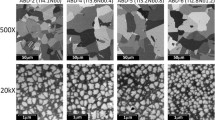
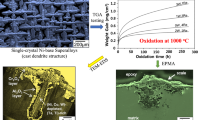
Abstract
The constituents of nickel-base superalloys have been classified into solid solution formers, precipitate formers, carbide formers and surface stabilizers. The characteristics of solutes which would make them most suitable in each category have been specified and appropriate alloying elements have been identified. Nickel-base superalloys are hardened primarily by the precipitation of Ni3X type compounds. The occurrence and crystallography of precipitation of various kinds of Ni3X type precipitates have been considered. The role of substitution by alloying elements on mismatch and stability of phases has been discussed. The free electron model and the Engel-Brewer model have been applied for evaluating the stabilities of precipitates, and the role of the alloying elements in determining the stabilities of external and internal surfaces such as grain boundaries have been briefly outlined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. J. Wahll, D. J. Maykuth and H. J. Hucek, in “Handbook of Superalloys” (Battelle Press, Columbus, 1979) p. 1.
R. W. Fawley, in “The Superalloys”, edited by C. T. Sims and W. C. Hagel (Wiley, New York, 1972) p. 3.
P. S. Kotval, Metallogr. 1 (1969) 251.
G. P. Sabol and R. Stickler, Phys. Status Solidi 35 (11) (1969) 11.
R. F. Decker and C. T. Sims, in “The Super-alloys”, edited by C. T. Sims and W. C. Hagel (Wiley, New York, 1979) p. 33.
R. T. Holt and W. Wallace, Int. Metals Rev. 21 (1976) 1.
Oleg D. Sherby and Peter M. Burke, Progr. Mater. Sci. 13 (7) (1967) 325.
W. Hume-Rothery and G. V. Raynor, “The Structure of Metals and Alloys”, 4th Edn. (Revised) (The Institute of Metals, London, 1967) p. 91.
M. Hansen and K. Anderko, “Constitution of Binary Alloys”, 2nd Edn. (McGraw Hill, New York, 1958); R. P. Elliott, first supplement (1965); F. A. Shunk, second supplement (1969).
R. M. N. Pelloux and N. J. Grant, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 218 (1960) 232.
B. E. P. Beeston and L. K. France, J. Inst. Metals 96 (1969) 105.
P. C. J. Gallagher, Met. Trans. 1 (1970) 2429.
W. B. Pearson, “A Handbook of Lattice Spacing and Structures of Metals and Alloys” (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1967).
A. K. Jena, D. Gulati and T. R. Ramachandran, Z. Metalkde 39 (1948) 111.
C. J. Smithells, “Metals Reference Book”, 5th Edn. (Butterworths, London, 1976) p. 860.
W. Koster and W. Rauscher, Z. Metalkde 39 (1948) 111.
L. W. Woodyatt, C. T. Sims and H. J. Beattie, Trans. AIME 236 (1966) 519.
M. Sakakibara and S. Sekino, in “Superalloy Processing” (Metals and Ceramics Information Centre, Battelle, Columbus, Ohio, 1972) p. I-1.
Y. S. Wang, X. M. Guan, H. Q. Ye, J. Bi and A. S. Xu, in “Superalloys 1980” (ASM, 1980) p. 63.
C. L. White, J. H. Schreibel and R. A. Padgett, Met. Tram. 14A (1983) 595.
C. L. White and R. A. Padgett, Scripta Metall. 16 (1982) 461.
P. M. Kelly, Int. Met. Rev. 18 (1973) 31.
P. Nash and D. R. F. West, Met. Sci. 17 (1983) 99.
O. H. Kriege and J. M. Baris, Trans. ASM 62 (1969) 195.
E. Hornbogen and M. Roth, Z. Metalkde 58 (1967) 842.
A. J. Ardell and R. B. Nicholson, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 27 (1966) 1793.
Idem, Acta Metall. 14 (1966) 1295.
