Abstract
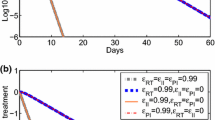
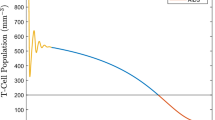
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) reduces the viral burden in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infected patients below the threshold of detectability. However, substantial evidence indicates that viral replication persists in these individuals. In this paper we examine the ability of several biologically motivated models of HIV-1 dynamics to explain sustained low viral loads. At or near drug efficacies that result in steady state viral loads below detectability, most models are extremely sensitive to small changes in drug efficacy. We argue that if these models reflect reality many patients should have cleared the virus, contrary to observation. We find that a model in which the infected cell death rate is dependent on the infected cell density does not suffer this shortcoming. The shortcoming is also overcome in two more conventional models that include small populations of cells in which the drug is less effective than in the main population, suggesting that difficulties with drug penetrance and maintenance of effective intracellular drug concentrations in all cells susceptible to HIV infection may underlie ongoing viral replication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. M. and R. M. May (1991). Infectious Diseases of Humans, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Bonhoeffer, S., J. M. Coffin and M. A. Nowak (1997). Human immunodeficiency virus drug therapy and virus load. J. Virol. 71, 3275–3278.
Callaway, D. S. and A. S. Perelson (2002). Intermittent viremia in HIV-1 infected patients may occur in patients fully adherent to potent antiretroviral drug therapy due to drug concentration heterogeneity (in review).
Callaway, D. S., R. M. Ribeiro and M. A. Nowak (1999). Phenotype switching and disease progression in HIV-1 infection. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, 266, 2523–2530.
Cavert, W. et al. (1997). Kinetics of response in lymphoid tissues to antiretroviral therapy of HIV-1 infection. Science 276, 960–964.
Chun, T. W., R. T. Davey Jr, D. Engel, H. C. Lane and A. S. Fauci (1999). Re-emergence of HIV after stopping therapy. Nature 401, 874–875.
Chun, T. W., L. Stuyver, S. B. Mizell, L. A. Ehler, J. A. Mican, M. Baseler, A. L. Lloyd, M. A. Nowak and A. S. Fauci (1997). Presence of an inducible HIV-1 latent reservoir during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 13193–13197.
De Boer, R. J. and A. S. Perelson (1995). Towards a general function describing T cell proliferation. J. Theor. Biol. 175, 567–576.
De Boer, R. J. and A. S. Perelson (1998). Target cell limited and immune control models of HIV infection: a comparison. J. Theor. Biol. 190, 201–214.
Dornadula, G. et al. (1999). Residual HIV-1 RNA in blood plasma of patients taking suppressive highly active antiretroviral therapy. JAMA 282, 1627–1632.
Ferguson, N. M. et al. (1999). Antigen-driven CD4+ T cell and HIV-1 dynamics: residual viral replication under highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 15167–15172.
Finzi, D. et al. (1999). Latent infection of CD4+ T cells provides a mechanism for lifelong persistence of HIV-1, even in patients on effective combination therapy. Nat. Med. 5, 512–517.
Finzi, D. et al. (1997). Identification of a reservoir for HIV-1 in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Science 278, 1295–1300.
Furtado, M. R., D. S. Callaway, J. P. Phair, K. J. Kunstman, J. L. Stanton, C. A. Macken, A. S. Perelson and S. M. Wolinsky (1999). Persistence of HIV-1 transcription in peripheral-blood mononuclear cells in patients receiving potent antiretroviral therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 340, 1614–1622.
Gartner, S., P. Markovits, D. M. Markovitz, M. H. Kaplan, R. C. Gallo and M. Popovic (1986). The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science 233, 215–219.
Haase, A. T. et al. (1996). Quantitative image analysis of HIV-1 infection in lymphoid tissue. Science 274, 985–989.
Haworth, S. J., B. Christofalo, R. D. Anderson and L. M. Dunkle (1998). A single-dose study to assess the penetration of stavudine into human cerebrospinal fluid in adults. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 17, 235–238.
Hlavacek, W. S., N. I. Stilianakis, D. W. Notermans, S. A. Danner and A. S. Perelson (2000a). Influence of follicular dendritic cells on decay of HIV during antiretroviral therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 10966–10971.
Hlavacek, W. S., N. I. Stilianakis and A. S. Perelson (2000b). Influence of follicular dendritic cells on HIV dynamics. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 355, 1051–1058.
