Abstract
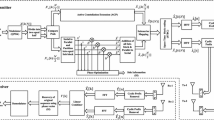
Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) modeling through the use of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) offers a viable alternative to reduce bandwidth and simultaneously improves the quality of service of wireless mobile communication. One of the major concerns in the MIMO-OFDM system is the high peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR). In this article, a combinational scheme, active partial sequence (APS), is proposed to combat PAPR in MIMO-OFDM under Rayleigh fading environment. The key idea of the APS method is to combine the approximate gradient project followed by partial transmit sequence technique. The simulation results show that the proposed method achieves a significant reduction in PAPR and maintains the same data rate without sacrificing the BER performance over other conventional techniques.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.M. Alamouti, A simple transmit diversity technique for wireless communications. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 16, 1451–1458 (1998)
J. Armstrong, Peak-to-average power reduction for OFDM by repeated clipping and frequency domain filtering. IEEE Electron. Lett. 38(8), 246–247 (2002)
R.W. Bäuml, R.F.H. Fischer, J.B. Huber, Reducing the peak-to-average power ratio of multicarrier modulation by selected mapping. IEEE Electron. Lett. 32(22), 2056–2057 (1996)
J.C. Chen, C.P. Li, Tone reservation using near-optimal peak reduction tone set selection algorithm for PAPR reduction in OFDM systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(11), 933–936 (2010)
Y.S. Cho, J. Kim, W.Y. Yang, C.G. Kang, MIMO-OFDM Wireless Communications with MATLAB (John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pte Ltd, 2010)
L.J. Cimini Jr, N.R. Sollenberger, Peak-to-average power ratio reduction of an OFDM signal using partial transmit sequences. IEEE Commun. Lett. 4(3), 86–88 (2000)
P.V. Eetvelt, G. Wade, M. Tomlinson, Peak to average power reduction for OFDM schemes by selective scrambling. IEEE Electron. Lett. 32(21), 1963–1964 (1996)
Y. Jabrane, V.P.G. Jimenez, A.G. Armeda, B.E. Said, A.A. Ouahman, Reduction of power envelope fluctuations in OFDM signals by using neural networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 14(7), 599–601 (2010)
T. Jiang, C. Ni, L. Gaun, A novel phase offset SLM scheme for PAPR reduction in Alamouti MIMO-OFDM systems without side information. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 20(4), 383–386 (2013)
T. Jiang, Y.W. Wu, An overview: peak to average power ratio reduction techniques for OFDM signals. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 54(2), 257–268 (2008)
D. Jones, Peak power reduction in OFDM and DMT via active constellation extension, in Proceedings Asliomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, vol. 2 (1999), pp. 1076–1079
B.S. Krongold, D.L. Jones, PAR reduction in OFDM via active constellation extension. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 49(3), 258–268 (2003)
C.M. Li, Y.Y. Cheng, A low complexity partition dummy sequence insertion PAPR reduction method for the OFDM system. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 68(3), 949–961 (2013)
X. Li, L.J. Cimini Jr, Effects of clipping and filtering on the performance of OFDM. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2(5), 131–133 (1998)
D.-W. Lim, S.-J. Heo, J.-S. No, An overview of peak-to-average power ratio reduction schemes for OFDM signals. J. Commun. Netw. 11(3), 229–239 (2009)
A. Mishra, R. Saxena, M. Patidar, OFDM link with a better performance using artificial neural network. Wirel. Pers. Commun. (2014). doi:10.1007/s11277-013-1593-y
M.F. Naeiny, F. Marvasti, Selected mapping algorithm for PAPR reduction of frequency coded OFDM systems without side information. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 60(3), 1211–1216 (2011)
R.O. Neill, L.B. Lopes, Envelope variations and spectral in clipped multicarrier signals, in Proceedings IEEE PIMRC, Toronto, Canada, vol. 95 (1995), pp. 71–75
K. Patterson, Generalized Reed–Muller codes and power control in OFDM modulation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 46(6), 104–120 (2000)
C. Tellambura, Improved phase factor computation for the PAR reduction of an OFDM signal using PTS. IEEE Commun. Lett. 5(4), 135–137 (2001)
J. Tellado, Peak power reduction for multicarrier transmission, PhD thesis, University of Stanford, Stanford (1999)
S.H. Wang, C.P. Li, A low complexity PAPR reduction scheme for SFBC MIMO-OFDM systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 16(10), 941–944 (2009)
Y. Wang, J. Ge, L. Wang, J. Li, Reduction of PAPR of OFDM signals using nonlinear companding transform. Wirel. Pers. Commun. (2012). doi:10.1007/s11277-012-0820-2
C.E. Weng, C.W. Chang, C.H. Chen, H.L. Hung, Novel low-complexity partial transmit sequences scheme for PAPR reduction in OFDM systems using adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Wirel. Pers. Commun. (2012). doi:10.1007/s11277-012-0836-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pachori, K., Mishra, A. PAPR Reduction in MIMO-OFDM by Using Active Partial Sequence. Circuits Syst Signal Process 34, 3999–4010 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-015-0039-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-015-0039-z