W. E. Quist, R. Taggart and D. H. Polonis, Met. Trans. 2 (1971) 825.
K. Saito and R. Watanabe, Jap. J. Appl. Phys. 8 (1969) 14.
D. H. Ben Israel and M. E. Fine, Acta Metall. 11 (1963) 1051.
B. R. Clark and F. B. Pickering, J. Iron Steel Inst. 205 (1967) 70.
H. A. Moreen, R. Taggart and D. H. Polonis, Met. Trans. 5 (1974) 79.
Idem, Metallogr. 7 (1974) 513.
M. Raghavan, Met. Trans. 8A (1977) 1071.
D. W. Chung and M. C. Chaturvedi, Met. Sci. 8 (1974) 215.
M. C. Chaturvedi and D. W. Chung, Met. Trans. 10 (1979) 1579.
J. Manenc, Acta Metall. 7 (1959) 124.
I. Kirman and D. H. Warrington, J. Iron Steel Inst. 205 (1967) 1264; 99 (1971) 197.
W. C. Hagel and H. J. Beattie, in “Precipitation Processes in Steel” (The Iron and Steel Institute, London, 1959) p. 98.
M. Raghavan, Met. Trans. 9A (1978) 734.
Idem, ibid. 10A (1979) 1399.
M. Frebel, B. Predel and U. Klisa, Z. Metalkde 65 (1974) 311.
J. K. Tien and R. P. Gamble, Met. Trans. 3 (1972) 2157.
T. Miyazaki, K. Nakamura and H. Mori, J. Mater. Sci. 14 (1979) 1827.
D. D. Pearson, F. D. Lemkey and B. H. Kear, in “Superalloys 1980” (ASM, 1980) p. 513.
S. E. Axter and D. H. Polonis, Meter. Sci. Eng. 36 (1978) 71.
A. K. Jena and M. C. Chaturvedi, to be published.
J. H. Moll, G. N. Maniar and D. R. Muzyka, Met. Trans. 2 (1971) 2153.
C. P. Sullivan and M. J. Donachie, Met. Eng. Q. 11(4) (1971) 1.
C. Ravindran and M. C. Chaturvedi, Met. Trans. 6a (1975) 213.
J. R. Mihalisin and R. F. Decker, Trans. AIME 218 (1960) 507.
R. Cozar and A. Pineau, Met. Trans. 5 (1974) 2471.
D. Raynor and J. M. Silcock, Metal. Sci. J. 4 (1970) 121.
R. W. Guard and J. H. Westbrook, Trans. AIME 215 (1959) 807.
P. Nash and D. R. F. West, Met. Sci. 13 (1979) 670.
A. Taylor and R. W. Floyd, J. Inst. Metals 81 (1952–53) 25.
E. L. Raymond and D. A. Wells, in “Superalloy Processing” (Metals and Ceramics Information Center, Battelle, Columbus, Ohio 1972) p. N-1.
R. Nordheim and N. J. Grant, Trans. AIME 200 (1954) 211.
E. C. Guo and F. J. Ma, in “Superalloys 1980” (ASM, 1980) p. 431.
W. Hume-Rothery, Progr. Mater. Sci. 13(5) (1967) 229.
L. Brewer, UCRL Report 10701 (University of California, Berkeley, 1964); “High Strength Materials”, edited by V. F. Zackay (Wiley, New York, 1965) Ch. 2.
C. Wagner, Z. Electrochem. 65 (1961) 581.
Ya-Fang Han, P. Deb and M. C. Chaturvedi, Met. Sci. 16 (1982) 555.
