Abstract
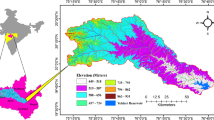
The process of urbanization has induced rapid changes in the land use leading to many infrastructural and environmental problems, one of them being the frequent flooding during rains in major cities across the world. Present paper analyses the spatio-temporal variations in the urban land use of the Mithi river catchment in Mumbai and its effect on the river, its drainage and flooding events in catchment area, specifically in conjunction with the July 26, 2005 flood event in Mumbai City. Multi sensor satellite data and GIS techniques have been used to generate land use/land cover at three different points of time and study variations in the Mithi river course, thus correlating the land use/cover changes vis-a-vis the hydrographic and meteorologic information for the Mithi river catchment. Results point to the adverse human-induced influences on the Mithi river and its catchment. Almost 50% reduction in river width and 70% decrease in mudlfats and open spaces have been observed. There is also a clear rise in builtup from 29% to 70% between 1966 and 2005, thus increasing the impervious surface which in turn increases run-off during major rainfall, eventually flooding the city.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clapham, W.B. Jr. (2003). Continuum-based classification of remotely sensed imagery to describe urban sprawl on a watershed scale.Remote Sensing of Environment,86(3): 322–340.
Dobosiewicz, J. (2001). Applications of DEM and GIS to coastal flood studies along the Shoreline of Raritan Bay, New Jersey.Environmental Geosciences,8(1): 11–20.
Gupta, Kapil (2002). Sewer System operation in the Metropolitan Cities of India. International Conference on Sewer Operation and Maintenance, held at University of Bradford, UK from November 26–28, 2002.
India Today, Mumbai’s Collapse, 08 August, 2005, 18–24pp.
India Today, Troubled Course, 19 December, 2005, 56–58pp.
Maingi, J.K. and Marsh, S.E. (2001). Assessment of environmental impacts of river basin development on the riverine forests of eastern Kenya using multi-temporal satellite data.International J. of Remote Sensing,22(14): 2701–2729.
MOEF/GOI No. S.O.114 (E) dated 19 February, 1991. Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (2004). Environment Status of Brihanmumbai 2003–2004, Scientific note:
Neelakantan, K. (2005). Urban Land use/cover change analysis of Greater Mumbai and its environs using Remote sensing and GIS techniques. Scientific note: NRSA-RS&GISAA-LU&USG-USD-1144-05/2005, National Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderabad.
Prasad, A.K. and Singh, R.P. (2005). Extreme rainfall event of July 25–27, 2005 over Mumbai, West Coast, India.J. of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,33(3): 365–370.
Raghavswamy, V. and Gautam, N.C. (1987). Mapping and monitoring of Land transformation changes due to Urban Sprawl in Lower Mahim Basin of Central Bombay using multi date Satellite data. Proceedings of National Symposium on Remote Sensing in Land Transformation and Management, held by ISRS on December 21-23, 1987, pp.151–156.
Rembold, F., Carnicelli, S., Nori, M. and Ferrari, A.G. (2000). Use of aerial photographs, Landsat TM imagery and multidisciplinary field survey for land-cover change analysis in the lakes region (Ethiopia).International J. of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2(3–4): 181–89.
Reynard, N.S., Prudhomme, C. and Crooks, S.M. (2001). The Flood Characteristics of Large U.K. rivers: Potential Effects of changing Climate and Land use.Climatic Change,48(2–3): 343–359.
Sala, M. (2003). Floods triggered by Natural conditions and by Human activities in a Mediterranean Coastal Environment.Geografiska Annaler: Series A, Physical Geography,85(3–4): 301–312.
Sharma, T., Satya Kiran., Singh, T.P., Trivedi, A.V. and Navalgund, R.R. (2001) Hydrologic response of a watershed to land use changes: a remote sensing and GIS approach.International J. of Remote Sensing,22(11): 2095–2108.
Sharma, V.K. and Priya, T. (2001). Development strategies for flood prone areas, case study: Patna, India.Disaster Prevention and Management: An International J.,10(2): 101–110.
Skilodimou, H., Livaditis, G., Bathrellos, G. and Papaspiridakou, E. (2003). Investigating the flooding events of the urban regions of Glyfada and Voula, Attica, Greece: A contribution to Urban Geomorphology.Geografiska Annaler: Series A, Physical Geography,85(2): 197–204.
Xian, George and Crane, Mike (2005). Assessments of urban growth in the Tampa Bay watershed using remote sensing data.Remote Sensing of Environment,97(2): 203–215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kamini, J., Jayanthi, S.C. & Raghavswamy, V. Spatio-temporal analysis of land use in urban mumbai -using multi-sensor satellite data and gis techniques. Journ. Ind. Soc. Remote Sensing 34, 385–396 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990923
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990923