodia. Cancer Res, 53:3159–3164.
Chen, W. T., and Wang, J. Y., 1999, Specialized surface protrusions of invasive cells, invadopodia and lamellipodia, have differential MT1-MMP, MMP-2, and TIMP-2 localization. Ann NY Acad Sci, 878:361–371.
Riikonen, T., Westermarck, J., Koivisto, L., Broberg, A., Kahari, V. M., and Heino, J., 1995, Integrin alpha 2 beta 1 is a positive regulator of collagenase (MMP-1) and collagen alpha 1(I) gene expression. J Biol Chem, 270:13548–13552.
von Bredow, D. C., Nagle, R. B., Bowden, G. T., and Cress, A. E., 1997, Cleavage of beta 4 integrin by matrilysin. Exp Cell Res, 236:341–345.
Akimov, S. S., Krylov, D., Fleischman, L. F., and Belkin, A. M., 2000, Tissue transglutaminase is an integrin-binding adhesion coreceptor for fibronectin. J Cell Biol, 148:825–838.
Belkin, A. M., Akimov, S. S., Zaritskaya, L. S., Ratnikov, B. I., Deryugina, E. I., and Strongin, A. Y., 2001, Matrix-dependent proteolysis of surface transglutaminase by membrane-type metalloproteinase regulates cancer cell adhesion and locomotion. J Biol Chem, 276:18415–18422.
Van Aken, E., De Wever, O., Correia da Rocha, A., and Mareel, M., 2001, Defective E-cadherin/catenin complexes in human cancer. Virchows Arch, 439:725–751.
Bracke, M. E., Van Roy, F. M., and Mareel, M. M., 1996, The E-cadherin/catenin complex in invasion and metastasis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol, 213:123–161.
De Leeuw, W. J., Berx, G., Vos, C. B., Peterse, J. L., Van de Vijver, M. J., Litvinov, S., Van Roy, F., Cornelisse, C. J., and Cleton-Jansen, A. M., 1997, Simultaneous loss of E-cadherin and catenins in invasive lobular breast cancer and lobular carcinoma in situ. J Pathol, 183:404–411.
Llorens, A., Rodrigo, I., Lopez-Barcons, L., Gonzalez-Garrigues, M., Lozano, E., Vinyals, A., Quintanilla, M., Cano, A., and Fabra, A., 1998, Down-regulation of E-cadherin in mouse skin carcinoma cells enhances a migratory and invasive phenotype linked to matrix metalloproteinase-9 gelatinase expression. Lab Invest, 78:1131–42.
Beavon, I. R., 2000, The E-cadherin-catenin complex in tumour metastasis: structure, function and regulation. Eur J Cancer, 36:1607–1620.
Christofori, G., and Semb, H., 1999, The role of the cell-adhesion molecule E-cadherin as a tumoursuppressor gene. Trends Biochem Sci, 24:73–76.
Perl, A. K., Wilgenbus, P., Dahl, U., Semb, H., and Christofori, G., 1998, A causal role for E-cadherin in the transition from adenoma to carcinoma. Nature, 392:190–3.
Perl, A. K., Dahl, U., Wilgenbus, P., Cremer, H., Semb, H., and Christofori, G., 1999, Reduced expression of neural cell adhesion molecule induces metastatic dissemination of pancreatic beta tumor cells. Nat Med, 5:286–91.
Lochter, A., Galosy, S., Muschler, J., Freedman, N., Werb, Z., and Bissell, M. J., 1997, Matrix metalloproteinase stromelysin-1 triggers a cascade of molecular alterations that leads to stable epithelial-to-mesenchymal conversion and a premalignant phenotype in mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Biol, 139:1861–1872.
Nikkola, J., Vihinen, P., Vlaykova, T., Hahka-Kemppinen, M., Kahari, V. M., and Pyrhonen, S., 2002, High expression levels of collagenase-1 and stromelysin-1 correlate with shorter disease-free survival in human metastatic melanoma. Int J Cancer. 97:432–438.
Sympson, C. J., Bissell, M. J., and Werb, Z., 1995, Mammary gland tumor formation in transgenic mice overexpressing stromelysin-1. Semin Cancer Biol, 6:159–163.
Thomasset, N., Lochter, A., Sympson, C. J., Lund, L. R., Williams, D. R., Behrendtsen, O., Werb, Z., and Bissell, M. J., 1998, Expression of autoactivated stromelysin-1 in mammary glands of transgenic mice leads to a reactive stroma during early development. Am J Pathol, 153:457–467.
Lochter, A., Werb, Z., and Bissell, M. J., 1999, Transcriptional regulation of stromelysin-1 gene expression is altered during progression of mouse mammary epithelial cells from functionally normal to malignant. Matrix Biol, 18:455–467.
Rudolph-Owen, L. A., Chan, R., Muller, W. J., and Matrisian, L. M., 1998, The matrix metalloproteinase matrilysin influences early-stage mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Res, 58:5500–5506.
Vargo-Gogola, T., Fingleton, B., Crawford, H. C., and Matrisian, L. M., 2002, Matrilysin (matrix metalloproteinase-7) selects for apoptosis-resistant mammary cells in vivo. Cancer Res, 62:5559–5563.
McGuire, J. K., Li, Q., and Parks, W. C., 2003, Matrilysin (matrix metalloproteinase-7) mediates Ecadherin ectodomain shedding in injured lung epithelium. Am J Pathol, 162:1831–1843.
Naot, D., Sionov, R. V., and Ish-Shalom, D., 1997, CD44: structure, function, and association with the malignant process. Adv Cancer Res, 71:241–319.
Pohl, M., Sakurai, H., Stuart, R. O., and Nigam, S. K., 2000, Role of hyaluronan and CD44 in in vitro branching morphogenesis of ureteric bud cells. Dev Biol, 224:312–325.
Okamoto, I., Kawano, Y., Murakami, D., Sasayama, T., Araki, N., Miki, T., Wong, A. J., and Saya, H., 2001, Proteolytic release of CD44 intracellular domain and its role in the CD44 signaling pathway. J Cell Biol, 155:755–62.
Cichy, J., and Pure, E., 2003, The liberation of CD44. J Cell Biol, 161:839–843.
Jalkanen, S., Joensuu, H., Soderstrom, K. O., and Klemi, P., 1991, Lymphocyte homing and clinical behavior of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Invest, 87:1835–1840.
Mori, H., Tomari, T., Koshikawa, N., Kajita, M., Itoh, Y., Sato, H., Tojo, H., Yana, I., and Seiki, M., 2002, CD44 directs membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase to lamellipodia by associating with its hemopexin-like domain. Embo J, 21:3949–3959.
Li, R., Huang, L., Guo, H., and Toole, B. P., 2001, Basigin (murine EMMPRIN) stimulates matrix metalloproteinase production by fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol, 186:371–9.
Folkman, J., 1990, What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent?. J Nat Cancer Inst, 82:4–6.
Folkman, J., and Shing, Y., 1992, Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem, 267:10931–10934.
Weidner, N., Folkman, J., Pozza, F., Bevilacqua, P., Allred, E. N., Moore, D. H., Meli, S., and Gasparini, G., 1992, Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst, 84:1875–1887.
Folkman, J., 1994, Tumor angiogenesis. Nature Medicine, 1:206–232.
Folkman, J., 1995, Tumor Angiogenesis. In The Molecular Basis of Cancer, Mendelsohn, J., Howley, P. M., Israel, M. A., and Liotta L. A., eds, Vol. 9:206–232. W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia.
Folkman, J., and D'Amore, P. A., 1996, Blood vessel formation: what is its molecular basis. Cell, 87:1153–1155.
