Abstract
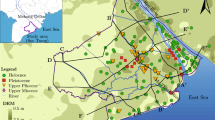
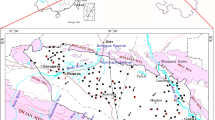
Hydrogeochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in a mid-western coastal aquifer system, Korea have been investigated to identify the salinization process. The spatial distributions of the groundwater components are well consistent with the groundwater flow pattern that follows topography in the study area. The groundwater at many locations in the study area is not suitable for drinking water because of its high salinity, which is mainly caused by seawater intrusion. The chemical composition of the groundwater is characterized by high chloride concentration and high variations in cation concentrations due to the cation exchange reaction between aquifer minerals and seawater components. The similar distributions of chemical components between rainy and dry seasons suggest that the groundwater flow system is almost in a steady state condition. The groundwater is classified into Ca(HCO3)2, CaCl2, and NaCl types based on its hydrogeochemical characteristics. The groundwater from the alluvial aquifer shows higher salinity in the rainy season than the dry season while the groundwater in the bedrock aquifer shows lower salinity year-round. Isotope data and factor analysis also indicate that the hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater are not only influenced by seawater intrusion but also by agricultural activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelo, C.A.J. and Postma, D., 1993, Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution. Balkema, Rotterdam, 519 p.
Appelo, C.A.J., 1996, Multicomponent ion exchange and chromatography in natural systems. Reviews in Mineralogy, 34, 193–227.
Choi, S.H. and Kim, Y.K., 1989, Geochemical characteristics of groundwater in Cheju Island. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 25, 230–238. (in Korean)
Choi, S.H., Kim, Y.K. and Lee, D.Y., 1991, Sea water intrusion in the coastal area of Cheju Vocanic Island, Korea. The Journal of the Korean Institute of Mining Geology, 24, 319–327.
Davis, J.C., 1986, Statistics and data analysis in geology. New York, John Wiley & Sons, 550 p.
Dazy, J., Drogue, C., Charmanidis, Ph. and Darlet, Ch., 1997, The influence of marine inflows on the chemical composition of groundwater in small islands: the example of the Cyclades (Greece). Environmental Geology, 31, 133–141.
Dixon, W. and Chiswell, B., 1992, The use of hydrochemical sections to identify recharge areas and saline intrusions in alluvial aquifers, outheast Queensland, Australia. Journal of Hydrology, 135, 259–274.
Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S. and Greenberg, A.E., 1995, Standard Methods for the Examitation of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed. AWWA, American Public Health Association, Washington.
Gimenez, E. and Morell, I., 1997, Hydrogeochemical analysis of salinization processes in the coastal aquifer of Oropesa (castellon, Spain), Environmental Geology, 29, 118–131.
Lee, S.B., Kim, K.Y., Han, S.R. and Hahn, J.S., 1997, The study on the increased causes of chloride(Cl−) concentration of the Samyan 3rd pumping station in Cheju Island. Journal of the Korea Society of Groundwater Environment, 4, 85–94. (in Korean)
Magaritz, M. and Luzier, J.E., 1985, Water-rock interactions and seawater-freshwater mixing effects in the coastal dune aquifer, Coos Bay, Oregon. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 49, 2515–2525.
Mercado, A., 1985, The use of hydrogeochemical patterns in carbonate sand and sandstone aquifers to identify intrusion and flushing of saline waters. Ground Water, 23, 635–645.
Nadler, A., Magaritz, M. and Mazar, E., 1981, Chemical reactions of seawater with rocks and freshwater-experimental and field observations on brackish waters in Israel. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 44, 879–886.
Plummer, L.N., Prestemon, E.C. and Parkhurst, D.I. 1994, An Interactive Code (NETPATH) for Modeling NET Geochemical Reactions along a Flow PATH, version 2.0. Water-Resources Investigations Report 94-4169, U.S. Geological Survey, 130 p.
Richter, B.C. and Kreitler, C.W., 1993, Geochemical Techniques for Identifying Sources of Ground-Water Salinization. CRC Press, 258 p.
Stoessell, R.K., 1997, Delineating the chemical composition of the salinity source for the saline ground waters: an example from East-Central Concordia Parish, Louisiana. Ground Water, 35, 409–417.
Sukhija, B.S., Varma, V.N., Nagabhushanam, P. and Reddy, D.V., 1996, Differentiation of paleomarine and modern seawater intruded salinities in coastal groundwaters (of Karaikal and Tanjavur, India) based on inorganic chemistry, organic biomarker fingerprints and radiocarbon dating. Journal of Hydrology, 174, 173–201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeen, SW., Kim, JM., Ko, KS. et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in a mid-western coastal aquifer system, Korea. Geosci J 5, 339–348 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912705
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912705