Abstract
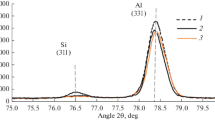
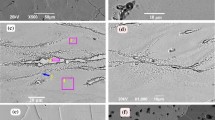
A two-piston splat-quenching technique has been used to prepare splat-quenched Fe-Mn alloys with 0 to 20 wt % Mn, and splat-quenched Fe-Ni-C alloys with a nominal carbon content of 0.1 wt % and 0 to 40 wt % Ni. The resulting alloy microstructures have been investigated by a combination of optical and scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffractometry, and microhardness testing; and the splat-quenched structures have been compared with the microstructures of similar alloys prepared by conventional solid-state quenching. In both alloy systems, splat-quenching produces a very small as-solidified austenite grain size, and a depression of the martensite transformation temperature as shown by an increased tendency to retain austenite to low temperatures. Because of the combination of a small austenite grain size and, therefore, fine scale martensite structure, splat-quenched martensitic alloys of Fe-Mn and Fe-Ni-C exhibit very high microhardness values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Inokuti and B. Cantor, Scripta Met. 10 (1976) 655.
L. Kaufman and M. Cohen, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 206 (1956) 1393.
T. Bell, in “Martensite”, edited by E. R. Petty (Longman, London, 1970) Ch. 4.
A. Gilbert and W. S. Owen, Acta Met. 10 (1962) 45.
R. C. Ruhl and M. Cohen, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 245 (1969) 253.
M. Hansen and K. Anderko, “Constitution of Binary Alloys” (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1958).
R. W. Cahn, K. D. Krishnanand, M. Laridjani, M. Greenholz and R. Hill, in “2nd International Conference on Rapidly Quenched Alloys”, Vol. Ii, edited by N. J. Grant and B. C. Giessen (Elsevier, Lausanne, 1976) p.83.
D. W. Gomersall and J. Gordon Parr, JISI 203 (1965) 275.
J. D. Bolton and E. R. Petty, Met. Sci. J. 5 (1971) 166.
H. Schumann, Arch. Eisenhüttenw. 38 (1967) 647.
Y. Inokuti and B. Cantor, to be published.
K. R. Satyanarayan and A. P. Miodownik, in “The Mechanism of Phase Transformations in Crystalline Solids” (Inst. Metals, London, 1969) p. 162.
J. W. Christian, in “Martensite”, edited by E. R. Petty (Longman, London, 1970) Ch. 2.
L. Kaufman, A. Leyenaar and J. S. Harvey, in “Progress in Very High Pressure Research”, edited by F. P. Bundy et al. (Wiley, New York, 1961) p. 90.
J. A. Klostermann, in “The Mechanism of Phase Transformations in Crystalline Solids” (Inst. Metals, London, 1969) p. 143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inokuti, Y., Cantor, B. The formation of martensite in splat-quenched Fe-Mn and Fe-Ni-C alloys. J Mater Sci 12, 946–958 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00540977
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00540977