Hlavacek, W. S., C. Wofsy and A. S. Perelson (1999). Dissociation of HIV-1 from follicular dendritic cells during HAART: mathematical analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 14681–14686.
Ho, D. D., A. U. Neumann, A. S. Perelson, W. Chen, J. M. Leonard and M. Markowitz (1995). Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature 373, 123–126.
Holte, S., A. Melvin, J. Mullins and L. Frenkel (2001). Density-dependent decay in HIV dynamics after HAART (abstr 394), in 8th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, Alexandria, VA, USA: Foundation for Retrovirology and Human Health.
Igarashi, T., C. R. Brown, Y. Endo, A. Buckler-White, R. Plishka, N. Bischofberger, V. Hirsch and M. A. Martin (2001). Macrophage are the principal reservoir and sustain high virus loads in rhesus macaques after the depletion of CD4+ T cells by a highly pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus/HIV type 1 chimera (SHIV): implications for HIV-1 infections of humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 658–663.
Kepler, T. B. and A. S. Perelson (1998). Drug concentration heterogeneity facilitates the evolution of drug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11514–11519.
Kim, R. B., M. F. Fromm, C. Wandel, B. Leake, A. J. Wood, D. M. Roden and G. R. Wilkinson (1998). The drug transporter P-glycoprotein limits oral absorption and brain entry of HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J. Clin. Invest. 101, 289–294.
Koenig, S., H. E. Gendelman, J. M. Orenstein, M. C. Dal Canto, G. H. Pezeshkpour, M. Yungbluth, F. Janotta, A. Aksamit, M. A. Martin and A. S. Fauci (1986). Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science 233, 1089–1093.
Lewin, S. R., M. Vesanen, L. Kostrikis, A. Hurley, M. Duran, L. Zhang, D. D. Ho and M. Markowitz (1999). Use of real-time PCR and molecular beacons to detect virus replication in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals on prolonged effective antiretroviral therapy. J. Virol. 73, 6099–6103.
Lewis, L. L. et al. (1996). Lamivudine in children with human immunodeficiency virus infection: a phase I/II study. The National Cancer Institute Pediatric Branch-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Working Group. J. Infect. Dis. 174, 16–25.
Lifson, J. D., G. R. Reyes, M. S. McGrath, B. S. Stein and E. G. Engleman (1986). AIDS retrovirus induced cytopathology: giant cell formation and involvement of CD4 antigen. Science 232, 1123–1127.
Louie, M., B. Ramratnam, R. Kost, A. Hurley, L. Zhang, E. Sun, S. Brun, I. Mcgowan, N. Ruiz, D. D. Ho and M. Markowitz (2001). Using viral dynamics to document the greater antiviral potency of a regimen containing Lopinavir/Ritonavir, Efavirenz, Tenofovir, and Lamivudine relative to standard HAART (abstr 383), in 8th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, Alexandria, VA, USA: Foundation for Retrovirology and Human Health.
McLean, A. R. and C. A. Michie (1995). In vivo estimates of division and death rates of human T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3707–3711.
Mittler, J. E., M. Markowitz, D. D. Ho and A. S. Perelson (1999). Improved estimates for HIV-1 clearance rate and intracellular delay. AIDS 13, 1415–1417.
Mohri, H., S. Bonhoeffer, S. Monard, A. S. Perelson and D. D. Ho (1998). Rapid turnover of T lymphocytes in SIV-infected rhesus macaques. Science 279, 1223–1227.
Natarajan, V., M. Bosche, J. A. Metcalf, D. J. Ward, H. C. Lane and J. A. Kovacs (1999). HIV-1 replication in patients with undetectable plasma virus receiving HAART. Lancet 353, 119–120.
Nowak, M. A. and C. R. Bangham (1996). Population dynamics of immune responses to persistent viruses. Science 272, 74–79.
Pantaleo, G., C. Graziosi, J. F. Demarest, L. Butini, M. Montroni, C. H. Fox, J. M. Orenstein, D. P. Kotler and A. S. Fauci (1993). HIV infection is active and progressive in lymphoid tissue during the clinically latent stage of disease. Nature 362, 355–358.
Pantaleo, G., C. Graziosi, J. F. Demarest, O. J. Cohen, M. Vaccarezza, K. Gantt, C. Muro-Cacho and A. S. Fauci (1994). Role of lymphoid organs in the pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Immunol. Rev. 140, 105–130.
