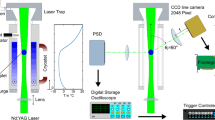
Abstract
Spontaneous condensation is induced by nucleation in supersaturated, i.e. in metastable vapour states of very short life-time. The rate of change of the thermal variables thus affects the so-called critical supersaturation, where the incipient condensation becomes observable. Consequently, a complete phenomenological description of spontaneous condensation requires the consideration of rate- or timevariables such as, e.g., a cooling- or an expansion-rate. Since comparatively few experimental results on the influence of these parameters are published and virtually all of them were attained in supersonic nozzle flow, i.e. at relative high expansion rate (P=1000–200000 s−1), two special cloud chambers were designed for low (0.5–130 s−1) and medium (100–500 s−1) expansion rate, respectively, with the intention to correlate critical supersaturation S W with P and temperature T in a wide range of vapour density — up to the critical point. The two cloud chambers are presented together with the relevant experimental procedures. First experimental results, obtained in both chambers with the pure vapours of carbon dioxide and ammonia, could be correlated with the respective data sets previously registered during Laval-nozzle experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham FF (1974) Homogeneous nucleation theory — Advances in theoretical chemistry. Suppl. I. Academic Press, New York and London
Allard EF; Kassner JL (1965) New cloud-chamber method for the determination of homogeneous nucleation rates. J Chem Phys 42: 1401–1405
Anderson RJ; Miller RC; Kassner Jr JL: Hagen DE (1980) A study of homogeneous condensation-freezing nucleation of small water droplets in an expansion cloud chamber. J Atmos Sci 37: 2508–2520
Bender E (1971) Die Berechnung von Phasengleichgewichten mit der thermischen Zustandsgleichung. Habilitationsschrift, Ruhr-Universität Bochum
Bender E (1973) The calculation of phase equilibria from a thermal equation of state applied to the pure fluids argon, nitrogen, oxygen, and their mixtures. C.F. Müller, Karlsruhe
Bier K; Ehrler F; Theis G (1984) Comparison of spontaneous condensation in supersaturated nozzle flow of different refrigerants. Proc. Int. VDI-Seminar ORC-HP-Technology, Zürich. VDI-Berichte 539, 749–768. VDI-Verlag, Düsseldorf
Bier K; Ehrler F; Theis G (1990) Spontaneous condensation in stationary nozzle flow of carbon dioxide in a wide range of density. Proc. IUTAM-Symp. Göttingen 1989: Adiabatic waves in liquidvapour systems. Meier, G.E.A., Thompson, P.A. (eds), Springer, Berlin, 129–144
Bier K; Ehrler F; Niekrawietz M (1990) Experimental investigation and computer analysis of spontaneous condensation in stationary nozzle flow of CO2-Air mixtures. Proc. IUTAM — Sympos. Göttingen 1989: Adiabatic waves in liquid-vapor systems. Meier, G.E.A., Thompson, P.A. (eds.), Springer, Berlin, 113–127
Bier K; Ehrler F; Treffinger P; Wright W (1995) Spontane Kondensation übersättigter reiner Dämpfe in Nebelkammem. VDI-Fort schritt-Berichte, Reihe 7, Strömungstechnik, Nr. 278. VDI-Verlag, Düsseldorf
van Dongen MEH; Smolders HJ; Braun CJM; Snoeijs CAM; Willems JFH (1994) Spectral light extinction to characterize fast fog formation. Appli Opt 33: 1980–88
Gyarmathy G (1965) Spontane Kondensation, Part 1: Ein analytisches Berechnungsverfahren für spontane Kondensationsvorgänge. VDI-Forschungsheft 508, 5–30, VDI-Verlag, Düsseldorf
Gyarmathy G; Meyer H (1965) Spontane Kondensation, Part 2: Versuche über den Einfluß der Entspannungsschnelligkeit auf die Nebelbildung in übersättigtem Wasserdampf. VDI-Forschungsheft 508, 31–48. VDI-Verlag, Düsseldorf
Hale BN (1982) Nucleation Symp. VPI, Blacksburg, Va
Hale BN (1986) Application of a scaled homogeneous nucleation rate formalism to experimental data at T ≪ T c, Phys Rev. A 33: 4156–4163
Hale BN (1988) Scaled models for nucleation. In: Lecture Notes in Physics 509, Atmospheric aerosols and nucleation Proc. eds. P.E. Wagner and G. Vali, Springer-Verlag Wien, 323–340