Carmeliet, P., and Jain, R. K., 2000, Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature, 407:249–257.
Carmeliet, P., 2003, Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med, 9:653–60.
Hanahan, D., and Folkman, J., 1996, Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell, 86:353–364.
Nagy, J. A., Brown, L. F., Senger, D. R., Lanir, N., Van de Water, L., Dvorak, A. M., and Dvorak, H. F., 1989, Pathogenesis of tumor stroma generation: a critical role for leaky blood vessels and fibrin deposition. Biochim Biophys Acta, 948:305–326.
Lindahl, P., Johansson, B. R., Leveen, P., and Betsholtz, C., 1997, Pericyte loss and microaneurysm formation in PDGF-B-deficient mice. Science, 277:242–245.
Paku, S., and Paweletz, N., 1991, First steps of tumor-related angiogenesis. Lab Invest, 65:334–346.
Giordano, F. J., and Johnson, R. S., 2001, Angiogenesis: the role of the microenvironment in flipping the switch. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 11:35–40.
Seandel, M., Noack-Kunnmann, K., Zhu, D., Aimes, R. T., and Quigley, J. P., 2001, Growth factor-induced angiogenesis in vivo requires specific cleavage of fibrillar type I collagen. Blood, 97:2323–2332.
Liu, X., Wu, H., Byrne, M., Jeffrey, J., Krane, S., and Jaenisch, R., 1995, A targeted mutation at the known collagenase cleavage site in mouse type I collagen impairs tissue remodeling. J Cell Biol, 130:227–237.
Xu, J., Rodriguez, D., Petitclerc, E., Kim, J. J., Hangai, M., Moon, Y. S., Davis, G. E., Brooks, P. C., and Yuen, S. M., 2001, Proteolytic exposure of a cryptic site within collagen type IV is required for angiogenesis and tumor growth in vivo. J Cell Biol, 154:1069–1079.
DiPietro, L. A., Burdick, M., Low, Q. E., Kunkel, S. L., and Strieter, R. M., 1998, MIP-1alpha as a critical macrophage chemoattractant in murine wound repair. J Clin Invest, 101:1693–1698.
Ferreras, M., Felbor, U., Lenhard, T., Olsen, B. R., and Delaisse, J., 2000, Generation and degradation of human endostatin proteins by various proteinases. FEBS Lett, 486:247–251.
O'Reilly, M. S., Holmgren, L., Shing, Y., Chen, C., Rosenthal, R. A., Moses, M., Lane, W. S., Cao, Y., Sage, E. H., and Folkman, J., 1994, Angiostatin: a novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell, 79:315–328.
Maeshima, Y., Colorado, P. C., Torre, A., Holthaus, K. A., Grunkemeyer, J. A., Ericksen, M. B., Hopfer, H., Xiao, Y., Stillman, I. E., and Kalluri, R., 2000, Distinct antitumor properties of a type IV collagen domain derived from basement membrane. J Biol Chem, 275:21340–8.
Petitclerc, E., Stromblad, S., von Schalscha, T. L., Mitjans, F., Piulats, J., Montgomery, A. M., Cheresh, D. A., and Brooks, P. C., 1999, Integrin αvβ3 promotes M21 melanoma growth in human skin by regulating tumor cell survival. Cancer Res, 59:2724–30.
Hamano, Y., Zeisberg, M., Sugimoto, H., Lively, J. C., Maeshima, Y., Changqing, Y., R.O., H., Werb, Z., Sudhakar, A., and Kalluri, R., 2003, Physiological levels of tumstatin, a fragment of collagen IV alpha3 chain, are generated by MMP-9 protelysis and suppress angioenesis via alphaVbeta3 integrin. Cancer Cell, 3:589–601.
Patterson, B. C., and Sang, Q. A., 1997, Angiostatin-converting enzyme activities of human matrilysin (MMP-7) and gelatinase B/type IV collagenase (MMP-9). J Biol Chem, 272:28823–5.
Sobrin, L., Liu, Z., Monroy, D. C., Solomon, A., Selzer, M. G., Lokeshwar, B. L., and Pflugfelder, S. C., 2000, Regulation of MMP-9 activity in human tear fluid and corneal epithelial culture supernatant. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 41:1703–1709.
Pozzi, A., LeVine, W. F., and Gardner, H. A., 2002, Low plasma levels of matrix metalloproteinase 9 permit increased tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene, 21:272–281.
Grunert, S., Jechlinger, M., and Beug, H., 2003, Diverse cellular and molecular mechanisms contribute to epithelial plasticity and metastasis. Mol Cell Biol, 4:657–665.
Birchmeier, C., Birchmeier, W., Gherardi, E., and Vande Woude, G., 2003, Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Med, 4:915–925.
Woodhouse, E. C., Chuaqui, R. F., and Liotta, L. A., 1997, General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer, 80:1529–37.
Yokota, J., 2000, Tumor progression and metastasis. Carcinogenesis, 21:497–503.
Fidler, I. J., 2001, Seed and soil revisited: contribution of the organ microenvironment to cancer metastasis. Surg Oncol Clin N Am, 10:257–269.
Fidler, I. J., 2002, Critical determinants of metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol, 12:89–96.
Comoglio, P. M., and Trusolino, L., 2002, Invasive growth: from development to metastasis, J Clin Invest 109:857–62.
Jussila, L., and Alitalo, K., 2002, Vascular growth factors and lymphangiogenesis. Physiol Rev, 82:673–700.
Engers, R., and Gabbert, H. E., 2000, Mechanisms of tumor metastasis: cell biological aspects and clinical implications. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 126:682–692.
Moser, P. L., Kieback, D. G., Hefler, L., Tempfer, C., Neunteufel, W., and Gitsch, G., 1999, Immunohistochemical detection of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) 1 and 2, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 (TIMP 2) in stage IB cervical cancer. Anticancer Res, 19:4391–4393.
Inoue, T., Yashiro, M., Nishimura, S., Maeda, K., Sawada, T., Ogawa, Y., Sowa, M., and Chung, K. H., 1999, Matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression is a prognostic factor for patients with advanced gastric cancer. Int J Mol Med, 4:73–77.
Yamashita, K., Azumano, I., Mai, M., and Okada, Y., 1998, Expression and tissue localization of matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin) in human gastric carcinomas. Implications for vessel invasion and metastasis. Int J Cancer, 79:187–194.
Gokaslan, Z. L., Chintala, S. K., York, J. E., Boyapati, V., Jasti, S., Sawaya, R., Fuller, G., Wildrick, D. M., Nicolson, G. L., and Rao, J. S., 1998, Expression and role of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 in human spinal column tumors. Clin Exp Metastasis, 16:721–728.
Garbisa, S., Scagliotti, G., Masiero, L., Di Francesco, C., Caenazzo, C., Onisto, M., Micela, M., Stetler-Stevenson, W. G., and Liotta, L. A., 1992, Correlation of serum metalloproteinase levels with lung cancer metastasis and response to therapy. Cancer Res, 52:4548–4549.
Nyormoi, O., Mills, L., and Bar-Eli, M., 2003, An MMP-2/MMP-9 inhibitor, 5a, enhances apoptosis induced by ligands of the TNF receptor superfamily in cancer cells. Cell Death Differ, 10:558–569.
Hotz, H. G., Hines, O. J., Hotz, B., Foitzik, T., Buhr, H. J., and Reber, H. A., 2003, Evaluation of vascular endothelial growth factor blockade and matrix metalloproteinase inhibition as a combination therapy for experimental human pancreatic cancer. J Gastrointest Surg, 7:220–227.
