Abstract
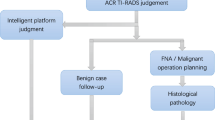
The thyroid is an indispensable gland of the human endocrine system that secretes hormones which have a significant effect on the metabolic rate and protein synthesis. The thyroid is susceptible to a variety of disorders. One among them is the formation of a thyroid nodule, an extraneous mass formed at the thyroid gland requiring medical attention and diagnosis. About 5–10 nodules out of 100 are malignant (cancerous). When a formation of nodules is discernible to the doctors, they call for a diagnostic blood test, often perfunctory, and do not differentiate malignant and benign tumours. This is where ultrasonography comes across as a better option. Automation of ultrasonography diagnosis results in a decrease in reporting time as well as provides a provisional diagnosis before the doctors’ expert opinion. Thus, deep learning methods were suggested and produced better results. Initially, region of interest (ROI) and feature extraction were done before applying machine learning models like support vector machines and multilayer perceptrons. Nevertheless, the feature selection required in machine learning methods was a long-drawn process, often involving the elements of trial and error. Deep convolutional neural networks along with histogram of gradients (HOG)-aided feature extraction which was used along classifiers have yielded high specificity and sensitivity values along with the accuracy. In this paper, we have studied and compared the efficacy of the application of various deep convolutional networks for the diagnosis of malignancy in thyroid nodules.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Horvath, S. Majlis, R. Rossi, C. Franco, J.P. Niedmann, A. Castro, M. Dominguez, An ultrasonogram reporting system for thyroid nodules stratifying cancer risk for clinical management. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 94(5), 1748–1751 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-1724
H.A. Ansari, S.M. Vasentwala, N. Saeed, K. Akhtar, S. Rehman, Diagnostic approach to thyroid nodules. Annals Int. Med. Dental Res. (2016). https://doi.org/10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.PT1
G. Popoveniuc, J. Jonklaas, Thyroid nodules. Med. Clin. North Am. 96(2), 329–349 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2012.02.002.PMID:22443979;PMCID:PMC3575959
V.N. Vapnik, The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory (Springer, New York, 1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-3264-1
N.H. Sweilam, A.A. Tharwat, N.K. Abdel, Support vector machine for diagnosis cancer disease: a comparative study. Egypt. Inform. J. 11(2), 81–92 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eij.2010.10.005
J. Kennedy, R. Eberhart, Particle swarm optimization, in Proceedings of ICNN ‘95—International Conference on Neural Networks, vol. 4 (Perth, WA, Australia, 1995), pp. 1942–194848. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
X. Fu, W. Liu, B. Zhang, H. Deng, Quantum behaved particle swarm optimization with neighborhood search for numerical optimization. Math. Probl. Eng. Article ID 469723, 10 pp. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/469723
M.H. Nguyen, F.D.L. Torre, Optimal feature selection for support vector machines. Pattern Recogn. 43(3) (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2009.09.003
M.-L. Huang, Y.-H. Hung, W.M. Lee, B.-R. Jiang, SVM-RFE based feature selection and Taguchi parameters optimization for multiclass SVM classifier. Sci. World J. Article ID 795624. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/795624
Z. Lai, H.F. Deng, Medical image classification based on deep features extracted by deep model and static feature fusion with multilayer perceptron. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. Article ID 2061516. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2061516
V. Nair, G.E. Hinton, Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines, in Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (Haifa, 2010), pp. 807–814
S. Belarouci, M. Chikh, Medical imbalanced data classification. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 2, 116–124. https://doi.org/10.25046/aj020316
D.-Z. Feng, Z. Bao, L.-C. Jiao, Total least mean squares algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 46(8), 2122–2130 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/78.705421
X.-Y. Liu, J.X. Wu, Z.-H. Zhou, Exploratory under-sampling for class-imbalance learning, in Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM ‘06) (IEEE, Hong Kong, 2006), pp. 965–969
H. He, E.A. Garcia, Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 21(9), 1263–1284 (2009)
C. Sun, A. Shrivastava, S. Singh, H. Mulam, Revisiting unreasonable effectiveness of data in deep learning era, in IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2017), pp. 843–852. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.97
M.A. Tanner, H.W. Wing, The calculation of posterior distributions by data augmentation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 82(398), 528–540 (1987). https://doi.org/10.2307/2289457
