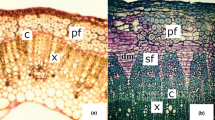
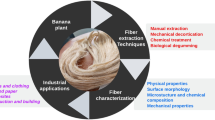
Abstract
The global waste problems resulting from the use of synthetic fiber are becoming increasing environmental concerns. It would be better if the synthetic fibers give way to the natural fibers as renewable resources for environmental sustainability. New sources of natural fibers are being developed in recent years as natural fibers offer many advantages over synthetic fibers. Mendong grass is one of the natural sources of fiber. It is easy to grow and cultivate, and it offers several harvests from one plantation. The fiber has found many applications for small-scale industries and helps in economic welfare of small farmers. This chapter provides a general overview of mendong grass cultivation and obtaining fiber. The chemical, physical, mechanical, and thermal properties and prospective application of the mendong fiber are also presented.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Yano H (2009) Comparison of the characteristics of cellulose microfibril aggregates of wood, rice straw and potato tuber. Cellulose 16:1017–1023. doi:10.1007/s10570-009-9334-9
Akil HM, Omar MF, Mazuki AAM et al (2011) Kenaf fiber reinforced composites: a review. Mater Des 32:4107–4121. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2011.04.008
Akutam A, Pappoe ANM, Armah FA, Enu-Kwesi L (2014) Phytoremediation potential of indigenous Ghanaian grass and grass-like species grown on used motor oil contaminated soils. J Ecol Environ 37:41–51. doi:10.5141/ecoenv.2014.006
Awal A, Cescutti G, Ghosh SB, Müssig J (2011) Interfacial studies of natural fibre/polypropylene composites using single fibre fragmentation test (SFFT). Compos Part A 42:50–56. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2010.10.007
Bavan S, Kumar M (2012) Morphological and thermal properties of maize fiber composites. Fibers Polym 13:887–893. doi:10.1007/s12221-012-0887-0
Beckermann GW, Pickering KL (2008) Engineering and evaluation of hemp fibre reinforced polypropylene composites: fibre treatment and matrix modification. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 39:979–988. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2008.03.010
Beckermann GW, Pickering KL (2009) Engineering and evaluation of hemp fibre reinforced polypropylene composites: micro-mechanics and strength prediction modelling. Compos Part A 40:210–217. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2008.11.005
Bergander A, Salmen L (2002) Cell wall properties and their effects on the mechanical properties of fibers. J Mater Sci 37:151–156. doi:10.1023/A:1013115925679
Bismarck A, Mishra S, Lampke T (2005) Plant fibers as reinforcement for green composites. In: Mohanty AK, Misra M, Drzal LT (eds) Natural fibers, biopolymer, and biocomposites. CRC Press Tailor and Francis Group, Boca Raton
Chen Y, Shen Z, Li X (2004) The use of vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides) in the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals. Appl Geochem 19:1553–1565. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.02.003
Chen C, Ma X, Liu K (2011) Thermogravimetric analysis of microalgae combustion under different oxygen supply concentrations. Appl Energy 88:3189–3196. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.03.003
Cheng G, Varanasi P, Li C et al (2011) Transition of cellulose crystalline structure and surface morphology of biomass as a function of ionic liquid pretreatment and its relation to enzymatic hydrolysis. Biomacromolecules 12:933–941. doi:10.1021/bm101240z
Cousins WJ (1976) Elastic modulus of lignin as related to moisture content. Wood Sci Technol 10:9–17. doi:10.1007/BF00376380
Danh LT, Truong P, Mammucari R et al (2009) Vetiver grass, Vetiveria zizanioides: a choice plant for phytoremediation of heavy metals and organic wastes. Int J Phytoremediat 11:664–691. doi:10.1080/15226510902787302
Davies P, Morvan C, Sire O, Baley C (2007) Structure and properties of fibres from sea-grass (Zostera marina). J Mater Sci 42:4850–4857. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-0546-1
De Jong E, Higson A, Walsh P, Wellisch M (2012) Product developments in the bio-based chemicals arena. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 6:606–624. doi:10.1002/bbb.1360
Foulk J, Akin D, Dodd R, Ulven C (2011) Production of flax fiber for biocomposite. In: Kalia S, Kaith BS, Kaur I (eds) Cellulose fibers: bio- and nanopolymer composites. Springer, Berlin
Gassan J, Bledzki AK (1999) Possibilities for improving the mechanical properties of jute/epoxy composites by alkali treatment of fibres. Compos Sci Technol 59:1303–1309. doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(98)00169-9