Perelson, A. S., P. Essunger, Y. Cao, M. Vesanen, A. Hurley, K. Saksela, M. Markowitz and D. D. Ho (1997). Decay characteristics of HIV-1-infected compartments during combination therapy. Nature 387, 188–191.
Perelson, A. S., A. U. Neumann, M. Markowitz, J. M. Leonard and D. D. Ho (1996). HIV-1 dynamics in vivo: virion clearance rate, infected cell life-span, and viral generation time. Science 271, 1582–1586.
Perno, C. F., F. M. Newcomb, D. A. Davis, S. Aquaro, R. W. Humphrey, R. Calio and R. Yarchoan (1998). Relative potency of protease inhibitors in monocytes/macrophages acutely and chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J. Infect. Dis. 178, 413–422.
Puddu, P., S. Fais, F. Luciani, G. Gherardi, M. L. Dupuis, G. Romagnoli, C. Ramoni, M. Cianfriglia and S. Gessani (1999). Interferon-gamma up-regulates expression and activity of P-glycoprotein in human peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages. Lab. Invest. 79, 1299–1309.
Ramratnam, B., S. Bonhoeffer, J. Binley, A. Hurley, L. Zhang, J. E. Mittler, M. Markowitz, J. P. Moore, A. S. Perelson and D. D. Ho (1999). Rapid production and clearance of HIV-1 and hepatitis C virus assessed by large volume plasma apheresis. Lancet 354, 1782–1785.
Ramratnam, B., J. E. Mittler, L. Zhang, D. Boden, A. Hurley, F. Fang, C. A. Macken, A. S. Perelson, M. Markowitz and D. D. Ho (2000). The decay of the latent reservoir of replication-competent HIV-1 is inversely correlated with the extent of residual viral replication during prolonged anti-retroviral therapy. Nat. Med. 6, 82–85.
Sachsenberg, N., A. S. Perelson, S. Yerly, G. A. Schockmel, D. Leduc, B. Hirschel and L. Perrin (1998). Turnover of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection as measured by Ki-67 antigen. J. Exp. Med. 187, 1295–1303.
Schlegel, P. N. and S. K. Chang (1998). Physiology of male reproduction: the testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens, in Campbell’s Urology, Vol. 7, P. C. Walsh, A. B. Retik, E. D. Vaughan and A. J. Wein (Eds), Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co., pp. 1254–1286.
Sharkey, M. E. et al. (2000). Persistence of episomal HIV-1 infection intermediates in patients on highly active anti-retroviral therapy. Nat. Med. 6, 76–81.
Siliciano, J. D. and R. F. Siliciano (2000). Latency and viral persistence in HIV-1 infection. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 823–825.
Smith, B. A. et al. (2001). Persistence of infectious HIV on follicular dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 166, 690–696.
Sodroski, J., W. C. Goh, C. Rosen, K. Campbell and W. A. Haseltine (1986). Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. Nature 322, 470–474.
Stevenson, M. (1996). Portals of entry—uncovering HIV-1 nuclear transport pathways. Trends Cell Biol. 6, 9–15.
Stevenson, M. and H. E. Gendelman (1994). Cellular and viral determinants that regulate HIV-1 infection in macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 56, 278–288.
Wei, X. et al. (1995). Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature 373, 117–122.
Wong, J. K., M. Hezareh, H. F. Gunthard, D. V. Havlir, C. C. Ignacio, C. A. Spina and D. D. Richman (1997). Recovery of replication-competent HIV despite prolonged suppression of plasma viremia. Science 278, 1291–1295.
Yerly, S., T. V. Perneger, S. Vora, B. Hirschel and L. Perrin (2000). Decay of cell-associated HIV-1 DNA correlates with residual replication in patients treated during acute HIV-1 infection. AIDS 14, 2805–2812.
Yoffe, B., D. E. Lewis, B. L. Petrie, C. A. Noonan, J. L. Melnick and F. B. Hollinger (1987). Fusion as a mediator of cytolysis in mixtures of uninfected CD4+ lymphocytes and cells infected by human immunodeficiency virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 1429–1433.
Zhang, L. et al. (1999). Quantifying residual HIV-1 replication in patients receiving combination antiretroviral therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 340, 1605–1613.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Callaway, D.S., Perelson, A.S. HIV-1 infection and low steady state viral loads. Bull. Math. Biol. 64, 29–64 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2001.0266
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2001.0266