Shinoda, K., Shibuya, M., Hibino, S., Ono, Y., Matsuda, K., Takemura, A., Zou, D., Kokubo, Y., Takechi, A., and Kudoh, S., 2003, A novel matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, FYK-1388 suppresses tumor growth, metastasis and angiogenesis by human fibrosarcoma cell line. Int J Oncol, 22:281–288.
Winding, B., NicAmhlaoibh, R., Misander, H., Hoegh-Andersen, P., Andersen, T. L., Holst-Hansen, C., Heegaard, A. M., Foged, N. T., Brunner, N., and Delaisse, J. M., 2002, Synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors inhibit growth of established breast cancer osteolytic lesions and prolong survival in mice. Clin Cancer Res, 8:1932–1939.
Katori, H., Baba, Y., Imagawa, Y., Nishimura, G., Kagesato, Y., Takagi, E., Ishii, A., Yanoma, S., Maekawa, R., Yoshioka, T., Nagashima, Y., Kato, Y., and Tsukuda, M., 2002, Reduction of in vivo tumor growth by MMI-166, a selective matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, through inhibition of tumor angiogenesis in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines of head and neck. Cancer Lett, 178:151–159.
Weber, M. H., Lee, J., and Orr, F. W., 2002, The effect of Neovastat (AE-941) on an experimental metastatic bone tumor model. Int J Oncol, 20:299–303.
Naglich, J. G., Jure-Kunkel, M., Gupta, E., Fargnoli, J., Henderson, A. J., Lewin, A. C., Talbott, R., Baxter, A., Bird, J., Savopoulos, R., Wills, R., Kramer, R. A., and Trail, P. A., 2001, Inhibition of angiogenesis and metastasis in two murine models by the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, BMS-275291. Cancer Res, 61:8480–8485.
Brown, P. D., 1999, Clinical studies with matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. APMIS, 107:174–180.
Drummond, A. H., Beckett, P., Brown, P. D., Bone, E. A., Davidson, A. H., Galloway, W. A., Gearing, A. J., Huxley, P., Laber, D., McCourt, M., Whittaker, M., Wood, L. M., and Wright, A., 1999, Preclinical and clinical studies of MMP inhibitors in cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 878:228–235.
Whittaker, M., Floyd, C. D., Brown, P., and Gearing, A. J., 1999, Design and therapeutic application of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Chem Rev, 99:2735–76.
Brown, P. D., 2000, Ongoing trials with matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 9:2167–2177.
Opdenakker, G., Van den Steen, P. E., and Van Damme, J., 2001, Gelatinase B: a tuner and amplifier of immune functions. Trends Immunol, 22:571–579.
Müller, A., Homey, B., Soto, H., Ge, N., Catron, D., Buchanan, M. E., McClanahan, T., Murphy, E., Yuan, W., Wagner, S. N., Barrera, J. L., Mohar, A., Verastegui, E., and Zlotnik, A., 2001, Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature, 410:50–56.
Van den Steen, P. E., Proost, P., Wuyts, A., Van Damme, J., and Opdenakker, G., 2000, Neutrophil gelatinase B potentiates interleukin-8 tenfold by aminoterminal processing, whereas it degrades CTAP-III, PF-4, and GRO-alpha and leaves RANTES and MCP-2 intact. Blood, 96:2673–2681.
Ramjeesingh, R., Leung, R., and Siu, C. H., 2003, Interleukin-8 secreted by endothelial cells induces chemotaxis of melanoma cells through the chemokine receptor CXCR1. Faseb J, 17:1292–1294.
Varney, M. L., Li, A., Dave, B. J., Bucana, C. D., Johansson, S. L., and Singh, R. K., 2003, Expression of CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptors in malignant melanoma with different metastatic potential and their role in interleukin-8 (CXCL-8)-mediated modulation of metastatic phenotype. Clin Exp Metastasis, 20:723–731.
Kawamata, H., Kawai, K., Kameyama, S., Johnson, M. D., Stetler-Stevenson, W. G., and Oyasu, R., 1995, Over-expression of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMP1 and TIMP2) suppresses extravasation of pulmonary metastasis of a rat bladder carcinoma. Int J Cancer, 63:680–687.
Onisto, M., Riccio, M. P., Scannapieco, P., Caenazzo, C., Griggio, L., Spina, M., Stetler-Stevenson, W. G., and Garbisa, S., 1995, Gelatinase A/TIMP-2 imbalance in lymph-node-positive breast carcinomas, as measured by RT-PCR. Int J Cancer, 63:621–6.
Bian, J., Wang, Y., Smith, M. R., Kim, H., Jacobs, C., Jackman, J., Kung, H. F., Colburn, N. H., and Sun, Y., 1996, Suppression of in vivo tumor growth and induction of suspension cell death by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP)-3. Carcinogenesis, 17:1805–1811.
Fong, K. M., Kida, Y., Zimmerman, P. V., and Smith, P. J., 1996, TIMP1 and adverse prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 2:1369–1372.
Grignon, D. J., Sakr, W., Toth, M., Ravery, V., Angulo, J., Shamsa, F., Pontes, J. E., Crissman, J. C., and Fridman, R., 1996, High levels of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) expression are associated with poor outcome in invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Res, 56:1654–1659.
Martin, D. C., Rüther, U., Sanchez-Sweatman, O. H., Orr, F. W., and Khokha, R., 1996, Inhibition of SV40 T antigen-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in TIMP-1 transgenic mice. Oncogene, 13:569–576.
Matsuzawa, K., Fukuyama, K., Hubbard, S. L., Dirks, P. B., and Rutka, J. T., 1996, Transfection of an invasive human astrocytoma cell line with a TIMP-1 cDNA: modulation of astrocytoma invasive potential. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 55:88–96.
Soloway, P. D., Alexander, C. M., Werb, Z., and Jaenisch, R., 1996, Targeted mutagenesis of Timp-1 reveals that lung tumor invasion is influenced by Timp-1 genotype of the tumor but not by that of the host. Oncogene, 13:2307–14.
Thorgeirsson, U. P., Yoshiji, H., Sinha, C. C., and Gomez, D. E., 1996, Breast cancer; tumor neovasculature and the effect of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) on angiogenesis. In Vivo, 10:137–144.
Kruger, A., Fata, J. E., and Khokha, R., 1997, Altered tumor growth and metastasis of a T-cell lymphoma in Timp-1 transgenic mice. Blood, 90:1993–2000.
Shoji, A., Sakamoto, Y., Tsuchiya, T., Moriyama, K., Kaneko, T., Okubo, T., Umeda, M., and Miyazaki, K., 1997, Inhibition of tumor promoter activity toward mouse fibroblasts and their in vitro transformation by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1). Carcinogenesis, 18:2093–100.
Kruger, A., Sanchez-Sweatman, O. H., Martin, D. C., Fata, J. E., Ho, A. T., Orr, F. W., Ruther, U., and Khokha, R., 1998, Host TIMP-1 overexpression confers resistance to experimental brain metastasis of a fibrosarcoma cell line. Oncogene, 16:2419–23.
Baker, A. H., George, S. J., Zaltsman, A. B., Murphy, G., and Newby, A. C., 1999, Inhibition of invasion and induction of apoptotic cell death of cancer cell lines by overexpression of TIMP-3. Br J Cancer, 79:1347–1355.
Brown, P. D., 1995, Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: a novel class of anticancer agents. Adv Enzyme Regul, 35:293–301.
Brown, P. D., 1997, Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in the treatment of cancer. Med Oncol, 14:1–10.
Hidalgo, M., and Eckhardt, S. G., 2001, Development of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst, 93:178–193.
