Abstract
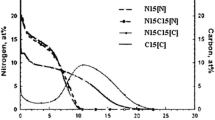
A mathematical model has been developed which, by means of finite difference computation techniques, permits the prediction of carbon concentration profiles in carburized high temperature alloys. It is assumed that a proportion of the carbon which diffuses into the alloy reacts with elements such as chromium to form carbide precipitates. The amount of carbon remaining in solution is determined from the solubility product of the carbide. Only this carbon in solution is able to diffuse through the alloy matrix, and thus the carbide precipitation process reduces the rate of carburization. Applying the model, the diffusion coefficient of carbon in Alloy 800 H at 900 °C has been determined as (3.3 ± 0.5) × 10−8 cm2/s. The model can also treat the carburization of an alloy containing two carbide-forming elements, but application to alloys containing both chromium and niobium (columbium) was successful only to a limited extent, probably as a result of the slow, complex kinetics of carbide precipitation. The model can be used to adapt carbon concentration profiles from one geometrical configuration to another. On the basis of profiles determined experimentally on small, cylindrical test specimens, carbon concenration profiles have been predicted for thick section tubes of Alloy 800 H exposed to a carburizing environment for up to 100,000 h.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Thorley and C. Tyzack:Proc. BNES Conf. on Effects of Environment on Material Properties in Nuclear Systems, pp. 143–54, British Nuclear Energy Society, London, 1971.
P. J. Ennis and D. F. Lupton:Proc. Int. Conf. on Behaviour of Alloys in Aggressive Environments, Petten, 1979 (to be published).
D. B. Roach: NACE Meeting, Corrosion/76, Paper No. 7, Houston, 1976.
A. Schnaas and H. J. Grabke:Werkst. Korros., 1978, vol. 29, pp. 635–44.
A. Schnaas and H. J. Grabke:Oxid. Met., 1978, vol. 12, pp. 387–404.
O. Demel:Radex Rundsch., 1977, vol. 2, pp. 201–09.
J. I. Goldstein and A. E. Moren:Met. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, pp. 1515–25.
J. Crank:The Mathematics of Diffusion, Oxford University Press, London, 1964.
H. Tůma, P. Gröbner, and K. Löbl:Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1969, vol. 40, pp. 727–31.
P. J. Ennis, D. F. Lupton, and H. Nickel: KFA Report JÜL, in press.
J. Jeanin, C. Mannerskantz, and F. D. Richardson:Trans. TMS-A1ME, 1963, vol. 227, pp. 300–05.
F. N. Mazandarany and R. D. Pehlke:Met. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 2067–76.
W. Slough, P. J. Spencer, and O. Kubaschewski:J. Chem. Thermodyn., 1970, vol. 2, pp. 117–24.
K. Natesan and T. F. Kassner:Met. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 2557–66.
E. Schürmann, K. H. Harre, and H. J. Rimkus:Giesserei-forschung, 1974, vol. 26, pp. 31–42.
A. V. Dean: Proc.Int. Conf. on Behaviour of Alloys in Aggressive Environments, Petten, 1979 (to be published).
R. P. Agarwala, M. C. Naik, M. S. Anand, and A. R. Paul:J. Nucl. Mater., 1970, vol. 36, pp. 41–47.
R. A. Perkins and P. T. Carlson:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 1511–14.
O. Kubaschewski and C. B. Alcock:Metallurgical Thermochemistry, 5th edition, p. 381, Pergamon, Oxford, 1979.
P. J. Spencer: Private communication, Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule, Aachen, Federal Republic of Germany.
S. K. Bose and H. J. Grabke:Z. Metallkd., 1978, vol. 69, pp. 8–15.
O. Böhm and M. Kahlweit:Acta Metall., 1964, vol. 12, pp. 641–48.
G. Roberts:Met. Sci., 1979, vol. 13, pp. 94–97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly of the Institute of Reactor Materials, Nuclear Research Centre (KFA), Jülich
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bongartz, K., Lupton, D.F. & Schuster, H. A model to predict carburization profiles in high temperature alloys. Metall Trans A 11, 1883–1893 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02655105
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02655105