Abstract
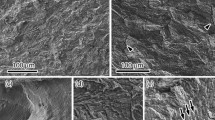
Hydrogen embrittlement of 316L type austenitic stainless steel has been studied by charging thin tensile specimens (0.2 mm thick) with hydrogen through cathodic polarization. The effects of hydrogen on the phase transition and the relative role of the metallurgical variables is discussed. Room temperature cathodic charging of unstressed specimens produces intergranular and secondary transgranular cracks along crystallographic planes. Severe grain boundary spelling has been observed at longer times of charging indicating that high stresses were formed. The surface cracking that was observed during the ageing is consistent with the development of high tensile surface stresses. TEM studies of the fracture surfaces of both annealed and sensitized, fine and coarse grain size, have revealed high dislocation structure. Thin plates of hydrogen inducedε (h c p)-martensite was observed. These plates appear in a heavily faulted region. The evidence of faults withinε-plates indicates that the overlapping stacking fault mechanism for the austenite toε transformation is in agreement with strain inducedε. The results of the tensile tests while undergoing cathodic charging show that the additional sensitization treatment and coarse-grained samples, lower the mechanical properties. The fracture surfaces of the sensitized steel contains regions of intergranular fracture where the micromechanism of the failure is microvoid nucleation and coalescence along grain boundaries. Finally, the microstructures are connected to various modes of cracking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Kolts, ASTM Publication ASTM STP 610 (ASTM, Pennsylvania, 1976) p. 336.
M. R. Louthan Jr, “Hydrogen in Metals”, edited by I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson (ASM, Metals Park, Ohio, 1974) p. 54.
A. W. Thompson, “Environment-Sensitive Fracture of Engineering Materials”, edited by A. Z. Foroulis (AIME, Warrendale, PA. 1979) p. 379.
D. Eliezer, D. G. Chakrpani, C. J. Altstetter andE. N. Pugh,Met. Trans. 10A (1979) 935.
E. Minkovitz andD. Eliezer,J. Mater. Sci. 17 (1982) 3165.
N. Narita, C. J. Altstetter andH. K. Birnbaum,Met. Trans. 13A (1982) 1355.
R. B. Benson, R. K. Dann andL. W. Roberts Jr,Trans. TMS-AIME 272 (1967) 2199.
C. L. Briant,Metall. Trans. 10A (1979) 181.
E. Minkovitz andD. Eliezer,J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1 (1982) 192.
B. C. Odegard, J. A. Brooks andA. J. West, “Effect of Hydrogen on Behavior of Materials”, edited by A. W. Thompson and I. M. Bernstein (TMS, New York, NY, 1976) p. 116.
A. J. West andM. R. Louthan Jr,Metall. Trans. 10A (1979) 1675.
M. R. Louthan Jr, G. R. Caskey Jr, J. A. Donovan andD. E. Rawl Jr,Mater. Sci. Eng. 10 (1972) 357.
J. A. Brooks andM. R. Louthan Jr,Metall. Trans. 11A (1980) 1981.
A. W. Thompson andJ. A. Brooks,Metall. Tram. 6A (1975) 1931.
E. Minkovitz andD. Eliezer,Scripta Metall. 16 (1982) 981.
R. M. Vennet andG. S. Ansell,Trans. ASM 60 (1967) 242.
N. Narita andH. K. Birnbaum,Scripta Metall. 14 (1980) 1355.
T. Takayama andM. Takano,Corrosion 38 (1982) 1.
A. Indue, Y. Hossoya andT. Nasumoto,Trans. Iron Steel Inst., Jpn. 19 (1979) 170.
M. L. Holzworth,Corrosion 25 (1969) 107.
R. Lagneborg,J. Iron Steel Inst. 207 (1969) 363.
H. E. Hanninen,Int. Met. Rev. 27 (1979) 85.
A. J. West Jr andM. R. Louthan Jr,Metall. Tran 13A (1982) 2049.
A. W. Thompson, “Environmental Degradation of Engineering Materials”, edited by M. R. Louthan Jr and R. P. McNitt (Virginia Polytechnic Institute, Blacksburg, VA, 1977.
C. L. Briant, “Hydrogen Effects in Metals”, edited by I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson (TMS-AIME, Pennsylvania, 1980) p. 527.
H. Hanninen, T. Hakkarainen andP. Nenonen,ibid.“ p. 575.
C. L. Briant andA. M. Ritter,Scripta Metall. 13 (1979) 177.
ASTM Standard Number E8.
M. Rigsbee,Metallography 11 (1978) 493.
D. Eliezer, “Hydrogen Effects in Metals”, edited by I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson (AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1981) p. 565.
P. Rozenak, L. Zevin andD. Eliezer,J. Mater. Sci. Lett. in press.
Idem, to be published.
A. Kummick andH. Johnson,Metall. Trans. 6A (1975) 1087.
M. Louthan andR. Derrick,Corros. Sci. 15 (1975) 565.
P. Studebaker, C. Altstetter andW. Conley, “Hydrogen Effects in Metals”, edited by I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson (AIME Warrendale, PA, 1981) p. 169.
A. Atrens, J. Bellina, N. Fiore andR. Coyle, “The Metal Science of Stainless Steels”, edited by E. Collings and H. King (AIME, New York, NY, 1979) p. 54.
C. L. Briant,Scripta Metall. 12 (1978) 541.
I. M. Bernstein andA. W. Thompson, “Alloy and Microstructural Design”, edited by J. K. Tien and G. S. Ansell (Academic Press, New York, 1976) Chap. 9, p. 303.
E. Minkovitz, M. Talianker andD. Eliezer,J. Mater. Sci. 16 (1981) 3506.
J. B. Brooks, N. H. Loretto andR. E. Smallman,Acta Metall. 27 (1979) 1839.
R. Lagneborg,ibid. 12 (1964) 823.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eliezer, D. The behaviour of 316L stainless steel in hydrogen. J Mater Sci 19, 1540–1547 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00563051
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00563051