Bernardo, M. M., Brown, S., Li, Z. H., Fridman, R., and Mobashery, S., 2002, Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of Potent, Slow-binding Inhibitors That Are Selective for Gelatinases. J Biol Chem, 277:11201–11207.
Coussens, L. M., B. Fingleton, B., and Matrisian, L. M., 2002, Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: trials and tribulations. Science, 295:2387–2392.
Brown, S., Bernardo, M. M., Li, Z. H., Kotra, L. P., Tanaka, Y., Fridman, R., and Mobashery, S., 2000, Potent and Selective Mechanism-Based Inhibition of Gelatinases. Journal of American Chemical Society, 122:6799–6800.
Brown, P. D., 2001, New hope for matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today, 6:615.
Koivunen, E., Arap, W., Valtanen, H., Rainisalo, A., Medina, O. P., Heikkila, P., Kantor, C., Gahmberg, C. G., Salo, T., Konttinen, Y. T., Sorsa, T., Ruoslahti, E., and Pasqualini, R., 1999, Tumor targeting with a selective gelatinase inhibitor. Nat Biotechnol, 17:768–774.
Garbisa, S., Biggin, S., Cavallarin, N., Sartor, L., Benelli, R., and Albini, A., 1999, Tumor invasion: molecular shears blunted by green tea. Nat Med, 5:1216.
Falardeau, P., Champagne, P., Poyet, P., Hariton, C., and Dupont, E., 2001, Neovastat, a naturally occurring multifunctional antiangiogenic drug, in phase III clinical trials. Semin Oncol, 28:620–625.
Reich, R., Thompson, E. W., Iwamoto, Y., Martin, G. R., Deason, J. R., Fuller, G. C., and Miskin, R., 1988, Effects of inhibitors of plasminogen activator, serine proteinases, and collagenase IV on the invasion of basement membranes by metastatic cells. Cancer Res, 48:3307–12.
Davies, B., Brown, P. D., East, N., Crimmin, M. J., and Balkwill, F. R., 1993, A synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor decreases tumor burden and prolongs survival of mice bearing human ovarian carcinoma xenografts. Cancer Res, 53:2087–2091.
Wang, X., Fu, X., Brown, P. D., Crimmin, M. J., and Hoffman, R. M., 1994, Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor BB-94 (batimastat) inhibits human colon tumor growth and spread in a patient-like orthotopic model in nude mice. Cancer Res, 54:4726–8.
Eccles, S. A., Box, G. M., Court, W. J., Bone, E. A., Thomas, W., and Brown, P. D., 1996, Control of lymphatic and hematogenous metastasis of a rat mammary carcinoma by the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat (BB-94). Cancer Res, 56:2815–2822.
Goss, K. J., Brown, P. D., and Matrisian, L. M., 1998, Differing effects of endogenous and synthetic inhibitors of metalloproteinases on intestinal tumorigenesis. Int J Cancer, 78:629–635.
Bergers, G., Javaherian, K., Lo, K. M., Folkman, J., and Hanahan, D., 1999, Effects of angiogenesis inhibitors on multistage carcinogenesis in mice. Science, 284:808–812.
Sledge, G. W., Jr., Qulali, M., Goulet, R., Bone, E. A., and Fife, R., 1995, Effect of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat on breast cancer regrowth and metastasis in athymic mice. J Natl Cancer Inst, 87:1546–50.
Wagenaar-Miller, R. A., Gorden, L., and Matrisian, L. M., 2004, Matrix metalloproteinases in colorectal cancer: is it worth talking about?. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 23:119–135.
Oba, K., Konno, H., Tanaka, T., Baba, M., Kamiya, K., Ohta, M., Kaneko, T., Shouji, T., Igarashi, A., and Nakamura, S., 2002, Prevention of liver metastasis of human colon cancer by selective matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor MMI-166. Cancer Lett, 175:45–51.
An, Z., Wang, X., Willmott, N., Chander, S. K., Tickle, S., Docherty, A. J., Mountain, A., Millican, A. T., Morphy, R., Porter, J. R., Epemolu, R. O., Kubota, T., Moossa, A. R., and Hoffman, R. M., 1997, Conversion of highly malignant colon cancer from an aggressive to a controlled disease by oral administration of a metalloproteinase inhibitor. Clin Exp Metastasis, 15:184–195.
Bramhall, S. R., Rosemurgy, A., Brown, P. D., Bowry, C., and Buckels, J. A., 2001, Marimastat as first-line therapy for patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer: a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol, 19:3447–3455.
Rao, J. S., 2003, Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer, 3:489–501.
Fielding, J., Scholefield, J., Stuart, R., Hawkins, R., McCulloch, P., Maughan, T., Seymour, M., Cutsem, E.V., Thorlacius-Ussing, O., and Hovendal, C., 2000, Presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO)'s 36th Annual Meeting, New Orleans.
Moore, M.J., Eisenberg, J.H., Dagenais, M., Hagan, K., Fields, A., Greenberg, B., Schwartz, B., Ottaway, J., Zee, B., and Seymour, L., posting date 2000, A Comparison Between Gemcitabine (GEM) and the Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP) Inhibitor BAY12-9566 (9566) in Patients (PTS) with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Published Online.
McIntyre, J. O., Fingleton, B., Wells, K. S., Piston, D. W., Lynch, C. C., Gautam, S., and Matrisian, L. M., 2004, Development of a novel fluorogenic proteolytic beacon for in vivo detection and imaging of tumour-associated matrix metalloproteinase-7 activity. Biochem J, 377:617–628.
Wang, Z., Juttermann, R., and Soloway, P. D., 2000, TIMP-2 is required for efficient activation of proMMP-2 in vivo. J Biol Chem, 275:26411–5.
Ward, R. V., Hembry, R. M., Reynolds, J. J., and Murphy, G., 1991, The purification of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 from its 72 kDa progelatinase complex. Demonstration of the biochemical similarities of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1. Biochem J, 278:179–87.
Howard, E. W., Bullen, E. C., and Banda, M. J., 1991, Preferential inhibition of 72-and 92-kDa gelatinases by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2. J Biol Chem, 266:13070–13075.
Quantin, B., Murphy, G., and Breathnach, R., 1989, Pump-1 cDNA codes for a protein with characteristics similar to those of classical collagenase family members. Biochemistry, 28:5327–34.
Knauper, V., Wilhelm, S. M., Seperack, P. K., DeClerck, Y. A., Langley, K. E., Osthues, A., and Tschesche, H., 1993, Direct activation of human neutrophil procollagenase by recombinant stromelysin. Biochem J, 295:581–6.
Murphy, G., Segain, J. P., O'shea, M., Cockett, M., Ioannou, C., Lefebvre, O., Chambon, P., and Basset, P., 1993, The 28-kDa N-terminal domain of mouse stromelysin-3 has the general properties of a weak metalloproteinase. J Biol Chem, 268:15435–41.
Knauper, V., Lopez-Otin, C., Smith, B., Knight, G., and Murphy, G., 1996, Biochemical characterization of human collagenase-3. J Biol Chem, 271:1544–50.
English, W. R., Puente, X. S., Freije, J. M., Knauper, V., Amour, A., Merryweather, A., Lopez-Otin, C., and Murphy, G., 2000, Membrane type 4 matrix metalloproteinase (MMP17) has tumor necrosis factor-alpha convertase activity but does not activate pro-MMP2. J Biol Chem, 275:14046–14055.
Stracke, J. O., Hutton, M., Stewart, M., Pendas, A. M., Smith, B., Lopez-Otin, C., Murphy, G., and Knauper, V., 2000, Biochemical characterization of the catalytic domain of human matrix metalloproteinase 19. Evidence for a role as a potent basement membrane degrading enzyme. J Biol Chem, 275:14809–14816.
