Abstract
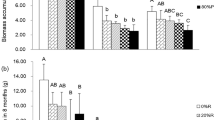
Revegetation was studied on stockpiled serpentine substrate. The native vegetation surrounding the revegetation site is annual grassland. The seed mixture applied to both subsoil and topsoil plots was largely ineffective for revegetation. No growth occurred in the subsoil plots and most of the growth in the topsoil plots was from indigenous seed. Phosphate application (100 kg P ha−1 as NaH2PO4 · H2O) to the topsoil plots resulted in a significant increase in total above-ground productivity. Annual legumes (mostlyLotus subpinnatus Lag.) and, to a lesser degree,Plantago erecta Morris responded to the added phosphate with an increased above-ground productivity. Other annual forbs and annual grasses showed no significant response. The legumes also increased in abundance. Mycorrhizal root colonization forPlantago was not significantly affected by phosphate application, but was lower in this disturbed serpentine site compared to other undisturbed serpentine annual grassland sites nearby.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Chapin, III, F. S., P. M. Vitousek, and K. van Cleve. 1986. The nature of nutrient limitation in plant communities.American Naturalist 127:48–58.
Chew, V. 1976. Comparing treatment means: a compendium.HortScience 11:348–357.
Crush, J. R. 1974. Plant regrowth responses to vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza. VII. Growth and nodulation of some herbage legumes.New Phytologist 73:743–749.
Gildon, A., and P. B. Tinker. 1983. Interactions of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection and heavy metals in plants. I. The effects of heavy metals on the development of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas.New Phytologist 95:247–261.
Hall, I. R. 1978. Effects of endomycorrhizas on the competitive ability of white clover.New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research 21:509–515.
Hobbs, R. J., and H. A. Mooney. 1985. Community and population dynamics of serpentine grassland annuals in relation to gopher disturbance.Oecologia (Berlin) 67:342–351.
Jones, M. B., and R. G. Woodmansee. 1979. Biogeochemical cycling in annual grassland ecosystems.Botanical Review 45:111–144.
Koide, R. 1985. The nature of growth depressions in sunflower caused by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection.New Phytologist 99:449–462.
Kruckeberg, A. R. 1954. The ecology of serpentine soils. III. Plant species in relation to serpentine soils.Ecology 35:267–274.
Kruckeberg, A. R. 1969. Soil diversity and the distribution of plants, with examples from western North America.Madrono 20:129–154.
Lambert, D. H., and H. Cole, Jr. 1980. Effects of mycorrhizae on establishment and performance of forage species in mine spoil.Agronomy Journal 72:257–260.
McNaughton, S. J. 1968. Structure and function in California grasslands.Ecology 49:962–972.
Miller, R. M. 1979. Some occurrences of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza in natural and disturbed ecosystems of the Red Desert.Canadian Journal of Botany 57:619–623.
Munz, P. A., and D. D. Keck. 1959. A California flora. University of California Press, Los Angeles.
Nielsen, J. D., and A. Jensen. 1983. Influence of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and uptake of various nutrients as well as uptake ratio of fertilizer P for lucerne (Medicago sativa).Plant and Soil 70:165–172.
Plenchette, C., J. A. Fortin, and V. Furlan. 1983. Growth responses of several plant species to mycorrhizae in a soil of moderate P-fertility. I. Mycorrhizal dependency under field conditions.Plant and Soil 70:199–209.
Powell, C. 1976. Mycorrhizal fungi stimulate clover growth in New Zealand hill country soils.Nature 264:436–438.
Reeves, F. B., D. Wagner, T. Moorman, and J. Kiel. 1979. The role of endomycorrhizae in revegetation practices in the semi-arid west. I. A comparison of incidence of mycorrhizae in severely disturbed vs. natural environments.American Journal of Botany 66:6–13.
Ross, J. P. 1971. Effect of phosphate fertilization on yield of mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal soybeans.Phytopathology 61:1400–1403.
Singh, O. S., and R. S. Singh. 1986. Effects of phosphorus andGlomus fasciculatus inoculation on nitrogen fixation, P uptake and yield of Lentil (Lens culinaris Medic) grown on an unsterilized sandy soil.Environmental and Experimental Botany 26:185–190.
Sokal, R. R., and F. J. Rohlf. 1981. Biometry, 2nd edn. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York.
Turitzin, S. N. 1982. Nutrient limitations to plant growth in a California serpentine grassland.American Midland Naturalist 107:95–99.
Van Schreven, D. A. 1958. Some factors affecting the uptake of nitrogen by legumes. In: Hallsworth, E. G. (ed.), Nutrition of legumes. Butterworths, London, p. 137.
Walker, R. B. 1954. The ecology of serpentine soils. II. Factors affecting plant growth on serpentine soils.Ecology 35:259–266.
Watanabe, F. S., and S. R. Olsen. 1965. Test of an ascorbic acid method for determining phosphorus in water and NaHCO3 extracts from soil.Proceedings of the Soil Science Society of America 26:677–678.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koide, R.T., Mooney, H.A. Revegetation of serpentine substrates: Response to phosphate application. Environmental Management 11, 563–567 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01867662
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01867662