Abstract
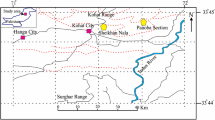
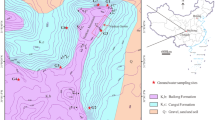
Stromatolitic limestone and calcareous shale belonging to Chattisgarh Supergroup of Proterozoic age dominate the upper part of the Mahanadi river basin. X-ray diffractogram (XRD) of limestone rocks show presence of a significant amount of calcite, dolomite and ankerite. Shales of various colours contain calcite and dolomite. It is observed that congruent dissolution of carbonate minerals in the Charmuria pure limestone has given rise to a typical karst topography. On the other hand, limestones are also seen to support red and black soil profiles. This indicates that the limestone bedrock undergoes a parallel incongruent weathering, which leaves a residue of decomposed rock. The XRD analyses reveal that the limestone soils thus formed contain an assemblage of quartz, clays and Fe-oxides. It is likely that the silicate component trapped during deposition of the stromatolitic limestone weathers incongruently resulting in diverse soil profiles. Carbonate and silicate mineral weathering schemes have been worked out to explain the soil formation, fixation of Al in clay minerals, and Fe in goethite. The water quality parameters such as Ca, Mg and HCO3 in the river water suggest under saturation with respect to calcite and dolomite. The mineral stability diagrams indicate that kaolinite and Ca-smectite are stable in the river water environment, hence they occur in suspended sediments and soils. The dominant influence of carbonate weathering on the water quality is observed even in the downstream part of the river outside the limestone terrain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berner E K and Berner R A 1987The Global Water Cycle: Geochemistry and Environment; Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., p. 397.
Burst J E 1958 Mineral heterogeneity in glauconite pellets;American Mineralogist.43 481–497.
Chakrapani G J and Subramanian V 1990 Preliminary studies on the geochemistry of the Mahanadi river basin, India;Chem. Geol. 81 241–253.
Drever J I 1988The Geochemistry of Natural Waters, 2nd edn, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., p. 437.
Drever J I 1997 Catchment mass balance, In:Geochemical processes, weathering and groundwater recharge in catchments; (eds) O M Saether and P de Caritat, Balkema, pp. 241–261.
Das N, Das M and Mishra V P 1989 Geology of Bemetra-Kodwa-Bera Area, Durga District, Madhya Pradesh;Rec. Geol. Surv. Ind. 122(6) 16–17.
Das N, Das M G and Arora Y K 1990 Microfacies assemblage of gypsum from Chattisgarh basin -A Sabkha model of evaporite formation;Geol. Surv. India, Spl. Publ. 28 639–647.
Garrels R M and Christ C L 1965Solutions, Minerals and Equilibria; (New York: Harper and Row), 450 pp.
Gibbs R J 1970 Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry;Science 170 1088.
Kale V S 1991 Constraints on the evolution of the Purana basins of Peninsular India;J. Geol. Soc. India 38 231–252.
Meybeck M 1987 Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved load;Am. J. Sci. 287 401–428.
Murti K S 1987 Stratigraphy and sedimentation in Chattishgarh basin;Proc. Purana Basins of India, Memoir 6,Geol. Soc. India, pp. 239–260.
Mukherjee A 1990 Phosphogenesis in Pre-Cambrian rocks of Durga district, Madhya Pradesh; unpublished Ph.D. thesis, Ravi Shankar University, Raipur, p. 246.
Naidu A S, Mowatt T C, Somayajulu B L K and Rao K S 1985 Characteristics of clay minerals in the bed loads of major rivers in India;SCOPE/UNEP, Hamburg, pp. 559–569.
Ohrui K and Mitchell M J 1998 Stream water chemistry in Japanese watersheds and its variability on a small regional scale,Water Resour. Res. 34 1553–1561.
Panigrahy B K 1991 Geochemistry of Rock weathering in upper part of Mahanadi Basin, Unpublished Ph.D thesis submitted to IIT, Kanpur.
Rao K L 1979Indian water wealth: Its assessment, uses and projections; Orient Longman, pp. 261.
Ray S B, Mohanti M and Somayajulu B L K 1984 Suspended matter, major cations and dissolved silicon in the estuarine waters of the Mahanadi river, India;J. Hydrol. 69 183–196.
Raymahashay B C 1986 Geochemistry of bicarbonate in river water;J. Geol. Soc. India 27 114–118.
Robie R A, Hemingway B S and Fisher J R 1978 Thermodynamic properties of minerals and related substances at 298.15 K and 1 Bar (105 Pascals) pressure and at higher temperatures;U.S. Geol. Surv. Bull. 1452 456.
Stallard R F and Edmond L M 1983 Geochemistry of the Amazon, 2: The influence of geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load;J. Geophys. Res. 88 9671–9688.
Subramanian V 1987 Environmental Geochemistry of Indian River basins -A review;J. Geol. Soc. India 29 205–220.
Tardy Y and Garrels R M 1974 A method for estimating the Gibbs energy of formation of layer silicates;Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 38 1101–1116.
Wolf R G 1967 X-ray and chemical study of weathering of glauconite;American Mineralogist. 52 1129–1138.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panigrahy, B.K., Raymahashay, B.C. River water quality in weathered limestone: A case study in upper Mahanadi basin, India. J Earth Syst Sci 114, 533–543 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702029
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702029