English, W. R., Velasco, G., Stracke, J. O., Knauper, V., and Murphy, G., 2001, Catalytic activities of membrane-type 6 matrix metalloproteinase (MMP25). FEBS Lett, 491:137–142.
Uria, J. A., and Lopez-Otin, C., 2000, Matrilysin-2, a new matrix metalloproteinase expressed in human tumors and showing the minimal domain organization required for secretion, latency, and activity. Cancer Res, 60:4745–4751.
DeClerck, Y. A., Yean, T. D., Chan, D., Shimada, H., and Langley, K. E., 1991, Inhibition of tumor invasion of smooth muscle cell layers by recombinant human metalloproteinase inhibitor. Cancer Res, 51:2151–2157.
Quesada, A. R., Barbacid, M. M., Mira, E., Fernandez-Resa, P., Marquez, G., and Aracil, M., 1997, Evaluation of fluorometric and zymographic methods as activity assays for stromelysins and gelatinases. Clin Exp Metastasis. 15:26–32.
Knauper, V., Osthues, A., DeClerck, Y. A., Langley, K. E., Blaser, J., and Tschesche, H., 1993, Fragmentation of human polymorphonuclear-leucocyte collagenase. Biochem J, 291 (Pt 3):847–854.
Will, H., Atkinson, S. J., Butler, G. S., Smith, B., and Murphy, G., 1996, The soluble catalytic domain of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves the propeptide of progelatinase A and initiates autoproteolytic activation. Regulation by TIMP-2 and TIMP-3. J Biol Chem, 271:17119–17123.
Shimada, T., Nakamura, H., Ohuchi, E., Fujii, Y., Murakami, Y., Sato, H., Seiki, M., and Okada, Y., 1999, Characterization of a truncated recombinant form of human membrane type 3 matrix metalloproteinase. Eur J Biochem, 262:907–914.
Llano, E., Pendas, A. M., Freije, J. P., Nakano, A., Knauper, V., Murphy, G., and Lopez-Otin, C., 1999, Identification and characterization of human MT5-MMP, a new membrane-bound activator of progelatinase a overexpressed in brain tumors. Cancer Res, 59:2570–2576.
Zhao, Y. G., Xiao, A. Z., Park, H. I., Newcomer, R. G., Yan, M., Man, Y. G., Heffelfinger, S. C., and Sang, Q. X., 2004, Endometase/matrilysin-2 in human breast ductal carcinoma in situ and its inhibition by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases-2 and-4: a putative role in the initiation of breast cancer invasion. Cancer Res, 64:590–598.
Apte, S. S., Olsen, B. R., and Murphy, G., 1995, The gene structure of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP)-3 and its inhibitory activities define the distinct TIMP gene family. J Biol Chem, 270:14313–14318.
Will, H., and Hinzmann, B., 1995, cDNA sequence and mRNA tissue distribution of a novel human matrix metalloproteinase with a potential transmembrane segment. Eur J Biochem, 231:602–8.
Bigg, H. F., Morrison, C. J., Butler, G. S., Bogoyevitch, M. A., Wang, Z., Soloway, P. D., and Overall, C. M., 2001, Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-4 inhibits but does not support the activation of gelatinase A via efficient inhibition of membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase. Cancer Res, 61:3610–3608.
Liu, Y. E., Wang, M., Greene, J., Su, J., Ullrich, S., Li, H., Sheng, S., Alexander, P., Sang, Q. A., and Shi, Y. E., 1997, Preparation and characterization of recombinant tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 4 (TIMP-4). J Biol Chem, 272:20479–20483.
Nomura, H., Fujimoto, N., Seiki, M., Mai, M., and Okada, Y., 1996, Enhanced production of matrix metalloproteinases and activation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (gelatinase A) in human gastric carcinomas. Int J Cancer, 69:9–16.
Ko, B. K., Cho, H. R., Choi, D. W., Nam, C. W., Park, C. J., Kim, G. Y., Kim, S. S., Woo, Y. J., Huh, J., and Kim, M. Y., 1998, Reduced expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase in nodal metastasis of stomach cancer. J Korean Med Sci, 13:286–90.
Joo, Y. E., Seo, K. S., Kim, H. S., Rew, J. S., Park, C. S., and Kim, S. J., 2000, Expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci, 45:114–121.
Hong, S. I., Park, I. C., Hong, W. S., Son, Y. S., Lee, S. H., Lee, J. I., Choi, D. W., Moon, N. M., Choe, T. B., and Jang, J. J., 1996, Overexpression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 and-2 in the stroma of gastric cancer. J Korean Med Sci, 11:474–479.
Thomas, P., Khokha, R., Shepherd, F. A., Feld, R., and Tsao, M. S., 2000, Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. J Pathol, 190:150–156.
Bolon, I., Gouyer, V., Devouassoux, M., Vandenbunder, B., Wernert, N., Moro, D., Brambilla, C., and Brambilla, E., 1995, Expression of c-ets-1, collagenase 1, and urokinase-type plasminogen activator genes in lung carcinomas. Am J Pathol, 147:1298–1310.
Nawrocki, B., Polette, M., Marchand, V., Monteau, M., Gillery, P., Tournier, J. M., and Birembaut, P., 1997, Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human bronchopulmonary carcinomas: quantificative and morphological analyses. Int J Cancer, 72:556–64.
Soini, Y., Paakko, P., and Autio-Harmainen, H., 1993, Genes of laminin B1 chain, alpha 1 (IV) chain of type IV collagen, and 72-kd type IV collagenase are mainly expressed by the stromal cells of lung carcinomas. Am J Pathol, 142:1622–1630.
Suzuki, M., Iizasa, T., Fujisawa, T., Baba, M., Yamaguchi, Y., Kimura, H., and Suzuki, H., 1998, Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases in non-small-cell lung cancer. Invasion Metastasis, 18:134–141.
Bolon, I., Devouassoux, M., Robert, C., Moro, D., Brambilla, C., and Brambilla, E., 1997, Expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator, stromelysin 1, stromelysin 3, and matrilysin genes in lung carcinomas. Am J Pathol, 150:1619–1629.
Nagashima, Y., Hasegawa, S., Koshikawa, N., Taki, A., Ichikawa, Y., Kitamura, H., Misugi, K., Kihira, Y., Matuo, Y., Yasumitsu, H., and Miyazaki, K., 1997, Expression of matrilysin in vascular endothelial cells adjacent to matrilysin-producing tumors. Int J Cancer, 72:441–5.
Michael, M., Babic, B., Khokha, R., Tsao, M., Ho, J., Pintilie, M., Leco, K., Chamberlain, D., and Shepherd, F. A., 1999, Expression and prognostic significance of metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in patients with small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 17:1802–8.
Kodate, M., Kasai, T., Hashimoto, H., Yasumoto, K., Iwata, Y., and Manabe, H., 1997, Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (gelatinase) in T1 adenocarcinoma of the lung. Pathol Int, 47:461–9.
Canete-Soler, R., Litzky, L., Lubensky, I., and Muschel, R. J., 1994, Localization of the 92 kd gelatinase mRNA in squamous cell and adenocarcinomas of the lung using in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol, 144:518–527.
Cox, G., Jones, J. L., and O'Byrne, K. J., 2000, Matrix metalloproteinase 9 and the epidermal growth factor signal pathway in operable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 6:2349–2355.
