Abstract
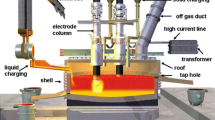
Aluminum baths are always covered with a layer of dross resulting from the aluminum surface oxidation. This dross represents 1–10% of the melt and may contain up to 75wt.% aluminum. Since aluminum production is highly energy intensive, dross recycling is very attractive from both energy and economic standpoints. The conventional recycling process using salt rotary furnaces is thermally inefficient and environmentally unacceptable because of the production of salt slags. Hydro-Quebec has developed a new technology using a rotary arc furnace with graphite electrodes. This process provides aluminum recovery rates of 80–90%, using a highly energy efficient, environmentally sound production method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Lavoie, C. Dubé, and G. Dubé, “The Plasma Dross Treatment Process,” Light Metals 1991 (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1991), pp. 981–985.
M.G. Drouet, “Use of a Radiating Arc Furnace for Treating a Dross Containing a Metal in Order to Recover this Metal,” U.S. patent.5.245.627 Washington (14 September 1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drouet, M.G., Handfield, M., Meunier, J. et al. Dross treatment in a rotary arc furnace with graphite electrodes. JOM 46, 26–27 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03220691
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03220691