Abstract
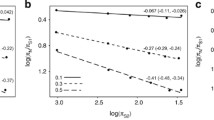
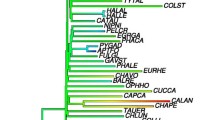
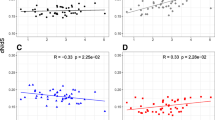
Attempts to analyze variation in the rates of molecular evolution among mammalian lineages have been hampered by paucity of data and by nonindependent comparisons. Using phylogenetically independent comparisons, we test three explanations for rate variation which predict correlations between rate variation and generation time, metabolic rate, and body size. Mitochondrial and nuclear genes, protein coding, rRNA, and nontranslated sequences from 61 mammal species representing 14 orders are used to compare the relative rates of sequence evolution. Correlation analyses performed on differences in genetic distance since common origin of each pair against differences in body mass, generation time, and metabolic rate reveal that substitution rate at fourfold degenerate sites in two out of three protein sequences is negatively correlated with generation time. In addition, there is a relationship between the rate of molecular evolution and body size for two nuclear-encoded sequences. No evidence is found for an effect of metabolic rate on rate of sequence evolution. Possible causes of variation in substitution rate between species are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi J, Cao Y, Hasegawa M (1993) Tempo and mode of mitochondrial DNA evolution in vertebrates at the amino acid sequence level: rapid evolution in warm blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol 36:270–281
Adsel SA (1964) Patterns of mammalian reproduction. Cornell University Press, New York
Avise JC, Bowden BW, Lamp T. Meylan AB, Bermingham E (1992) Mitochondrial DNA evolution at a turtles pace—evidence for low genetic variability and reduced microrevolutionary rate in the testudines. Mol Biol Evol 9:457–472
Bailey WJ, Fitch DHA, Tagle DA, Czelusniak J (1991) Molecular evolution of the psi-eta-globin gene locus: gibbon phylogeny and the molecular clock. Mol Biol Evol 8:155–184
Bearder SK (1987) Lorises, bushbabies and tarsiers: diverse societies in solitary foragers. In: Smuts BB, Cheney DL, Seyfarth RM, Wrangham RW (eds) pp 11–25
Boitani L, Bartoli S (1982) Simon and Schuster's guide to mammals. Simon and Schuster, New York
Boitani L, Bartoli S (1986) Macdonald encyclopedia of mammals. Macdonald, London
Britten RJ (1986) Rates of DNA sequence evolution differ between taxonomic groups. Science 231:1393–1398
Brown WM (1983) Evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. In: Nei M, Koehn RK (ed) Evolution of genes and proteins. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA, pp 62–88
Brown WM, Prager EM, Wang A, Wilson AC (1982) Mitochondrial DNA sequences of primates: tempo and mode of evolution. J Mol Evol 18:225–239
Bulmer M, Wolfe K, Sharp PM (1991) Synonymous nucleotide substitution rate in mammalian genes: implications for the molecular clock and the relationship of mammalian orders. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:5974–5978
Burt A (1989) Comparative methods using phylogenetically independent contrasts. Oxf Surv Evol Biol 6:33–53
Chang BH-J, Shimmin LC, Shyue S-K, Hewett-Emmett D, Li W-H (1994) Weak male-driven molecular evolution in rodents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:827–831
Cockburn A, Mansergh IM, Broome MS, Ward S (1990) Molecular clocks and generation time in Burramyid marsupials. Mol Biol Evol 7:283–285
Corbet GB, Harris S (1991) The handbook of British mammals. Black-well Scientific, Oxford
Corbet GB, Hill JE (1991) A world list of mammalian species. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Crockett CM, Eisenberg JF (1987) Howlers: variations in group size and demography. In: Smuts BB, Cheney DL, Seyfarth RM, Wrangham RW, Struhsaker TT (eds) Primate societies. University of Chicago, Chicago, pp 54–68
Dagosto M, Terranova CJ (1992) Estimating the body size of Eocene primates—a comparison of results from dental and postcranial variables. Int J Primatol 13:307–344
Damuth J (1993) Copes rule, the island rule and the scaling of mammalian population density. Nature 365:748–750
Davidson MM (1990a) White-tailed deer. In: King CM (ed) The handbook of New Zealand mammals. Oxford University Press, Auckland, pp 507–514
Davidson MM (1990b) Sika deer. In: King CM (ed) The handbook of New Zealand mammals. Oxford University Press, Auckland, pp 468–477
Douglas MJW (1990) Sambar deer. In: King CM (ed) The handbook of New Zealand mammals. Oxford University Press, Auckland, pp 477–483
Easteal S, Collett C (1994) Consistent variation in amino-acid substitution rate, despite uniformity of mutation rate: protein evolution in mammals is not neutral. Mol Biol Evol 11:643–647
Echols H, Goodman MF (1991) Fidelity mechanisms in DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem 60:477–511