Gratão PL, Prasad MNV, Cardoso PF et al (2005) Phytoremediation: green technology for the clean up of toxic metals in the environment. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:53–64. doi:10.1590/S1677-04202005000100005
Han W, Chen K, Yang R-D et al (2010) Utilization of bagasse fiber for preparation of biodegradable flame retarding composites (BFRCS). BioResources 5:1605–1617. doi:10.15376/biores.5.3.1605-1617
Ioelovich M, Leykin A (2008) Structural investigations of various cotton fibers and cotton celluloses. BioResources 3:170–177. doi:10.15376/biores.3.1.170-177
Jayaraman K (2003) Manufacturing sisal–polypropylene composites with minimum fibre degradation. Compos Sci Technol 63:367–374. doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(02)00217-8
Kaith BS, Kalia S (2008) Graft copolymerization of MMA onto flax under different reaction conditions: a comparative study. Express Polym Lett 2:93–100. doi:10.3144/expresspolymlett.2008.13
Kurnia U, Suganda H, Saraswati R (2004) Pollution control technology in paddy fields. In: Fahmudin A (ed) Paddy fields and Processing Technology (in Indonesian Language). Center of Research and Development for Agroclimate Land, Bogor Indonesia, pp 249–283
Leppänen K, Andersson S, Torkkeli M et al (2009) Structure of cellulose and microcrystalline cellulose from various wood species, cotton and flax studied by X-ray scattering. Cellulose 16:999–1015. doi:10.1007/s10570-009-9298-9
Li X, Tabil LG, Panigrahi S (2007) Chemical treatments of natural fiber for use in natural fiber-reinforced composites: a review. J Polym Environ 15:25–33. doi:10.1007/s10924-006-0042-3
Li Y, Mai Y, Ye L (2000) Sisal fibre and its composites: a review of recent developments. Compos Sci Technol 60:2037–2055. doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(00)00101-9
Liu W, Mohanty AK, Askeland P et al (2004) Influence of fiber surface treatment on properties of Indian grass fiber reinforced soy protein based biocomposites. Polymer (Guildf) 45:7589–7596. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2004.09.009
Marsyahyo E, Soekrisno S, Rohardjo HSB, Jamasri J (2008) Identification of ramie single fiber surface topography influenced by solvent-based treatment. J Ind Text 38:127–137. doi:10.1177/1528083707087835
Mishra S, Mohanty AK, Drzal LT et al (2004) A review on pineapple leaf fibers, sisal fibers and their biocomposites. Macromol Mater Eng. doi:10.1002/mame.200400132
Mohanty AK, Misra M, Drzal LT, Selke SE, Harte BR, Hinrichsen G (2005) Natural fibers, biopolymers, and biocomposites: an introduction. In: Mohanty AK, Misra M, Drzal LT (eds) Natural fibers, biopolymers, and biocomposites. CRC Press: Boca Raton, pp 1–36
Mu Q, Wei C, Feng S (2009) Studies on mechanical properties of sisal fiber/phenol formaldehyde resin in-situ composites. Polym Compos 30:131–137. doi:10.1002/pc.20529
Muhammad S, Shah MT, Khan S et al (2013) Wild plant assessment for heavy metal phytoremediation potential along the mafic and ultramafic terrain in northern Pakistan. Biomed Res Int 2013:1–10. doi:10.1155/2013/194765
Mwaikambo LY (2009) Tensile properties of alkalised jute fibres. BioResources 4:566–588. doi:10.15376/biores.4.2.566-588
Mwaikambo LY, Ansell MP (2006) Mechanical properties of alkali treated plant fibres and their potential as reinforcement materials. I. Hemp fibres. J Mater Sci. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-5098-x
Nwaichi EO, Frac M, Nwoha PA, Eragbor P (2015) Enhanced phytoremediation of crude oil-polluted soil by four plant species: effect of inorganic and organic bioaugumentation. Int J Phytoremediat. doi:10.1080/15226514.2015.1058324
Paquin DG, Sun WH, Tang C-S, Li QX (2006) A phytoremediation study: selection of tropical and other vascular plants for decolorization of Poly R-478 dye. Remediat J 16:97–107. doi:10.1002/rem.20104
Park J, Tran S, Hwang B, Devries KL (2006) Interfacial evaluation of modified Jute and Hemp fibers/polypropylene (PP)-maleic anhydride polypropylene copolymers (PP-MAPP) composites using micromechanical technique and nondestructive acoustic emission. Compos Sci Technol 66:2686–2699. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.03.014
Poniedzialek M, Sekara A, Jedrszczyk E, Ciura J (2010) Phytoremediation efficiency of crop plants in removing cadmium, lead and zinc from soil. Folia Hortic 22:25–31. doi:10.2478/fhort-2013-0155
Reddy N, Yang Y (2005) Biofibers from agricultural byproducts for industrial applications. Trends Biotechnol 23:22–27. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2004.11.002
Reddy N, Yang Y (2006) Properties of high-quality long natural cellulose fibers from rice straw. J Agric Food Chem 54:8077–8081. doi:10.1021/jf0617723
