Abstract
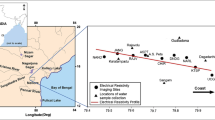
Seawater intrusion is a major problem in urbanized coastal regions of India which is due to over exploitation of groundwater for various purposes. This study was carried out with the objective of assessing the zone of mixing between seawater and groundwater in the coastal aquifer in south of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India using high resolution electrical resistivity tomography. High resolution electrical resistivity tomography was carried out in five profiles perpendicular to the sea using IRIS make SYSCAL Pro-96 system with 2.5 m or 5 m inter-electrode separation. The maximum length of the profile was 170 m which resulted in a depth of investigation of 28.7 m. The apparent resistivity measured in this area varies from 0.3 ohm-m to 30,000 ohm-m. The apparent resistivity of saturated zone decreases towards the sea, indicating the influence of seawater. This was also confirmed by measuring the electrical conductivity of groundwater, which gradually increases from 156 μS/cm to 3430 μS/cm towards the sea. Further, the concentration profiles of electrical conductivity, sodium, chloride and chloride / bicarbonate ratio are compared with the high resolution electrical resistivity tomography profile. The distance of influence of seawater is comparatively high in northern part than in southern part of the area. The high resolution electrical resistivity tomography was effectively used to determine the effect of seawater mixing with groundwater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apello, C. A. J.; Willemsen, A., (1987). Geochemical calculations and observations on saltwater intrusions, a combined geochemical and mixing cell model. J. Hydrol., 94(3–4), 313–330 (18 pages).
APHA; AWWA; WEF, (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 20th. Ed. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and the Water Environment Federation. Washington DC., USA.
Aris, A. Z.; Abdullah, M. H.; Ahmed, A.; Woong, K. K., (2007). Controlling factors of groundwater hydrochemistry in a small island’s aquifer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(4), 441–450 (20 pages).
Bakker, M., (2000). Simple groundwater flow models for seawater intrusion. Proceedings of SWIM16, Wolin Island, Poland.
Calvache, M. L.; Duque, C.; Gomez Fontalva, J. M.; Crespo, F. (2011). Processes affecting groundwater temperature patterns in a coastal aquifer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 8(2), 223–236 (14 pages).
Chenini, I.; Khemiri, S., (2009). Evaluation of ground water quality using multiple linear regression and structural equation modeling. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(3), 509–519 (11 pages).
Chien, M. K.; Shih, L. H., (2007). An empirical study of the implementation of green supply chain management practices in the electrical and electronic industry and their relation to organizational performances. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(3), 383–394 (12 Pages).
Choudhury, K.; Saha, D. K.; Chakraborty, P., (2001). Geophysical study for saline water intrusion in a coastal alluvial terrain. J. Appl. Geophys., 46(3), 189–200 (12 pages).
Cimino, A.; Cosentino, C.; Oieni, A.; Tranchina, L., (2008). A geophysical and geochemical approach for seawater intrusion assessment in the Acquedolci coastal aquifer (Northern Sicily). Environ. Geol., 55(7), 1473–1482 (10 pages).
Dahlin, T., (1996). Resistivity surveying for environmental and engineering applications. First Break, 14(7), 275–284 (10 pages).
Di Sipio, E.; Galgaro, A.; Zuppi, G. M., (2006). New geophysical knowledge of groundwater systems in Venice estuarine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 66(1–2), 6–12 (7 pages).
Ebraheem, A. M.; Hamburge, M. W.; Bayless, E. R.; Krothe, N. C., (1990). A study of acid mine drainage using earth resistivity measurements. Groundwater, 28(3), 361–368 (8 pages).
Ebraheem, A. M.; Senosy, M. M., Dahab, K. A., (1997). Geoelectrical and hydrogeo-chemical studies for delineating groundwater contamination due to salt-water intrusion in the northern part of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Groundwater, 35(2), 216–222 (7 pages).
Ehirim, C. N.; Ofor, W., (2010). Assessing aquifer vulnerability to contaminants near solid waste landfill sites in a coastal environment, port harcourt, Nigeria. Trends. Appl. Sci. Res., 6(2), 165–173 (9 pages).
Frohlich, R. K.; Urish, D. W.; Fuller, J.; Reilley, M. O., (1994). Use of geoelectrical method in groundwater pollution surveys in a coastal environment. J. Appl. Geophys., 32(2–3), 139–154 (16 pages).
