Abstract
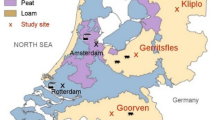
In 1994 the atmospheric deposition on three moorland pools in The Netherlands was only one third of its value in 1980. The effects of this reduction on these moorland pool ecosystems were examined by regular sampling of surface water chemistry and diatoms between 1979 and 1994. Moreover, diatom samples taken at irregular intervals between 1916 and 1978 were studied. In the pools Gerritsfles and Achterste Goorven, the median sulphate concentrations in 1994 were only one third of recorded values in 1980. Peak concentrations of sulphate were found after extremely dry summers. In the pool Kliplo, with an initially low concentration of sulphate, there was 16% increase of the concentration over the same period. Ammonium increased significantly in Kliplo and showed large variations in the other pools. Redundancy analysis showed that sulphate was the most important variable for the distribution of diatoms. As a consequence, the abundance of the acidification indicatorEunotia exigua in 1994 was only 25% of its value in 1980 in Achterste Goorven and 14% in Gerritsfles. Peaks ofE. exigua were found after drought periods. In Kliplo no clear change was observed. In 1994 the diatom assemblages of Achterste Goorven were much more similar to those of 1916–1925 than they were in 1980. In Gerritsfles a new situation, without historical analogue, developed. Overall, the large reduction of SOx-deposition had very positive consequences for the diatom assemblages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ALLES, E., M. NÖRPEL-SCHEMPP and H. LANGE-BERTALOT, 1991. Zur Systematik und Ökologie charakteristischerEunotia Arten (Bacillariophyceae) in elektrolytarmen Bachoberlöufen. Nova Hedwigia 53: 171–213.
ALLOTT, T.E.H., R. HARRIMAN and R.W. BATTARBEE,(1992): Reversibility of lake acidification at the Round Loch of Glenhead, Galloway, Scotland. Environm. Poll. 77: 219–225.
AQUASENSE TEC, 1995a. Chemical and biological monitoring in acid sensitive surface waters in The Netherlands 1994. Wageningen.
AQUASENSE TEC, 1995b. Veluwse vennen en leemkuilen onder de loep: ontwikkeling van een beleidsvisie voor toekomstig onderzoek en beheer. Wageningen.
BAL, D., H.M. BEIJE, Y.R. HOOGEVEEN, S.R.J. JANSEN and P.J. VAN DER REEST, 1995. Handboek natuurdoeltypen in Nederland. Informatie- en Kenniscentrum Natuurbeheer, Wageningen.
BATTARBEE, R.W., 1994. Diatoms, lake acidification and the Surface Water Acidification Programme (SWAP): a review. Hydrobiologia 274: 1–7.
BATTARBEE, R.W., R.J. FLOWER, A.C. STEVENSON, V.J. JONES, R. HARRIMAN and P.G. APPLEBY, 1988: Diatom and chemical evidence for reversibility of acidification of Scottish lochs. Nature 332: 530–532.
BELLEMAKERS, M.J.S., M. MAESSEN, M.J.R. CALS and J.G.M. ROELOFS, 1993. Effectgerichte maatregelen tegen verzuring en eutrofiëring van oppervlaktewateren: eindrapport monitoringsprogramma eerste fase. Vakgroep Oecologie, Werkgroep Milieubiologie, Katholieke Universiteit Nijmegen, Nijmegen.
BRAKKE, D.F., A. HENRIKSEN and S. NORTON, 1987. The relative importance of acidity sources for humic lakes in Norway. Nature 329: 432–434.
BOBBINK, R. and J.G.M. ROELOFS, 1995. Nitrogen critical loads for natural and semi-natural ecosystems: the empirical approach. Water, Air, Soil Poll. 85: 2413–2418.
CHARLES, D.F., R.W. BATTARBEE, I. RENBERG, H. VAN DAM and J.P. SMOL, 1989. Paleoecological analysis of lake acidification trends in North America and Europe using diatoms and chrysophytes. In: S.A. Norton, S.E. Lindberg and A.L. Page, Eds., Soils, aquatic processes, and lake acidification. Springer, New York. p. 207–276.
DENYS, L. and D. VAN STRAATEN, 1992. A survey of the acid water diatom assemblages of two heathland relics in the Belgian northern Campine (Groot & Klein Schietveld, Brasschaat) with an assessment of their conservational value. Diatom Res. 7: 1–13.
DIXIT, S.S., A.S. DIXIT and J.P. SMOL, 1992. Assessment of changes in lake water chemistry in Sudbury area lakes since preindustrial times. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sc. 49 (Suppl. 1): 8–16.
ERISMAN, J.W., 1992. Atmospheric deposition of acidifying compounds in the Netherlands. Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University.
HENRIKSEN, A. and H.M. SEIP, 1980. Strong and weak acids in surface water of southern Norway and southwestern Scotland. Water Res. 14: 809–813.