Anderson, I. C., Sugarbaker, D. J., Ganju, R. K., Tsarwhas, D. G., Richards, W. G., Sunday, M., Kobzik, L., and Shipp, M. A., 1995, Stromelysin-3 is overexpressed by stromal elements in primary non-small cell lung cancers and regulated by retinoic acid in pulmonary fibroblasts. Cancer Res, 55:4120–4126.
Cho, N. H., Hong, K. P., Hong, S. H., Kang, S., Chung, K. Y., and Cho, S. H., 2004, MMP expression profiling in recurred stage IB lung cancer. Oncogene, 23:845–851.
Bodey, B., Bodey, B., Jr., Groger, A. M., Siegel, S. E., and Kaiser, H. E., 2001, Invasion and metastasis: the expression and significance of matrix metalloproteinases in carcinomas of the lung. In Vivo, 15:175–180.
Polette, M., Nawrocki, B., Gilles, C., Sato, H., Seiki, M., Tournier, J. M., and Birembaut, P., 1996, MTMMP expression and localisation in human lung and breast cancers. Virchows Arch, 428:29–35.
Marchenko, G. N., Ratnikov, B. I., Rozanov, D. V., Godzik, A., Deryugina, E. I., and Strongin, A. Y., 2001, Characterization of matrix metalloproteinase-26, a novel metalloproteinase widely expressed in cancer cells of epithelial origin. Biochem J, 356:705–718.
Polette, M., Gilbert, N., Stas, I., Nawrocki, B., Noel, A., Remacle, A., Stetler-Stevenson, W. G., Birembaut, P., and Foidart, M., 1994, Gelatinase A expression and localization in human breast cancers. An in situ hybridization study and immunohistochemical detection using confocal microscopy. Virchows Arch, 424:641–5.
Ioachim, E. E., Athanassiadou, S. E., Kamina, S., Carassavoglou, K., and Agnantis, N. J., 1998, Matrix metalloproteinase expression in human breast cancer: an immunohistochemical study including correlation with cathepsin D, type IV collagen, laminin, fibronectin, EGFR, c-erbB-2 oncoprotein, p53, steroid receptors status and proliferative indices. Anticancer Res, 18:1665–1670.
Bodey, B., Bodey, B., Jr., Siegel, S. E., and Kaiser, H. E., 2001, Matrix metalloproteinases in neoplasm-induced extracellular matrix remodeling in breast carcinomas, Anticancer Res 21:2021–2028.
Basset, P., Wolf, C., Rouyer, N., Bellocq, J. P., Rio, M. C., and Chambon, P., 1994, Stromelysin-3 in stromal tissue as a control factor in breast cancer behavior. Cancer, 74:1045–1049.
Ueno, H., Nakamura, H., Inoue, M., Imai, K., Noguchi, M., Sato, H., Seiki, M., and Okada, Y., 1997, Expression and tissue localization of membrane-types 1, 2, and 3 matrix metalloproteinases in human invasive breast carcinomas. Cancer Res, 57:2055–2060.
Bisson, C., Blacher, S., Polette, M., Blanc, J. F., Kebers, F., Desreux, J., Tetu, B., Rosenbaum, J., Foidart, J. M., Birembaut, P., and Noel, A., 2003, Restricted expression of membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase by myofibroblasts adjacent to human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer, 105:7–13.
Djonov, V., Hogger, K., Sedlacek, R., Laissue, J., and Draeger, A., 2001, MMP-19: cellular localization of a novel metalloproteinase within normal breast tissue and mammary gland tumours. J Pathol, 195:147–155.
Boag, A. H., and Young, I. D., 1994, Increased expression of the 72-kd type IV collagenase in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Demonstration by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol, 144:585–591.
Stearns, M. E., and Wang, M., 1993, Type IV collagenase (M(r) 72,000) expression in human prostate: benign and malignant tissue. Cancer Res, 53:878–883.
Upadhyay, J., Shekarriz, B., Nemeth, J. A., Dong, Z., Cummings, G. D., Fridman, R., Sakr, W., Grignon, D. J., and Cher, M. L., 1999, Membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) and MMP-2 immunolocalization in human prostate: change in cellular localization associated with high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Clin Cancer Res, 5:4105–4110.
Knox, J. D., Wolf, C., McDaniel, K., Clark, V., Loriot, M., Bowden, G. T., and Nagle, R. B., 1996, Matrilysin expression in human prostate carcinoma. Mol Carcinog, 15:57–63.
Kuniyasu, H., Ellis, L. M., Evans, D. B., Abbruzzese, J. L., Fenoglio, C. J., Bucana, C. D., Cleary, K. R., Tahara, E., and Fidler, I. J., 1999, Relative expression of E-cadherin and type IV collagenase genes predicts disease outcome in patients with resectable pancreatic carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res, 5:25–33.
Zhao, Y. G., Xiao, A. Z., Newcomer, R. G., Park, H. I., Kang, T., Chung, L. W., Swanson, M. G., Zhau, H. E., Kurhanewicz, J., and Sang, Q. X., 2003, Activation of pro-gelatinase B by endometase/matrilysin-2 promotes invasion of human prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem, 278:15056–15064.
Shiozawa, J., Ito, M., Nakayama, T., Nakashima, M., Kohno, S., and Sekine, I., 2000, Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human colorectal carcinoma. Mod Pathol, 13:925–933.
Otani, Y., Okazaki, I., Arai, M., Kameyama, K., Wada, N., Maruyama, K., Yoshino, K., Kitajima, M., Hosoda, Y., and Tsuchiya, M., 1994, Gene expression of interstitial collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase 1) in gastrointestinal tract cancers. J Gastroenterol, 29:391–7.
Grigioni, W. F., D'Errico, A., Fiorentino, M., Baccarini, P., Onisto, M., Caenazzo, C., Stetler-Stevenson, W. G., Garbisa, S., and Mancini, A. M., 1994, Gelatinase A (MMP-2) and its mRNA detected in both neoplastic and stromal cells of tumors with different invasive and metastatic properties. Diagn Mol Pathol, 3:163–169.
Kikuchi, R., Noguchi, T., Takeno, S., Kubo, N., and Uchida, Y., 2000, Immunohistochemical detection of membrane-type-1-matrix metalloproteinase in colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer, 83:215–8.
Poulsom, R., Pignatelli, M., Stetler-Stevenson, W. G., Liotta, L. A., Wright, P. A., Jeffery, R. E., Longcroft, J. M., Rogers, L., and Stamp, G. W., 1992, Stromal expression of 72 kda type IV collagenase (MMP-2) and TIMP-2 mRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Am J Pathol, 141:389–96.
Bodey, B., Bodey, B., Jr., Siegel, S. E., and Kaiser, H. E., 2000, Prognostic significance of matrix metalloproteinase expression in colorectal carcinomas. In Vivo, 14:659–666.
McDonnell, S., Navre, M., Coffey, R. J., Jr., and Matrisian, L. M., 1991, Expression and localization of the matrix metalloproteinase pump-1 (MMP-7) in human gastric and colon carcinomas. Mol Carcinog, 4:527–33.
Adachi, Y., Yamamoto, H., Itoh, F., Arimura, Y., Nishi, M., Endo, T., and Imai, K., 2001, Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of matrilysin expression at the invasive front in human colorectal cancers. Int J Cancer, 95:290–294.
Ring, P., Johansson, K., Hoyhtya, M., Rubin, K., and Lindmark, G., 1997, Expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases TIMP-2 in human colorectal cancer—a predictor of tumour stage. Br J Cancer, 76:805–811.
Porte, H., Chastre, E., Prevot, S., Nordlinger, B., Empereur, S., Basset, P., Chambon, P., and Gespach, C., 1995, Neoplastic progression of human colorectal cancer is associated with overexpression of the stromelysin-3 and BM-40/SPARC genes. Int J Cancer, 64:70–5.