Gallardo, A. H.; Marui, A., (2007). Modeling the dynamics of the freshwater-seawater interface in response to construction activities at a coastal site. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(3), 285–294 (10 pages).
Gnanasundar. D.; Elango, L., (1998). Groundwater quality of a coastal urban aquifer. Indian J. Environ. Protect., 18(10), 752–757 (6 pages).
Gnanasundar. D.; Elango, L., (1999). Groundwater quality assessment of a coastal aquifer using geoelectrical techniques. Int. J. Environ. Hydrol., 7(2), 21–33 (13 pages).
Griffiths, D. H.; Barker, R. D., (1993). Two-dimensional resistivity, imaging and modeling in areas of complex geology. J. Appl. Geophysics, 29(3–4), 211–226 (16 pages).
Griffith, D. H.; Turnbull, J., (1985). A multi-electrode array for resistivity surveying. First Break, 3(7), 16–20 (5 pages).
Griffiths, D. H.; Turnbull, J.; Olayinka, A. I.; (1990). Two-dimensional resistivity mapping with a computer-controlled array. First Break, 8(4), 121–129 (9 pages).
Ibrahim, A. N.; Harith, Z. Z. T.; Nawawi, M. N. M., (2003). Resistivity imaging and borehole investigation of the Banting area aquifer, Shelangor, Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Hydrol., 11(10), 1–7 (7 pages).
Koefoed, O., (1979). Geosounding Principles 1, resistivity sounding measurements (methods in geochemistry and geophysics 1 4A), Asterdam. Elsevier.
Loke, M. H.; Barker R. D., (1995). Least-squares disconvolution of apparent resistivity pseudo-sections. Geophysics, 60(6), 1682–1690 (9 pages).
Loke, M. H,; Barker, R. D., (1996). Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosecions by a quasi-newton method. Geophysic. Prospect., 44(1), 131–152 (22 pages).
Loke, M. H.; Wilkinson, P. B.; Chambers, J. E., (2010). Fast computation of optimized electrode arrays for 2D resistivity surveys. J. Comput. Geosci., 36(11), 1414–1426 (13 pages).
Martinez, J.; Benavente, J.; Garcia-Arostegui, J. L.; Hidalgo, M. C.; Rey, J., (2009). Contribution of electrical resistivity tomography to the study of detrital aquifers affected by seawater intrusion-extrusion effects: The rivel Velez delta (Velez-Malaga, southern Spain). Engin. Geol., 108(3–4), 161–168 (8 pages).
Melloul, A. J.; Goldenberg, L. C., (1997). Monitoring of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: basic and local concerns. J. Environ. Manage., 51(1), 73–86 (14 pages).
Nouri, J.; Danehkar, A.; Sharifipour, R. (2008). Evaluation of ecotourism potential in the northern coastline of the Persian Gulf. Environ. Geo., 55(3), 681–686 (6 pages).
Nowroozi, A. A.; Stephen, B. H.; Henderson, P., (1999). Saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer in the eastern shore of Virginia: A reconnaissance electrical resistivity survey. J. Appl. Geophys., 42(1), 1–22 (22 pages).
Praveena, S. M.; Aris, A. Z., (2010). Groundwater resources assessment using numerical model: A case study in low-lying coastal area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(1), 135–146 (12 pages).
Sasaki, Y., (1992). Resolution of resistivity tomography inferred from numerical simulation. Geophys. Prospect., 40(4), 453–464 (11 pages).
Senthil Kumar, M.; Gnanasundar, D.; Elango, L., (2001). Geophysical studies in determining hydraulic characteristics of an alluvial aquifer. J. Environ. Hydrol., 9(15), 1–8 (8 pages).
Shammas, M. I.; Jacks, G., (2007). Seawater intrusion in the Salalah plain aquifer. Oman. Environ. Geol., 53(3), 575–587 (13 pages).
Todd, D. K., (1959). Groundwater Hydrology, p. 293. John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York.
Urish, D. W.; Frohlich, R. K., (1990). Surface electrical resistivity in coastal groundwater exploration. Geoexploration, 26(4), 267–289 (23 pages).
Yechieli, Y.; Sivan, O., (2008). Chemical and isotopic evidences for seawater intrusion-Examples from the coastal aquifers of the Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. Proceedings of 20th. salt water intrusion meeting, Naples, Florida, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sathish, S., Elango, L., Rajesh, R. et al. Assessment of seawater mixing in a coastal aquifer by high resolution electrical resistivity tomography. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 8, 483–492 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326234
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326234