Eisenberg JF (1981) The mammalian radiations. The Athalone Press, London
Eisenberg JF (1989) Mammals of the neotropics: the northern neotropics. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Elgar MA, Harvey PH (1987) Basal metabolic rate in mammals: allometry, phylogeny and ecology. Funct Ecol 1:25–36
Emmons LH, Feer F (1990) Neotropical rainforest mammals: a field guide. University of Chicago, Chicago
Felsenstein J (1985) Phylogenies and the comparative method. Am Nat 125:1–15
Filipski J (1988) Why the rate of silent codon substitutions is variable within a vertebrate's genome. J Theor Biol 134:159–164
Fleagle JG (1988) Primate adaptation and evolution. Academic Press, San Diego
Flux JEC (1990) Brown hare. In: King CM (ed) The handbook of New Zealand mammals. Oxford University Press, Auckland, pp 161–174
Garland T, Janis CM (1993) Does metarsal/femur ratio predict maximal running speed in cursorial mammals? J Zool (London) 229:133–151
Grzimek B (ed) (1990) Grzimek's encyclopedia of mammals. McGraw-Hill, New York
Haim A, van Aarde RJ, Skinner JD (1990) Metabolism and thermoregulation in the cape porcupine,Hystrix africaeaustralis. Physiol Zool 63:795–802
Hart RW, Setlow RB (1974) Correlation between deoxyribonucleic acid excision-repair and life-span in a number of mammal species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:2169–2173
Harvey PH, Pagel M (1991) The comparative method in evolutionary biology. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Harvey PH, Martin RD, Clutton-Brock TH (1987) Life histories in comparative perspective. In: Smuts BB, Cheney DL, Seyfarth RM, Wrangham RW, Struhsaker TT (ed) Primate societies. University of Chicago, Chicago, pp 181–198
Hasegawa MH, Kishino H, Yano T (1989) Estimation of branching dates among primates by molecular clocks of nuclear DNA which slowed down in Hominidae. J Hum Evol 18:461–476
Hayssen V, van Tienhoven A, van Tienhoven A (1993) Asdell's patterns of mammalian reproduction: a compendium of species-specific data. Cornell University Press, New York
Heaney LR (1984) Climatic influences on life-history tactics and behavior of North American tree squirrels. In: Murie JO, Michener GR (ed) The biology of ground-dwelling squirrels. University of Nebraska Press, pp 43–78
Heusner AA (1991) Size and power in mammals. J Exp Biol 160:25–54
Holmes EC (1991) Different rates of substitution may produce different phylogenies of eutherian mammals. J Mol Evol 33:209–215
Holmquist GP, Filipski J (1994) Organization of mutations along the genome: a prime determinant of genome evolution. Trends Evol Ecol 9:65–68
Husar SL (1978)Dugong dugon. Mamm Species 88-1-7
Ina Y (1995) New methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions. J Mol Evol 40:190–226
Irwin DM, Arnason U (1994) Cytochrome b gene of marine mammals: phylogeny and evolution. M Mamm Evol 2:37–55
Irwin DM, Kocher TD, Wilson AC (1991) Evolution of the cytochrome b gene of mammals. J Mol Evol 32:128–144
Kappeller PM (1990) The evolution of sexual size dimorphism in prosimian primates. Am J Primatol 21:201–214
King JE (1983) Seals of the world. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Kornberg A (1980) DNA replication. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (1993) MEGA: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 1.01. The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA
Kunkel TA (1992) DNA replication fidelity. J Biol Chem 267:18251–18254
Langman VA, Roberts TJ, Black J, Maloiy MO, Hegland NC, Weber J-M, Kram R, Taylor CR (1995) Moving cheaply: energetics of walking in the African elephant. J Exp Biol 198:629–632
Li W-H, Graur D (1991) Fundamentals of molecular evolution. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA
Li W-H, Tanimura M, Sharp PM (1987) An evaluation of the molecular clock hypothesis using mammalian DNA sequences. J Mol Evol 25:330–342
Li W-H, Gouy M, Sharp P, O'Huigin C, Yang Y-W (1990) Molecular phylogeny of Rodentia, Lagomorpha, Artiodactyla and Carniova and molecular clocks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6703–6707
Li W-H, Ellesworth DL, Krushkal J, Chang BH-J, Hewett-Emmett D (1996) Rates of nucleotide substitution in primates and rodents and the generation-time effect hypothesis. Mol Phylog Evol 5:182–187
Ma D-P, Zahkikh A, Graur D, Vandenberg JL, Li W-H (1993) Structure and evolution of opossum, guinea pig and porcupine cytochrome b genes. J Mol Evol 36:327–334
Macdonald D (ed) (1989) The encyclopedia of mammals. Unwin Hyman, London
Macdonald D, Barrett P (1993) Field guide to British and European mammals. Harper Collins, London
Martin AP (1995) Metabolic rate and directional nucleotide substitution in animal mitochondrial DNA. Mol Biol Evol 12:1124–1131
Martin AP, Palumbi SR (1993) Body size, metabolic rate, generation time and the molecular clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:4087–4091