W. I. Mitchell, Z. Metalkde 55 (1964) 613.
E. A. Fell, Metallurgia 63 (1961) 157.
D. W. Chung and M. C. Chaturvedi, Metallogr. 8 (1975) 329.
G. Chen, X. Xie, K. Ni, Z. Xu, D. Wang, M. Zhang and Y. Ju, in “Superalloys 1980” (ASM, 1980) p. 323.
G. Chen, C. Yao, Z. Zhong and W. Yu, in “Superalloys 1980” (ASM, 1980) p. 355.
C. T. Sims, in “The Superalloys”, edited by C. T. Sims and W. C. Hagel (Wiley, New York, 1972) p. 259.
L. R. Woodyatt, C. T. Sims and H. J. Beattie, Tram. AIME 236 (1966) 519.
J. R. Mihalisin, C. G. Bieber and R. T. Grant, Trans. AIME 242 (1968) 2399.
F. J. Rizzo and J. D. Buzzanell, J. Metals 21(10) (1969) 24.
C. T. Sims, ibid. 18 (1966) 1119.
C. Lund and J. F. Radavich, in “Superalloys 1980” (ASM, 1980) p. 85.
H. J. Beattie and W. C. Hagel, Trans. AIME 233 (1965) 277.
L. A. Jackman, H. B. Canada and F. E. Sczerzenie, in “Superalloys 1980” (ASM, 1980) p. 365.
Y. S. Wang, X. M. Guan, H. Q. Ye, J. Bi and A. S. Xu, ibid., p. 63.
H. E. Collins, Trans. ASM 62 (1969) 82.
G. E. Wasielewski and R. A. Rapp, in “The Superalloys”, edited by C. T. Sims and W. C. Hagel (Wiley, New York, 1972) p. 287.
D. P. Whittle and J. Stringer, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. A295 (1980) 309.
A. M. Beltran and D. A. Shores, in “The Superalloys”, edited by C. T. Sims and W. C. Hagel (Wiley, New York, 1972) p. 317.
R. Morbioli and H. Gilder, in “High Temperature Alloys for Gas Turbines”, edited by D. Coutsouradis, P. Felix, H. Fischmeister, L. Habraken, Y. Lindblom and M. O. Speidel (Applied Science, London, 1978) p. 125.
G. S. Giggins and F. S. Pettit, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 245 (1969) 2495.
E. P. Whelan, in “Superalloys 1980” (ASM, 1980) p. 53.
A. U. Seybolt, G.E. Research Conference Report 70-C-189, June (1970).
A. U. Seybolt and A. M. Beltram, “Hot Corrosion Problems Associated with Gas Turbines”, STP421 (American Society for Testing and Materials, 1967).
G. R. Wallwork and A. Z. Hbd, Oxidat. Metals 3 (1971) 171.
D. P. Whittle, in “High Temperature Alloys for Gas Turbines”, edited by D. Coutsouradis, P. Felix, H. Fischmeister, L. Habraken, Y. Lindblom and M. O. Speidel (Applied Science, London, 1978) p. 109.
K. R. Peters, D. P. Whittle and J. Stringer, Corrosion Sci. 16 (1976) 791.
D. L. Douglass and J. S. Armijo, Oxidat. Metals 2 (1970) 207.
A. U. Seybolt, Corrosion Sci. 11 (1971) 751.
P. Elliot and T. K. Ross, Werkstoffe u. Korrosion 72 (1971) 531.
G. B. Thomas and T. B. Gibbons, in “Superalloys 1980” (ASM, 1980) p. 699.
D. R. Wood and R. M. Cook, Metallurgia 67 (1963) 109.
D. A. Vermilyea, C. S. Tedmon and D. E. Broecker, Corrosion 31 (1975) 222.
W. C. Johnson, J. E. Doherty, B. H. Kear and A. F. Giamei, Scripta Metall. 8 (1974) 971.
R. F. Decker and J. W. Freeman, Trans. AIME 218 (1961) 277.
J. M. Walsh and B. H. Kear, Met. Trans. 6 (1975) 226.
J. E. Doherty, A. F. Giamei and B. H. Kear, Canad. Met. Q. 13 (1974) 229.
R. S. Cremisio, Elec. Furn. Steel. Conf. Proc. 29 (1971) 19.
D. N. Duhl and C. P. Sullivan, J. Metals 23(7) (1971) 88.
T. V. Svistunova and G. V. Estulin, Stal 9 (1963) 725.
H. J. Goldschmidt, J. Iron Steel Inst. (Lond.) 160 (1948) 345; quoted in C. S. Barret, “Structure of Metals” (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1952) p. 247.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jena, A.K., Chaturvedi, M.C. The role of alloying elements in the design of nickel-base superalloys. J Mater Sci 19, 3121–3139 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00549796
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00549796