HUSTEDT, F., 1927–1966. Die Kieselalgen Deutschlands, Österreichs und der Schweiz unter Berücksichtigung der übrigen Länder Europas sowie der angrenzenden Meeresgebiete. In: Dr. L. Rabenhorst's Kryptogamen-Flora von Deutschland, Österreich und der Schweiz 7. Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft/Geest & Portig, Leipzig.
HUSTEDT, F., 1930. Bacillariophyta (Diatomeae). In: A. Pascher, Ed., Die Süßwasser-Flora Mitteleuropas 10. Fischer, Jena.
JONGMAN, R.H.G., C.J.F. TER BRAAK and O.F.R. VAN TONGEREN, 1987. Data analysis in community and landscape ecology. Pudoc, Wageningen.
JUGGINS, S., R.J. FLOWER and R.W. BATTARBEE, 1996. Palaeolimnological evidence for recent chemical and biological changes in the U.K. acid waters monitoring network sites. Freshw. Biol. 36: 203–219.
KOBAYASI, H. and T. NAGUMO, 1988. Examination of the type materials ofNavicula subtilissima Cleve (Bacillariophyceae). Botan. Magaz. (Tokyo) 101: 239–254.
KRAMMER, K. 1992.Pinnularia. Eine Monographie der Europöischen Taxa. Cramer, Berlin.
KRAMMER, K. and H. LANGE-BERTALOT, 1986–1991. Bacillariophyceae. In: H. Ettl, J. Gerloff, H. Heynig and D. Mollenhauer, Eds. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa 2/1-4. Fischer, Stuttgart.
KWAKKESTEIN, R., 1977. Onderzoek naar de Desmidiaceeënflora van de vennen in het gebied rond Oisterwijk. I. De vennen in het westelijk gedeelte. Hugo de Vrieslaboratorium, Universiteit van Amsterdam, Amsterdam.
LANCASTER, J., M. REAL, S. JUGGINS, D.T. MONTEITH, R.J. FLOWER and W.R.C. BEAUMONT, 1996. Monitoring temporal changes in the biology of acid waters. Freshw. Biol. 36: 179–201.
LAST, F.T. and R. WATLING, 1991. Acidic deposition: its nature and impacts. Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinburgh, B, 97: 1–343.
LEUVEN, R.S.E.W., H.L.M. KERSTEN, J.A.A.R. SCHUURKES, J.G.M. ROELOFS and G.H.P. ARTS, 1986. Evidence for recent acidification of lentic soft waters in The Netherlands. Water, Air, Soil Poll. 30: 387–392.
LNV, 1995. Ecosystemen in Nederland. Ministerie van Landbouw, Natuurbeheer en Visserij, Den Haag.
MARNETTE, E.C.L., H. HOUWELING, H. VAN DAM and J.W. ERISMAN, 1993. Effects of decreased atmospheric deposition on the sulfur budgets of two Dutch moorland pools. Biogeochemistry 23: 119–144.
NEWELL, A.D., 1993. Inter-regional comparison of patterns and trends in surface water acidification across the United States. Water, Air, Soil Poll. 67: 257–280.
NIJPELS, E.H.T.M., 1987. Tussentijdse evaluatie verzuringsbeleid. Ministerie van Volkshuisvesting, Ruimtelijke Ordening en Milieubeheer/Ministerie van Verkeer en Waterstaat/Ministerie van Landbouw, 's-Gravenhage.
NIJPELS, E., 1989. Bestrijdingsplan verzuring: de problematiek van de verzuring. Tweede Kamer der Staten-Generaal, vergaderjaar 1988–1989 18 225, nr. 31. SDU, 's-Gravenhage.
OLIVER, B.G., E.M. THURMAN and R.L. MALCOLM, 1983. The contribution of humic substances to the acidity of colored natural waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 47: 2031–2035.
REUSS, J.O. and D.W. JOHNSON, 1986. Acid deposition and the acidification of soils and waters. Springer, New York.
RIVM, 1993. Milieurendement van het NMP-2: aanvulling op de nationale milieuverkenning 3. Samsom H.D. Tjeenk Willink, Alphen aan den Rijn.
RIVM, 1995. Milieubalans 95. Samsom H.D. Tjeenk Willink, Alphen aan den Rijn.
ROELOFS, J.G.M., 1983. Impact of acidification and eutrophication on macrophyte communities in soft waters in The Netherlands. I. Field observations. Aquat. Bot. 17: 139–155.
SCHUURKES, J.A.A.R., C.J. KOK and C. DEN HARTOG, 1986. Ammonium and nitrate uptake by aquatic plants from poorly buffered and acidified waters. Aquat. Bot. 24: 131–146.
SCHUURMANS, C.J.E., 1977. Meteorologische aspecten van de droge zomer van 1976. H2,O 10: 178–180.
SHAFFER, P.W., R.P. HOOPER, K.N ESHLEMAN and M.R. CHURCH, 1988. Watershed vs in-lake alkalinity generation: a comparison of rates using input-output studies. Water, Air, Soil Poll. 39: 263–273.
