Abstract
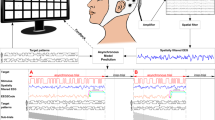
The present work proposes an embedded real time hardware-software platform for brain computer interfaces (BCI) based on steady state visual evoked potentials (SSVEP) and alpha rhythm. The complete implementation of the embedded system is described, including the electroencephalogram (EEG) amplifier, signal acquisition and processing stages, and practical implementation. The device is a 25 characters hybrid-BCI speller that uses 5 visual stimulus and visual alpha waves for control instructions. The system focuses on simplicity and portability, using only two electrodes, a simple EEG amplifier and an embedded computer. The speller does not require any training from the user and provides real time biofeedback to increase attention on stimuli. The platform is based on an embedded system with a real time operative system, Windows CE. Experimental results are presented in order to show the feasibility of the proposed system.
Working as a speller, the current average speed is around 7 characters per minute.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. R. Wolpaw, N. Birbaumer, D. J. McFarland, G. Pfurtscheller, and T. M. Vaughan, “Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control,” Clin. Neurophysiol., vol. 113, no. 6, pp. 767–791, 2002.
N. Birbaumer, “Breaking the silence: Brain-Computer-interfaces (BCI) for communication and motor control”, Psychophysiology, vol. 43, pp. 517-532, 2006.
D. Marshall, D. Coyle, S. Wilson, and M. Callaghan, “Games, Gameplay, and BCI: The State of the Art”, IEEE Trans. on computational intelligence and ai in games, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 82-99, 2013.
J. E. Huggins, C. Guger, B. Allison, C. W. Anderson, A. Batista, A-M. Brouwer, C. Brunner, R. Chavarriaga, M. Fried-Oken, A. Gunduz, D. Gupta, A. Kübler, R. Leeb, F. Lotte, L. E. Miller, G. Müller-Putz, T. Rutkowski, M. Tangermann & D. E. Thompson, “(2014) Workshops of the Fifth International Brain-Computer Interface Meeting: Defining the Future, Brain-Computer Interfaces”, 1:1, 27-49, DOI: 10.1080/2326263X.2013.876724.
P. A. García, M. Haberman and E. Spinelli, “A versatile hardware platform for brain computer interfaces”, Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE, pp. 4193 – 4196.
N. Neumann and A. Kubler, “Training locked-in patients: a challenge for the use of brain-computer interfaces”, IEEE Trans. on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 11, issue 2, pp. 169-172, 2003.
C. Postelnicu and D. Talaba, “P300-Based Brain-Neuronal Computer Interaction for Spelling Applications”, IEEE Trans. on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 60, issue 2, pp. 534 – 543, 2012.
R. Ortner, B. Z. Allison, G. Korisek, H. Gaggl and G. Pfurtscheller, “An SSVEP BCI to Control a Hand Orthosis for Persons with Tetraplegia”, IEEE Trans. on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 19, issue 1, pp. 1-5, 2011.
Y. Tianyou, X. Jun, W. Fangyi, R. Zhang, G. Zhenghui, A. Cichocki and L. Yuanqing, “Enhanced Motor Imagery Training Using a Hybrid BCI with Feedback”, IEEE Trans. on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 62, issue 7, pp. 1706 –1717, 2015.
H. Cecotti, “A Self-Paced and Calibration-Less SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface Speller”, IEEE Trans. on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 127-133, 2010.
G. Pfurtscheller, B. Allison, C. Brunner, G. Bauernfeind, T. Solis-Escalante, R. Scherer, T. Zander, G. Müller-Putz, C. Neuper, and N. Birbaumer, “The hybrid BCI,” Frontiers in Neuroscience, vol. 4, art. 42, pp. 1-11.
E. Spinelli, N. Martinez y M. Mayosky, “A Single Supply Biopotential Amplifier”. Medical Engineering and Physics, ISSN 1350-4533, Vol. 23/3, pp. 235-238, 2001.
J. Millán, R. Rupp, G. Müller-Putz, R. Murray-Smith, C. Giugliemma, M. Tangermann, C. Vidaurre, F. Cincotti,A. Kübler,R. Leeb, C. Neuper,K-R. Müller and D. Mattia, “Combining brain-computer interfaces and assistive technologies: state-of-the-art and challenges”, Frontiers in Neuroscience, DOI: 10.3389, 2010.
P. A. García, E. M. Spinelli, and G. M. Toccaceli, ”An embedded system for evoked biopotential acquisition and processing”, Int. J. Embedded Systems, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp.86–93, 2014.
Y. Ishikawa, M. Takata and K. Joe, “Constitution and phase analysis of alpha waves”, Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), 2012, DOI: 10.1109/BMEiCon.2012.6465482.
Gao X, Xu D, Cheng M and Gao S, “A BCI-Based Environmental Controller for the Motion-Disabled”. IEEE Transactions on neural systems and rehabilitation engineering, vol. 11, Nº. 2, June 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
García, P.A., Spinelli, E.M., Toccaceli, G.M. (2017). An Embedded Hybrid BCI Speller. In: Torres, I., Bustamante, J., Sierra, D. (eds) VII Latin American Congress on Biomedical Engineering CLAIB 2016, Bucaramanga, Santander, Colombia, October 26th -28th, 2016. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 60. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4086-3_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4086-3_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-4085-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-4086-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)