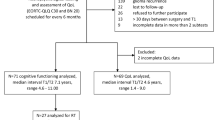
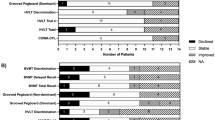
With the advent of effective treatment regimes increasing survival rates, delayed treatment-related cognitive dysfunction has been recognized as a significant problem. It is considered the most frequent complication among long-term survivors. WBRT may lead to deep brain atrophy and leukoencephalopa-thy associated with severe cognitive dysfunction, single-fraction dosages of greater than 2 Gy are related to an increased risk of late neurotoxicity, and other factors such as old age, concomitant chemotherapy and preexisting neurological disease increase this risk. However, the potential of focal radiotherapy (RT) with single dosages of 2 Gy or less to a maximal total dose of 60 Gy to produce significant neurotoxicity is less clear. There is a need for a concise neuropsychological test battery to be included in clinical trials, which should meet the following criteria: assess several domains found to be most sensitive to tumor and treatment effects, have standardized stimuli and administration procedures, have published normative data, have moderate to high test-retest reliability, have alternate forms or be relatively insensitive to practice effects, and therefore be suitable to monitor changes in cognitive function over time, include tests that have been translated into several Languages, which can be administered by a trained psy-chometrician or clinical research associate under supervision of a neuropsychologist, and have a relatively short total administration time. The neuropsychological domains to be evaluated should comprise the cognitive core deficit in brain-tumor patients, namely attention, executive functions (i.e., working memory, processing speed, sequencing abilities), verbal memory, and motor speed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong CL, Ruffer J, Corn B, et al. (1995) Biphasic patterns of memory deficits following moderate-dose partial-brain irradiation: neuropsychologic outcome and proposed mechanisms. J Clin Oncol 13:2263–2271
Armstrong CL, Stern CH, Corn BW (2001) Memory performance used to detect effects on cognitive functioning. Appl Neuropsych 8:129–139
Behin A, Delattre JY (2004) Complications of radiation therapy on the brain and spinal cord. Semin Neurol 24:405–17
Brown PD, Buckner JC, Uhm JH (2003) The neuro-cognitive effects of radiation in adult low-grade glioma patients. Neurooncology 5:161–167
Brown PD, Buckner JC, O'Fallon JR, et al. (2003) Effects of radiotherapy on cognitive function in patiens with low-grade glioma measured by the Folstein Mini-Mental State examination. J Clin Oncol 21:2519–2524
Byrne T (2005) Cognitive sequelae of brain tumor treatment. Curr Opin Neurol 18:662–666
Correa DD, De Angelis LM, Shi W, et al. (2006) Cognitive functions in low-grade gliomas: disease and treatment effects. J Neurooncol Jul 19; [Epub ahead of print]
Danoff BF, Cowchock S, Marquette C, et al. (1982) Assessment of the long-term effects of primary radiation therapy for brain tumours in children. Cancer 49:1580–1586
Gregor A, Cull A, Traynor E, et al. (1996) Neuropsychometric evaluation of adult brain tumours: relationship with tumour and treatment parameters. Radiother Oncol 41:55–59
Karim AB, Maat B, Hatlevoll R, et al. (1996) A randomized trial on dose-response in radiation therapy of low-grade cerebral glioma: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Study 22844. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 36:549–556
Karim AB, Afra D, Cornu P, et al. (2002) Randomized trial on the efficacy of radiotherapy for cerebral low-grade glioma in the adult: European Organization for research and treatment of Cancer Study 22845 with the Medical Research Council study BRO4: an interim analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 52:316–324
Klein M, Heimans JJ, Aaronson NK, et al. (2002) Effect of radiotherapy and other treatment- related factors on mid-term to long-term cognitive sequelae in low-grade gliomas: a comparative study. Lancet 360:1361–1368
Klein M, Engelberts NHJ, van der Ploeg HM et al. (2003) Epilepsy in low-grade gliomas: the impact on cognitive function and quality of life. Ann Neurol 54:514–520
Klein M, Fagel S, Taphoorn MJB, et al. (2006) Neurocognitive functioning in long-term low-grade glioma survivors: a six-year follow-up study. Presented at the 7th congress of the European Association for Neurooncology (EANO), Vienna, Austria
Kleinberg L, Wallner K, Malkin MG (1993) Good performance status of long-term disease- free survivors of intracranial gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 26:129–133
Laack NN, Brown PD, Ivnik RJ, et al. (2005) Cognitive function after radiotherapy for supratentorial low-grade glioma: a north central cancer treatment group prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:1175–1183
North CA, North RB, Epstein JA, et al. (1990) Low grade cerebral astrocytomas. Cancer 66:6–14
Postma TJ, Klein M, Verstappen CC, et al. (2002) Radiotherapy-induced cerebral abnormalities in patients with low-grade glioma. Neurology 59:121–123
Rottenberg D (1991) Acute and chronic effects of radiation therapy on the nervous system. In: Rottenberg D (ed) Neurological complications of cancer treatment. Butterworth-Heineman, Boston, pp 3–18
Shaw E, Arusell R, Scheithauer B, et al. (2002) Prospective randomized trial of low- versus high-dose radiation therapy in adults with supratento-rial low-grade glioma: initial report of a North Central Cancer Treatment Group/Radiation Therapy Oncology Group/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 20:2267–2276
Taphoorn MJB, Klein M, Schiphorst A, et al. (1994) Cognitive functions and quality of life in Patients with low-grade gliomas: the impact of radiotherapy. Ann Neurol 36:48–54
Van den Bent MJ, Afra D, de Witte O et al. (2005) Long-term efficacy of early versus delayed radiotherapy for low-grade astrocytoma and oli-godendroglioma in adults: the EORTC 22845 randomised trial. Lancet 366:985–990
Vigliani MC, Sichez N, Poisson M, Delattre JY (1996) A prospective study of cognitive functions following conventional radiotherapy for supratentorial gliomas in young adults: 4-year results. Int J Rad Oncol Biol Phys 35: 527–533
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Calabrese, P., Schlegel, U. (2009). Neurotoxicity of Treatment. In: von Deimling, A. (eds) Gliomas. Recent Results in Cancer Research, vol 171. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-31206-2_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-31206-2_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-31205-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31206-2
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)