Reddy N, Yang Y (2007a) Preparation and characterization of long natural cellulose fibers from wheat straw. J Agric Food Chem. doi:10.1021/jf071470g
Reddy N, Yang Y (2007b) Natural cellulose fibers from switchgrass with tensile properties similar to cotton and linen. Biotechnol Bioeng 97:1021–1027. doi:10.1002/bit.21330
Reddy K, Maheswari CU, Reddy DJP, Rajulu AV (2009) Thermal properties of Napier grass fibers. Mater Lett 63:2390–2392. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2009.08.035
Rouison D, Sain M, Couturier M (2004) Resin transfer molding of natural fiber reinforced composites: cure simulation. Compos Sci Technol 64:629–644. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2003.06.001
Rowell RM, Han JS, Rowell JS (2000) Characterization and factors effecting fiber properties. In: Frollini E, Leao A, Mattoso LHC (eds) Natural polymer and agrofibre based composites. Embrapa Instrumentação Agropecuária, Sao Carlos, pp 115–134
Sa’ad NS, Artanti R, Dewi T (2011) Phyto-remediation for rehabilitation of agricultural land contaminated by cadmium and copper. Indones J Agric 4:17–21
Sinha E, Rout SK (2009) Influence of fibre-surface treatment on structural, thermal and mechanical properties of jute fibre and its composite. Bull Mater Sci 32:65–76. doi:10.1007/s12034-009-0010-3
Sonibare OO, Ehinola OA, Egashira R, KeanGiap L (2005) An investigation into the thermal decomposition of Nigerian Coal. J Appl Sci 5:104–107. doi:10.3923/jas.2005.104.107
Summerscales J, Dissanayake N, Virk AS, Hall W (2010) A review of bast fibres and their composites. Part 1—fibres as reinforcements. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 41:1329–1335. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2010.06.001
Suryanto H, Zakia N, Marsyahyo E (2013) The exploration of cellulose nanocrystal from Mendong Fibers using Pulsed Electric Field (PEF), and the utilization for biopackaging applications (in Indonesian language). Research report, Universitas Negeri Malang
Suryanto H, Irawan YS, Marsyahyo E, Soenoko R (2014a) Effect of alkali treatment on crystalline structure of cellulose fiber from mendong (Fimbristylis globulosa) straw. Key Eng Mater 594–595:720–724. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.594-595.720
Suryanto H, Marsyahyo E, Irawan YS, Soenoko R (2014b) Morphology, structure, and mechanical properties of natural cellulose fiber from mendong grass (Fimbristylis globulosa). J Nat Fibers 11:333–351. doi:10.1080/15440478.2013.879087
Suryanto H, Marsyahyo E, Irawan YS et al (2015) Improvement of interfacial shear strength of mendong fiber (Fimbristylis globulosa) reinforced epoxy composite using the AC electric fields. Int J Poly Sci 2015, Article ID 542376, 10 pages. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/542376
Terinte N, Ibbett R, Schuster KC (2011) Overview on native cellulose and microcrystalline cellulose I structure studied by X-ray diffraction (WAXD): comparison between measurement techniques. Lenzing Ber 89:118–131
USDA (2015) Plant Profile. http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=FIGL#. Accessed 11 Jan 2015
Venkateshwaran N, Elayaperumal A (2010) Banana fiber reinforced polymer composites—a review. J Reinf Plast Compos 29:2387–2396. doi:10.1177/0731684409360578
Wang W, Cai Z, Yu J, Xia Z (2009) Changes in composition, structure, and properties of jute fibers after chemical treatments. Fibers Polym 10:776–780. doi:10.1007/s12221-009-0776-3
Yi C, Tian L, Tang F et al (2010) Crystalline transition behavior of sisal in cycle process. Polym Compos 31:933–938. doi:10.1002/pc.20885
Żurek G, Pogrzeba M, Rybka K, Prokopiuk K (2013) Suitability of grass species for phytoremediation of soils polluted with heavy-metals. In: Barth S, Milbourne D (eds) Breeding strategies for sustainable forage and turf grass improvement. Springer, Dordrecht
Acknowledgments
Gratefulness to the Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education, Indonesia, through the competitive research Grant 2013 and the fundamental research Grant with Contract No. 9.4.3/UN32.14/LT/2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Suryanto, H., Solichin, S., Yanuhar, U. (2016). Natural Cellulose Fiber from Mendong Grass (Fimbristylis globulosa). In: Ramawat, K., Ahuja, M. (eds) Fiber Plants. Sustainable Development and Biodiversity, vol 13. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44570-0_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44570-0_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-44569-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-44570-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)