H. Kim, J. Park, H.-Y. Jung, An efficient color space for deep-learning based traffic light recognition. J. Adv. Transp. (2018), pp. 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2365414
Z. Hussain, F. Gimenez, D. Yi, D. Rubin, Differential data augmentation techniques for medical imaging classification tasks, in AMIA ... Annual Symposium Proceedings. AMIA Symposium (2017), pp. 979–984
R. Lee, F. Gimenez, A. Hoogi, K. Miyake, M. Gorovoy, D. Rubin, A curated mammography data set for use in computer-aided detection and diagnosis research. Sci. Data 4, 170177 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2017.177
S. Karen, Z. Andrew, Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv:1409.1556v6
N. Tajbakhsh, J. Shin, S. Gurudu, R.T. Hurst, M.B. Gotway, J. Liang, Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: full training or fine tuning? IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1299–1312 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2535302
O. Russakovsky, J. Deng, H. Su, J. Krause, S. Satheesh, S. Ma, Z. Huang, A. Karpathy, A. Khosla, M. Bernstein, A.C. Berg, L. Fei-Fei, ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vision (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y
R. Dhaya, Deep net model for detection of Covid-19 using radiographs based on ROC analysis. J. Innov. Image Process. (JIIP) 2(03), 135–140 (2020)
F. Abdolali, J. Kapur, J.L. Jaremko, M. Noga, A.R. Hareendranathan, K. Punithakumar, Automated thyroid nodule detection from ultrasound imaging using deep convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 122, 103871 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103871
K.V.S. Sundar, K. Rajamani, S. Sai, Exploring image classification of thyroid ultrasound images using deep learning, in Published in Proceedings of the International Conference on ISMAC in Computational Vision and Bio-Engineering 2018 (ISMAC-CVB) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00665-5_151
C. Szegedy, V. Vanhoucke, S. Ioffe, J. Shlens, Z. Wojna, Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision, in 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (Las Vegas, NV, 2016), pp. 2818–2826. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.308
T. Liu, S. Xie, J. Yu, L. Nia, W. Sun, Classification of thyroid nodules in ultrasound images using deep model based transfer learning and hybrid features, in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (New Orleans, LA, 2017), pp. 919–923. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2017.7952290
O. Mouse, Khachnaoui, R. Guetari, N. Khlifa, Thyroid nodules classification and diagnosis in ultrasound images using fine-tuning deep convolutional neural network. Int. J. Imag. Syst. Technol. 30(1) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22363
K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, J. Sun, Deep residual learning for image recognition, in 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (Las Vegas, NV, 2016), pp. 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
M. Zhou, R. Wang, P. Fu, Y. Bai, L. Cui, Automatic malignant thyroid nodule recognition in ultrasound images based on deep learning, in E3S Web Conference (2020). https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202018503021
O. Ronneberger, P. Fischer, T. Brox, U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation, in N. Navab, J. Hornegger, W. Wells, A. Frangi (eds.), Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015. MICCAI 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 9351 (Springer, Cham, 2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
D.P. Kingma, M. Welling, Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. CoRR, abs/1312.6114
D. Avola, L. Cinque, A. Fagioli, S. Filetti, G. Grani, E. Rodol, Knowledge-driven learning via experts consult for thyroid nodule classification, 28 May 2020. arXiv:2005.14117v1 [eess. IV]
G. Huang, Z. Liu, L. Maaten, K. Weinberger, Densely Connected Convolutional Networks (Cornell University paper, 2018). arXiv:1608.06993v5
Y. Chai, J. Song, M. Shear, Artificial Intelligence for thyroid nodule ultrasound image analysis. Annals Thyroid 5 (2020). https://aot.amegroups.com/article/view/5429
K.C. Aishwarya, S. Gannamaneni, G. Gowda, A. Abhishiek, TIRADS classification of thyroid nodules: a pictorial review. Int. J. Med. Res. 4(2), 35–40 (2019). www.medicinesjournal.com
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Baldota, S., Malathy, C. (2021). Classification of Ultrasound Thyroid Nodule Images by Computer-Aided Diagnosis: A Technical Review. In: Smys, S., Tavares, J.M.R.S., Bestak, R., Shi, F. (eds) Computational Vision and Bio-Inspired Computing. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1318. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6862-0_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6862-0_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-33-6861-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-33-6862-0
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)