Hechler C (1988) Untersuchung zur spontanen Kondensation in übersättigten Strömungen von Wasserdampf und Entwicklung eines Streulichtverfahrens zur Bestimmung der Tropfengröße und -konzentration. Dissertation, Universität Karlsruhe (TH)
van de Hulst HC (1981) Light scattering by small particles. Dover, New York
Kerker M (1969) The scattering of light and other electromagnetic radiation. Academic Press, New York
Looijmans KNH; Kriesels PC; van Dongen MEH (1993) Gasdynamic aspects of a modified expansion-shock tube for nucleation and condensation studies. Exp Fluids 15: 61–64
Niekrawietz M (1989) Experimentelle Untersuchungen und Modellrechungen zur spontanen Kondensation in Düsenströmungen übersättigter Kohlendioxid/Luft-Gemische. Dissertation, Universität Karlsruhe (TH)
Oswatitsch K (1942) Kondensationserscheinungen in Überschalldüsen. ZAMM 22: 1–14
Peters F (1983) A new method to measure homogeneous nucleation rates. Exp Fluids 1: 143–148
Polt A (1987) Zur Beschreibung der thermodynamischen Eigenschaften reiner Fluide mit “Erweiterten BWR-Gleichungen”. Dissertation, Universität Kaiserslautern
Schaber K; Schenkel A; Zahoransky RA (1994) Drei-WellenlängenExtinktionsverfahren zur Charakterisierung von Aerosolen unter industriellen Bedingungen, tm -Technisches Messen 61: 295–300
Schmitt JL (1981) Precision expansion cloud chamber for homogeneous nucleation studies. Rev Sci Instrum 52: 1749–1754
Springer GS (1978) Homogeneous nucleation. Adv Heat Transfer 14: 281–346
Strey R; Wagner PE; Viisanen Y (1994) The problem of measuring homogeneous nucleation rates and the molecular contents of nuclei: Progress in the form of nucleation pulse measurements. J Phys Chem 98: 7748–7758
Theis G (1985) Spontankondensation in übersättigten Dampfströmungen von Kohlendioxid und Difluormonochlormethan. Dissertation, Universität Karlsruhe (TH)
Treffinger P (1994) Untersuchungen zur spontanen Kondensation in übersättigten Dämpfen. Dissertation, Universität Karlsruhe (TH)
Treffinger P; Ehrler F; Bier K (1994) Spontane Kondensation in Überschallströmungen. VDI-Fortschritt-Berichte, Reihe 7, Strömungstechnik, Nr. 251. VDI-Verlag, Düsseldorf
Viisanen Y; Strey R; Reiss H (1993) Homogeneous nucleation rates for water. J Chem Phys 99: 4680–4692
Wagner PE; Strey R (1981) Homogeneous nucleation rates of water vapour measured in a two-piston expansion chamber. J Phys Chem 85: 2694–2698
Wilson CTR (1897) Condensation of water vapour in the presence of dust-free air and other gases. Phil Trans Roy Soc London A 189: 265–307
Wittig S; Feld H-J; Müller A; Samenfink W; Tremmel A (1990) Application of the dispersion-quotient method under technical system conditions. Proc. 2nd Int. Congress of optical particle sizing, Tempe, Arizona
Wright W (1993) Zum Einfluß der Entspannungsgeschwindigkeit auf die spontane Kondensation übersättigter Dämpfe. Dissertation, Universität Karlsruhe (TH)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors wish to thank Prof. Dr. K. Bier, the previous director of this institute, for his interest in the development of the two chambers, for many valuable discussions, and for his continuing involvement to settle the questions of financing the project. Thanks are also due to Mrs. M. Urbanek, who took care of the figures, and, last but not least, to the team in the workshops of the institute, who realized the devices and equipped their periphery.
Part of this work was supported by grants Bi 102/53-1 and 2 as well as Bi 102/57-1 and 2 of Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), which is gratefully acknowledged.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehrler, F., Repple, K.H., Schüßler, J. et al. Special cloud chambers for investigations into the time-behaviour of homogeneously nucleated spontaneous condensation. Experiments in Fluids 21, 363–373 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00189057
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00189057