SKJELKVÅLE B.L, A.D. NEWELL, G. RADDUM, M. JOHANNESSEN, H. HOVIND, T. TJOMSLAND and B. WATHNE, 1994. The six years report: Acidification of surface water in Europe and North America. Dose/response relationships and long-term trends. Norwegian Institute for Water Research, Oslo.
SHAFFER, P.W., R.P. HOOPER, K.N ESHLEMAN and M.R. CHURCH, 1988. Watershed vs in-lake alkalinity generation: a comparison of rates using input-output studies. Water, Air, Soil Poll. 39: 263–273.
SIEGEL, S., 1956. Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences. McGraw-Hill, New York.
SMIT, H.D.W., 1976. Desmidiaceeën in zuid-west Drenthe. Hugo de Vries-Laboratorium, Universiteit van Amsterdam, Amsterdam.
STUYFZAND, P.J., 1989. Hydrochemische onderzoeksmethoden ter analyse van grondwaterstroming. 1. H2O 22: 141–146.
TER BRAAK, C.J.F., 1988. CANOCO — a FORTRAN program for canonical community ordination by [partial] [detrended] [canonical] correspondence analysis, principal components analysis and redundancy analysis (version 2.1). DLO-Groep Landbouwwiskunde, Wageningen.
TER BRAAK, C.J.F., 1990. Update notes: Canoco version 3.10. DLO-Groep Landbouwwiskunde, Wageningen.
TER BRAAK, C.J.F., 1994. Canonical community ordination. Part I: Basic theory and linear methods. Ecoscience 1: 127–140.
TER BRAAK, C.J.F., and H. VAN DAM, 1989. Inferring pH from diatoms: a comparison of old and new calibration methods. Hydrobiologia 178: 209–223.
UNITED NATIONS, 1994. Protocol to the 1979 Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution on Further Reduction of Sulphur Emissions. United Nations, New York, Geneva.
VAN DAM, H., 1984. A guide to the literature for the identification of freshwater diatoms in The Netherlands. Hydrobiol. Bull. 18: 11–16.
VAN DAM, H., 1988. Acidification of three moorland pools in The Netherlands by acid precipitation and extreme drought periods over seven decades. Freshw. Biol. 20: 157–176.
VAN DAM, H. and G.H.P. ARTS, 1993. Ecologische veranderingen in Drentse vennen sinds 1900 door menselijke beïnvloeding en beheer.Provincie Drenthe, Assen/DLO-Instituut voor Bos- en Natuuronderzoek, Leersum/Grontmij Advies en Techniek, De Bilt.
VAN DAM, H. and B. BELTMAN, 1992. Effects of climatic change on chemistry and vegetation of peatlands, with special reference to interaction with atmospheric deposition. Wetl. Ecol. Managern. 2: 63–68.
VAN DAM, H. and R.F.M. BUSKENS, 1993. Ecology and management of moorland pools: balancing acidification and eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 265: 225–263.
VAN DAM, H. and H. KOOYMAN-VAN BLOKLAND, 1978. Man-made changes in some Dutch moorland pools, as reflected by historical and recent data about diatoms and macrophytes. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 63: 587–607.
VAN DAM, H. and A. MERTENS, 1989. Diatomeeën van oude en recente aquatische macrofyten uit het Beuven in relatie tot het beheer. Diatomededelingen 8: 15–23.
VAN DAM, H. and A. MERTENS, 1990. A comparison of recent epilithic diatom assemblages from the industrially acidified and copper polluted Lake Orta (Northern Italy) with old literature data. Diatom Res. 5: 1–13.
VAN DAM, H., A. MERTENS and J. SINKELDAM, 1994. A coded checklist and ecological indicator values of freshwater diatoms from The Netherlands. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol. 28: 117–131.
VAN DAM, H., G. SUURMOND and C.J.F. TER BRAAK, 1981. Impact of acidification on diatoms and chemistry of Dutch moorland pools. Hydrobiologia 83: 425–459.
VAN DAM, H., H. HOUWELING, F.G. WORTELBOER and J.W. ERISMAN, 1996. Long-term changes of chemistry and biota in moorland pools in relation to changes of atmospheric deposition. AquaSense TEC, Wageningen / DLO-Institute for Forestry and Nature Reseach (IBN-DLO), Wageningen / National Institute for Health and Environmental Protection, Bilthoven.
VAN DOBBEN, H.F, J. MULDER, H. VAN DAM and H. HOUWELING, 1992. The impact of atmospheric deposition on the biogeochemistry of moorland pools and surrounding terrestrial environment. Pudoc, Wageningen.
VERKAAR, D., L. VAN DUUREN and J. SCHAMINÉE, 1992. De internationale betekenis van Nederland voor hogere planten op grand van biografische gegevens. De Levende Natuur 93: 34–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Dam, H. Partial recovery of moorland pools from acidification: Indications by chemistry and diatoms. Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology 30, 203–218 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02272240
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02272240