Martin AP, Naylor G, Palumbi SR (1992) Rates of mitochondrial DNa evolution in sharks are slow compared with mammals. Nature 357:153–155
May RM (1993) Resisting resistance. Nature 361:593–594
McNab BK (1986) The influence of food habits on the energetics of euterian mammals. Ecol Monogr 56:1–19
McNab BK (1988) Complications inherent in scaling the basal rate of metabolism in mammals. Q Rev Biol 63:25–54
McNab BK (1989) Basal rate of metabolism, body size, and food habits in the Order Carnivora. In: Gittleman JL (ed) Carnivore behavior, ecology and evolution. Cornell University Press, New York, pp 335–354
Mooers AØ, Harvey PH (1994) Metabolic rate, generation time and the rate of molecular evolution in birds. Mol Phylog Evol 3:344–350
Moors PJ (1990) Norway rat. In: King CM (ed) The handbook of New Zealand mammals. Oxford University Press, Auckland, pp 192–206
Nash LT, Bearder SK, Olson TR (1989) Synopsis ofGalago species characteristics. Int J Primatol 10:57–80
Novacek MJ (1992) Mammal phylogenies: shaking the tree. Nature 356:121–125
Nowak RM (1991) Walker's mammals of the world. John Hopkins University Press, London
Oftedal OT, Gittleman JL (1989) Patterns of energy output during reproduction in Carnivores. In: Gittleman JL (ed) Carniovre behavior, ecology and evolution. Cornell University Press, New York, pp 355–378
Ohta T (1993) An examination of the generation time effect on molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10676–10680
Pagés-Feuillade E (1988) Modalités de l'occupation de l'espace et relations interindividuelles chez un prosimien nocturne malagache (Microcebus murinus). Folia Primatol 50:204–220
Palavcan JM, Gomez AM (1993) Dental scaling in the Callitrichinae. Int J Primatol 14:177–192
Promislow DEL (1994) DNA repair and the evolution of longevity: a critical analysis. J Theor Biol 170:291–300
Purvis AP (1995) A composite estimate of primate phylogeny. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Biol 348:405–421
Purvis AP, Harvey PH (1995) Mammal life-history evolution—a comparative test of Charnov's model. J Zool 237:259–283
Purvis AP, Bromham LD (in press) Estimating the transition/transversion ratio from independent pairwise comparisons with an assumed phylogeny. J Mol Evol
Rand DM (1994) Thermal habit, metabolic rate and the evolution of mitochondrial DNA. TREE 9:125–131
Richard AF (1987) Malagasy prosimians: female domiannce. In: Smuts BB, Cheney DL, Seyfarth RM, Wrangham RW, Struhsaker TT (eds) Primate societies. University of Chicago, Chicago, pp 25–33
Rohde K (1992) Latitudinal gradients in species diversity: the search for the primary cause. Oikos 65:514–527
Rosenheim JA, Tabashnik BE (1991) Influence of generation time on the rate of response to selection. Am Nat 137:527–541
Rosenheim JA, Tabashnik BE (1993) Generation time and evolution. Nature 365:791–792
Ross C (1992) Basal metabolic rate, body weight and diet in primates. Folia Primatol 58:7–23
Rudge MR (1990) Feral goat. In: King CM (ed) The handbook of New Zealand mammals. Oxford University Press, Auckland, pp 406–423
Sarich VM, Wilson AC (1973) Generation time and genomic evolution in primates. Science 179:1144–1147
Seino S, Bell GI, Li W-H (1992) Sequences of primate insulin genes support the hypothesis of a slower rate of molecular evolution in humans and apes than in monkeys. Mol Biol Evol 9:193–203
Shimmin LC, Chang BH-J, Li W-H (1993) Male-driven evolution of DNA sequences. Nature 362:745–747
Shimmin LC, Chang BH-J, Li W-H (1994) Contrasting rates of nucleotide substitution in the X-linked and Y-linked zinc-finger genes. J Mol Evol 39:569–578
Simons EL (1988) A new species ofPropithecus (Primates) from Northeast Madagascar. Folia Primatol 50:143–151
Skinner JD, Smithers RHN (1990) The mammals of the Southern African subregion. University of Pretoria
Smuts BB, Cheney DL, Seyfarth RM, Wrangham RW, Struhsaker TT (eds) (1987) Primate societies. University of Chicago, Chicago
Sowls L (1984) The peccaries. University of Arizona Press, Tucson
Springer MS, Kirsch JAW (1989) Rates of single-copy DNA evolution in phalangeriform marsupials. Mol Biol Evol 6:331–341
Stephan H, Baron G, Frahm HD (1981) Insectivora: with a stereotaxic atlas of the hedgehog brain. Springer Verlag, New York
Strahan R (1983) Complete book of Australian mammals. Angus and Robertson, Sydney
Sullivan DT (1995) DNA excision-repair and transcription—implications for genome evolution. Curr Opin Genet Dev 5:786–791
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bromham, L., Rambaut, A. & Harvey, P.H. Determinants of rate variation in mammalian DNA sequence evolution. J Mol Evol 43, 610–621 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02202109
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02202109