Abstract
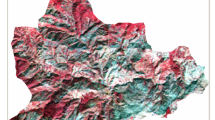
Visual interpretation of IRS ID LISS-III fused with PAN data (1:12,500 scale) ofPatloinala micro-watershed of Puruliya district, West Bengal was carried out for delineating the physiographic units based on the variations in image characteristics. The major physiographic units identified were upland(Tanr), medium land(Baid), and low land(Bahal andKanali). The satellite remote sensing data coupled with ground truth were translated in terms of soils using composite interpretation map as base. The abstraction level attained was phases of soil series based on Soil Taxonomy. On the basis of physiographic variation and soil or soil site characteristics such as texture, depth, slope, erosion etc. the problem areas were identified and land use plan has been suggested for the overall development of the micro-watershed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AIS & LUS (1970). Soil Survey Manual. All India Survey Organization, I.A.R.I., New Delhi.
Black, C.A. (Ed.) (1965). Methods of Soil Analysis. Am. Soc. Agron: Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A.
FAO (1976). A frame work for land evaluation. FAO Soil Bulletin, 32 Food and Agriculture Organization, United Nations, Rome, Italy.
Jackson, M.L. (1967). Soil Chemical Analysis, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.
Karale, R.L., Seshagiri Rao, K.V. and Singh, A.N. (1978). Evaluation of Landsat Imagery for Reconnaissance Soil Mapping, presented at A.P. Appreciation Seminar, New Delhi, October, 1978.
Klingebiel, A.A. and Montgomery, P.H. (1961). Land Capability Classification. USDA Hand Book, 210. Soil Conservation Service, USDA, Washington, 21p.
Rao, B.R.M., Ravishankar, T., Sujatha, S., Venkatratram, L., Fyzee, M.A. and Thammappa, S.S. (1997). Watershed development plan for sustainable development in tribal areas of Andhra Pradesh -A GIS Approach. Proceedings of the ISRS Symposium held at Pune during November 1997. In Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, pp. 466-474.
Sehgal, J.L., Sharma, P.K. and Karale, R.L. (1988). Soil Resource Inventory of Punjab using Remote Sensing Technique.J. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, 16(3): 39–47.
Soil Survey Staff (1998). ‘Keys to Soil Taxonomy’. Eighth Edition (USDA: Washington, DC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, D., Gangopadhyay, S.K. & Sahoo, A.K. Soil resource appraisal towards land use planning using satellite remote sensing and gis a case study in patloinala micro-watershed, district puruliya, west bengal. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 34, 245–260 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990653
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990653