Yang, W., Arii, S., Gorrin-Rivas, M. J., Mori, A., Onodera, H., and Imamura, M., 2001, Human macrophage metalloelastase gene expression in colorectal carcinoma and its clinicopathologic significance. Cancer, 91:1277–1283.
Ohtani, H., Motohashi, H., Sato, H., Seiki, M., and Nagura, H., 1996, Dual over-expression pattern of membrane-type metalloproteinase-1 in cancer and stromal cells in human gastrointestinal carcinoma revealed by in situ hybridization and immunoelectron microscopy. Int J Cancer, 68:565–70.
Ahokas, K., Lohi, J., Lohi, H., Elomaa, O., Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M. L., Kere, J., and Saarialho-Kere, U., 2002, Matrix metalloproteinase-21, the human orthologue for XMMP, is expressed during fetal development and in cancer. Gene, 301:31–41.
Davidson, B., Reich, R., Berner, A., Givant-Horwitz, V., Goldberg, I., Risberg, B., Kristensen, G. B., Trope, C. G., Bryne, M., Kopolovic, J., and Nesland, J. M., 2001, Ovarian carcinoma cells in serous effusions show altered MMP-2 and TIMP-2 mRNA levels. Eur J Cancer, 37:2040–2049.
Paju, A., Sorsa, T., Tervahartiala, T., Koivunen, E., Haglund, C., Leminen, A., Wahlstrom, T., Salo, T., and Stenman, U. H., 2001, The levels of trypsinogen isoenzymes in ovarian tumour cyst fluids are associated with promatrix metalloproteinase-9 but not promatrix metalloproteinase-2 activation. Br J Cancer, 84:1363–1371.
Westerlund, A., Apaja-Sarkkinen, M., Hoyhtya, M., Puistola, U., and Turpeenniemi-Hujanen, T., 1999, Gelatinase A-immunoreactive protein in ovarian lesions-prognostic value in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol, 75:91–98.
Davidson, B., Goldberg, I., Gotlieb, W. H., Kopolovic, J., Ben-Baruch, G., Nesland, J. M., Berner, A., Bryne, M., and Reich, R., 1999, High levels of MMP-2, MMP-9, MT1-MMP and TIMP-2 mRNA correlate with poor survival in ovarian carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis, 17:799–808.
Naylor, M. S., Stamp, G. W., Davies, B. D., and Balkwill, F. R., 1994, Expression and activity of MMPS and their regulators in ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer, 58:50–56.
Tanimoto, H., Underwood, L. J., Shigemasa, K., Parmley, T. H., Wang, Y., Yan, Y., Clarke, J., and O'Brien, T. J., 1999, The matrix metalloprotease pump-1 (MMP-7, Matrilysin): A candidate marker/target for ovarian cancer detection and treatment. Tumour Biol, 20:88–98.
Huang, L. W., Garrett, A. P., Bell, D. A., Welch, W. R., Berkowitz, R. S., and Mok, S. C., 2000, Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 protein and mRNA in epithelial ovarian tumors. Gynecol Oncol, 77:369–376.
Davidson, B., Goldberg, I., Berner, A., Nesland, J. M., Givant-Horwitz, V., Bryne, M., Risberg, B., Kristensen, G. B., Trope, C. G., Kopolovic, J., and Reich, R., 2001, Expression of membrane-type 1, 2, and 3 matrix metalloproteinases messenger RNA in ovarian carcinoma cells in serous effusions. Am J Clin Pathol, 115:517–524.
Mueller, J., Brebeck, B., Schmalfeldt, B., Kuhn, W., Graeff, H., and Hofler, H., 2000, Stromelysin-3 expression in invasive ovarian carcinomas and tumours of low malignant potential. Virchows Arch, 437:618–24.
Tsukifuji, R., Tagawa, K., Hatamochi, A., and Shinkai, H., 1999, Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1,-2 and-3 in squamous cell carcinoma and actinic keratosis. Br J Cancer, 80:1087–91.
Shimada, T., Nakamura, H., Yamashita, K., Kawata, R., Murakami, Y., Fujimoto, N., Sato, H., Seiki, M., and Okada, Y., 2000, Enhanced production and activation of progelatinase A mediated by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in human oral squamous cell carcinomas: implications for lymph node metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis, 18:179–188.
Pyke, C., Ralfkiaer, E., Huhtala, P., Hurskainen, T., Dano, K., and Tryggvason, K., 1992, Localization of messenger RNA for Mr 72,000 and 92,000 type IV collagenases in human skin cancers by in situ hybridization. Cancer Res, 52:1336–41.
Airola, K., Johansson, N., Kariniemi, A. L., Kahari, V. M., and Saarialho-Kere, U. K., 1997, Human collagenase-3 is expressed in malignant squamous epithelium of the skin. J Invest Dermatol, 109:225–231.
Karelina, T. V., Goldberg, G. I., and Eisen, A. Z., 1994, Matrilysin (PUMP) correlates with dermal invasion during appendageal development and cutaneous neoplasia. J Invest Dermatol, 103:482–7.
Stahle-Backdahl, M., and Parks, W. C., 1993, 92-kd gelatinase is actively expressed by eosinophils and stored by neutrophils in squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol, 142:995–1000.
Kerkela, E., Ala-aho, R., Lohi, J., Grenman, R., V, M. K., and Saarialho-Kere, U., 2001, Differential patterns of stromelysin-2 (MMP-10) and MT1-MMP (MMP-14) expression in epithelial skin cancers. Br J Cancer, 84:659–69.
Thewes, M., Worret, W. I., Engst, R., and Ring, J., 1999, Stromelysin-3 (ST-3): immunohistochemical characterization of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-11 in benign and malignant skin tumours and other skin disorders. Clin Exp Dermatol, 24:122–126.
Kerkela, E., Ala-Aho, R., Jeskanen, L., Rechardt, O., Grenman, R., Shapiro, S. D., Kahari, V. M., and Saarialho-Kere, U., 2000, Expression of human macrophage metalloelastase (MMP-12) by tumor cells in skin cancer. J Invest Dermatol, 114:1113–9.
Impola, U., Toriseva, M., Suomela, S., Jeskanen, L., Hieta, N., Jahkola, T., Grenman, R., Kahari, V. M., and Saarialho-Kere, U., 2003, Matrix metalloproteinase-19 is expressed by proliferating epithelium but disappears with neoplastic dedifferentiation. Int J Cancer, 103:709–716.
Nakamura, H., Fujii, Y., Inoki, I., Sugimoto, K., Tanzawa, K., Matsuki, H., Miura, R., Yamaguchi, Y., and Okada, Y., 2000, Brevican is degraded by matrix metalloproteinases and aggrecanase-1 (ADAMTS4) at different sites. J Biol Chem, 275:38885–90.
Fernandez-Patron, C., Radomski, M. W., and Davidge, S. T., 1999, Vascular matrix metalloproteinase-2 cleaves big endothelin-1 yielding a novel vasoconstrictor. Circ Res, 85:906–911.
Rodriguez-Manzaneque, J. C., Milchanowski, A. B., Dufour, E. K., Leduc, R., and Iruela-Arispe, M. L., 2000, Characterization of METH-1/ADAMTS1 processing reveals two distinct active forms. J Biol Chem, 275:33471–9.
Agostini, C., Trentin, L., Facco, M., Sancetta, R., Cerutti, A., Tassinari, C., Cimarosto, L., Adami, F., Cipriani, A., Zambello, R., and Semenzato, G., 1996, Role of IL-15, IL-2, and their receptors in the development of T cell alveolitis in pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Immunol, 157:910–918.
