Abstract
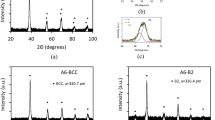
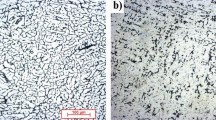
The development of the microstructure on aging of an (α + β) type titanium alloy containing 6A1-1.6Zr-3.3Mo-0.3Si (VT9) (in weight percent) has been studied. The β-transus temperature of this alloy is approximately 1243 K. Solution treatment in the β-phase field of the alloy followed by quenching in water at room temperature resulted in the formation of a single-phase martensite struc-ture. The martensitic structure was confirmed to be orthorhombic (α″) using X-ray diffraction. The water-quenched (WQ) specimens were subjected to aging treatments at temperatures of 823, 873, and 973 K for various lengths of time. Aging at 823 K for times between 24 and 100 hours did not bring about any noticeable change in the microstructure. Aging at 823 K for 200 and 300 hours resulted in the heterogeneous precipitation ofs 2 silicide particles and thin films of β sandwiched between the interplatelet boundaries of martensite. Electron diffraction analysis confirms that the crystal structure of silicide particles is hexagonal with lattice parameters α= 0.70(1) nm andc = 0.36(8) nm. Aging at 873 K for 12 and 24 hours resulted only in the precipitation ofs 2 silicide particles, while aging at the same temperatures for longer times (48, 100, and 200 hours) and also at 973 K for 6 to 100 hours resulted in the precipitation of silicides and also thin films of β and acicular martensite. The relative sizes of silicide precipitates and width of thin films of β phase increase with increasing aging time. The sites for silicide precipitation are mainly at α′-α′ boundaries, α-β interfaces, and sometimes within regions of transformed β. The kinetics ofs 2 silicide precipi-tation in this alloy is faster than in commercial near-α titanium alloys. This is attributed to the presence of Mo, a strong β stabilizer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Eylon, S. Fujishiro, P.J. Postans, and F.H. Froes:J. Met, 1984, vol. 1, pp. 55–62.
M. Kehoe and R.W. Broomfield:Defence Sci. J., 1986, vol. 36 (4), p. 2167.
M.R. Winstone, R.D. Rawlings, and D.R.F. West:J. Less-Common Met, 1975, vol. 37, pp. 205–17.
Y. Imbert:J. Less-Common Met, 1974, vol. 37, pp. 71–89.
W. Cho, J.W. Jones, J.E. Allison, and W.T. Donlon:Proc. 6th World Conf. on Titanium, Les Editions de Physique, Paris, 1988, vol. 1, pp. 187–92.
H.M. Flower, P.R. Swann, and D.R.F. West:Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 3289–97.
A.T.K. Assadi, H.M. Flower, and D.R.F. West:Met. Technol. 1979, Jan., pp. 8–15.
H.M. Flower, K. Lipscombe, and D.R.F. West:J. Mater. Sci., 1982, vol. 17, pp. 1221–31.
C. Ramachandra and V. Singh:J. Mater. Sci., 1988, vol. 23, pp. 835- 41.
G. Sridhar and D.S. Sarma:Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20A, pp. 55- 62.
D. Banerjee, J.E. Allison, F.H. Froes, and J.C. Williams: inTitanium Science and Technology, G. Lutjering, U. Zwicker, and W. Bunk, eds., DGM, 1985, vol. 3, pp. 1519-26.
A.P. Woodfield, P.J. Postans, M.H. Loretta, and R.E. Smallman:Acta Metall, 1988, vol. 36, pp. 507–15.
C. Ramachandra and V. Singh:Scripta Metall., 1987, vol. 21, pp. 633–36.
C. Ramachandra, V.K. Verma, and V. Singh:Int. J. Fatigue, 1988, vol. 10, pp. 21–26.
WJ. Plumbridge and M. Stanley:Int. J. Fatigue, 1986, vol. 8, pp. 209–16.
K.C. Antony:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1968, vol. 242, pp. 1454–56.
P.C. Kotval and R.W. Calder:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 1308- 11.
F. Barbier, C. Servant, C. Quesne, and P. Lacombe:J. Microsc. Spectrosc. Electron, 1981, vol. 6, pp. 299–310.
F.A. Crossley and D.H. Turner:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1958, vol. 212, p. 60.
C. Ramachandra and V. Singh:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 771–75.
C. Ramachandra, A.K.. Singh, and G.M.K. Sarma:Metall. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 1273–80.
C. Ramachandra and V. Singh:Scripta Metall, 1986, vol. 20, pp. 509- 12.
D. Banerjee, D. Mukherjee, R.L. Saha, and K. Bose:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 413–20.
A.K. Singh, C. Ramachandra, M. Tavafoghi, and V. Singh:J. Alloys Compounds, 1992, vol. 179, pp. 125–35.
A.K. Singh, C. Ramachandra, M. Tavafoghi, and V. Singh:J. Mater. Sci. Lett, 1993, vol. 12, pp. 697–99.
CF. Yolton, F.H. Froes, and R.F. Malone:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 132–34.
T.J. Headly and H.J. Rack:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 909- 20.
D. Banerjee and J.C. Williams:Scripta Metall, 1983, vol. 17, pp. 1125–28.
D. Banerjee, C.G. Shelton, B. Ralph, and J.C. Williams:Acta Metall, 1988, vol. 36(1), pp. 125–41.
C. Servant, C. Quesne, T. Baudin, and R. Penelle:J. Mater. Res., 1991, vol. 6 (5), pp. 987–98.
F. Cortial:Metall. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 241–48.
N.E. Paton and H.L. Fraser:Proc. 6th World Conf. on Titanium, Les Editions de Physique, Paris, 1988, vol. 3, pp. 1469–79.
T.T. Ye and H. Ling:Scripta Metall, 1989, vol. 23, pp. 1755–59.
C.E. Shamblen:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 1299–1305.
M. Young, E. Levine, and H. Margolin:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 359–65.
T. Sujimoto, Shinya Komatru, and Kizoshi Kamei:Titanium 80, Science and Technology, H. Kimura and O. Izumi, eds., TMS-AIME, New York, NY, 1980, pp. 2981–90.
H.W. Rosenberg:The Science Technology and Application of Titanium, R.I. Jafee and N.E. Promisel, eds., Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 1970, pp. 851–59.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly Reader, Department of Metallurgical Engineering, Centre of Advanced Study, Institute of Technology, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221 005, India
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A.K., Roy, T. & Ramachandra, C. Microstructural stability on aging of an α + β titanium alloy: ti- 6ai- 1.6zr-3.3mo- 0.30si. Metall Mater Trans A 27, 1167–1173 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649855
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649855