Ogata, Y., Enghild, J. J., and Nagase, H., 1992, Matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) activates the precursor for the human matrix metalloproteinase 9. J Biol Chem, 267:3581–3584.
Lijnen, H. R., and Collen, D., 1990, Serine proteases and their serpin inhibitors in the nervous system. Plenum Press, New York.
Ugwu, F., Van Hoef, B., Bini, A., Collen, D., and Lijnen, H. R., 1998, Proteolytic cleavage of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by stromelysin-1 (MMP-3). Biochemistry, 37:7231–7236.
Preece, G., Murphy, G., and Ager, A., 1996, Metalloproteinase-mediated regulation of L-selectin levels on leucocytes. J Biol Chem, 271:11634–40.
Imai, K., Yokohama, Y., Nakanishi, I., Ohuchi, E., Fujii, Y., Nakai, N., and Okada, Y., 1995, Matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin) from human rectal carcinoma cells. Activation of the precursor, interaction with other matrix metalloproteinases and enzymic properties. J Biol Chem, 270:6691–6697.
Agnihotri, R., Crawford, H. C., Haro, H., Matrisian, L. M., Havrda, M. C., and Liaw, L., 2001, Osteopontin, a novel substrate for matrix metalloproteinase-3 (stromelysin-1) and matrix metalloproteinase-7 (matrilysin). J Biol Chem, 276:28261–28267.
Fernandez-Patron, C., Zouki, C., Whittal, R., Chan, J. S., Davidge, S. T., and Filep, J. G., 2001, Matrix metalloproteinases regulate neutrophil-endothelial cell adhesion through generation of endothelin-1. Faseb J, 15:2230–2240.
Ochieng, J., Fridman, R., Nangia-Makker, P., Kleiner, D. E., Liotta, L. A., Stetler-Stevenson, W. G., and Raz, A., 1994, Galectin-3 is a novel substrate for human matrix metalloproteinases-2 and-9. Biochemistry, 33:14109–14114.
Nicholson, R., Murphy, G., and Breathnach, R., 1989, Human and rat malignant-tumor-associated mRNAs encode stromelysin-like metalloproteinases. Biochemistry, 28:5195–203.
Nakamura, H., Fujii, Y., Ohuchi, E., Yamamoto, E., and Okada, Y., 1998, Activation of the precursor of human stromelysin 2 and its interactions with other matrix metalloproteinases. Eur J Biochem, 253:67–75.
Knauper, V., Smith, B., Lopez-Otin, C., and Murphy, G., 1997, Activation of progelatinase B (proMMP-9) by active collagenase-3 (MMP-13). Eur J Biochem, 248:369–73.
Banda, M. J., Clark, E. J., and Werb, Z., 1983, Selective proteolysis of immunoglobulins by mouse macrophage elastase. J Exp Med, 157:1184–1196.
Knauper, V., Cowell, S., Smith, B., Lopez-Otin, C., O'shea, M., Morris, H., Zardi, L., and Murphy, G., 1997, The role of the C-terminal domain of human collagenase-3 (MMP-13) in the activation of procollagenase-3, substrate specificity, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase interaction. J Biol Chem, 272:7608–16.
d'Ortho, M. P., Clerici, C., Yao, P. M., Delacourt, C., Delclaux, C., Franco-Montoya, M. L., Harf, A., and Lafuma, C., 1997, Alveolar epithelial cells in vitro produce gelatinases and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Am J Physiol, 273:663–675.
Deryugina, E. I., Ratnikov, B. I., Postnova, T. I., Rozanov, D. V., and Strongin, A. Y., 2002, Processing of integrin alpha(v) subunit by membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase stimulates migration of breast carcinoma cells on vitronectin and enhances tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem, 277:9749–56.
d'Ortho, M. P., Will, H., Atkinson, S., Butler, G., Messent, A., Gavrilovic, J., Smith, B., Timpl, R., Zardi, L., and Murphy, G., 1997, Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 2 exhibit broad-spectrum proteolytic capacities comparable to many matrix metalloproteinases. Eur J Biochem, 250:751–757.
Morrison, C. J., Butler, G. S., Bigg, H. F., Roberts, C. R., Soloway, P. D., and Overall, C. M., 2001, Cellular activation of MMP-2 (gelatinase A) by MT2-MMP occurs via a TIMP-2-independent pathway. J Biol Chem, 276:47402–47410.
Shofuda, K., Yasumitsu, H., Nishihashi, A., Miki, K., and Miyazaki, K., 1997, Expression of three membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases (MTMMPs) in rat vascular smooth muscle cells and characterization of MT3-MMPs with and without transmembrane domain. J Biol Chem, 272:9749–9754.
Wang, Y., Johnson, A. R., Ye, Q. Z., and Dyer, R. D., 1999, Catalytic activities and substrate specificity of the human membrane type 4 matrix metalloproteinase catalytic domain. J Biol Chem, 274:33043–33049.
Stracke, J. O., Fosang, A. J., Last, K., Mercuri, F. A., Pendas, A. M., Llano, E., Perris, R., Di Cesare, P. E., Murphy, G., and Knauper, V., 2000, Matrix metalloproteinases 19 and 20 cleave aggrecan and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP). FEBS Lett, 478:52–56.
Yang, M., and Kurkinen, M., 1998, Cloning and characterization of a novel matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), CMMP, from chicken embryo fibroblasts. CMMP, Xenopus XMMP, and human MMP19 have a conserved unique cysteine in the catalytic domain. J Biol Chem, 273:17893–17900.
Velasco, G., Cal, S., Merlos-Suarez, A., Ferrando, A. A., Alvarez, S., Nakano, A., Arribas, J., and Lopez-Otin, C., 2000, Human MT6-matrix metalloproteinase: identification, progelatinase A activation, and expression in brain tumors. Cancer Res, 60:877–882.
de Coignac, A. B., Elson, G., Delneste, Y., Magistrelli, G., Jeannin, P., Aubry, J. P., Berthier, O., Schmitt, D., Bonnefoy, J. Y., and Gauchat, J. F., 2000, Cloning of MMP-26. A novel matrilysin-like proteinase. Eur J Biochem, 267:3323–3329.
Lohi, J., Wilson, C. L., Roby, J. D., and Parks, W. C., 2001, Epilysin, a novel human matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-28) expressed in testis and keratinocytes and in response to injury. J Biol Chem, 276:10134–44.
Balbin, M., Fueyo, A., Knauper, V., Lopez, J. M., Alvarez, J., Sanchez, L. M., Quesada, V., Bordallo, J., Murphy, G., and Lopez-Otin, C., 2001, Identification and enzymatic characterization of two diverging murine counterparts of human interstitial collagenase (MMP-1) expressed at sites of embryo implantation. J Biol Chem, 276:10253–10262.
Hahn-Dantona, E. A., Aimes, R. T., and Quigley, J. P., 2000, The isolation, characterization, and molecular cloning of a 75-kDa gelatinase B-like enzyme, a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family. An avian enzyme that is MMP-9-like in its cell expression pattern but diverges from mammalian gelatinase B in sequence and biochemical properties. J Biol Chem, 275:40827–40838.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Diaz, R.J., Eichten, A., de Visser, K.E., Coussens, L.M. (2005). Matrix Metalloproteinases: Mediators of Tumour-Host Cell Interactions. In: Meadows, G.G. (eds) Integration/Interaction of Oncologic Growth. Cancer Growth and Progression, vol 15. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3414-8_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3414-8_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-3413-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-3414-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)