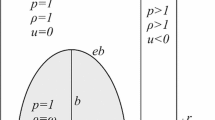
Abstract
The interaction of a planar shock wave with a spherical density inhomogeneity is studied experimentally under reshock conditions. Reshock occurs when the incident shock wave, which has already accelerated the spherical bubble, reflects off the tube end wall and reaccelerates the inhomogeneity for a second time. These experiments are performed at the Wisconsin Shock Tube Laboratory, in a 9m-long vertical shock tube with a large square cross section (25.4×25.4 cm2). The bubble is prepared on a pneumatically retracted injector and released into a state of free fall. Planar diagnostic methods are used to study the bubble morphology after reshock. Data are presented for experiments involving two Atwood numbers (A = 0.17 and 0.68) and three Mach numbers (1.35 < M < 2.33). For the low Atwood number case, a secondary vortex ring appears immediately after reshock which is not observed for the larger Atwood number. The post-reshock vortex velocity is shown to be proportional to the incident Mach number, M, the initial Atwood number, A, and the incident shock wave speed, W i.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Richtmyer R.D.: Taylor instability in shock acceleration of compressible fluids. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 12, 1–3 (1984)
Lindl J.: Development of the indirect-drive approach to inertial confinement fusion and the target physics basis for ignition and gain. Phys. Plasmas 2, 3933–4024 (1995)
Klein R.I., Budil K.S., Perry T.S., Bach D.R.: Interaction of supernova remnants with interstellar clouds: from the NOVA laser to the galaxy. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 127, 379–383 (2000)
Yang J., Kubota T., Zukoski E.E.: A model for characterization of a vortex pair formed by shock passage over a light-gas inhomogeneity. J. Fluid Mech. 258, 217–244 (1994)
Delius M., Ueberle F., Eisenmenger W.: Extracorporeal shock waves act by shock wave-gas bubble interaction. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 24, 1055–1059 (1998)
Taylor G.I.: The instability of liquid surfaces when accelerated in a direction perpendicular to their planes. I. Proc. R. Soc. A 201, 192–196 (1950)
Ranjan D., Niederhaus J., Motl B., Anderson M., Oakley J., Bonazza R.: Experimental investigation of primary and secondary features in high-mach-number shock–bubble interaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 024502 (2007)
Ranjan, D.: Experimental investigation of the shock-induced distortion of a spherical gas inhomogeneity. PhD thesis, University of Wisconsin-Madison (2008)
Rudinger G., Somers L.M.: Behaviour of small regions of different gases carried in accelerated gas flows. J. Fluid Mech. 7, 161–176 (1960)
Haas J.F., Sturtevant B.: Interaction of weak shock waves with cylindrical and spherical gas inhomogeneities. J. Fluid Mech. 181, 41–76 (1987)
Layes G., Jourdan G., Houas L.: Experimental investigation of the shock wave interaction with a spherical gas inhomogeneity. Phys. Fluids 17, 028103 (2005)
Layes G., LeMetayer O.: Quantitative numerical and experimental studies of the shock accelerated heterogeneous bubbles motion. Phys. Fluids 19, 042105 (2007)
Layes G., Jourdan L., Houas L.: Experimental study on a plane shock wave accelerating a gas bubble. Phys. Fluids 21, 074102 (2009)
Ranjan D., Anderson M.H., Oakley J.G., Bonazza R.: Experimental investigation of a strongly shocked gas bubble. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 184507 (2005)
Brouillette M., Sturtevant B.: Experiments on the Richtmyer–Meshkov instability: small-scale perturbations on a plane interface. Phys. Fluids A 5, 916–930 (1993)
Kelvin L.: The translatory velocity of a circular vortex ring. Philos. Mag. 33, 511–512 (1867)
Haehn N., Weber C., Oakley J., Anderson M., Ranjan D., Bonazza R.: Experimental investigation of a twice-shocked spherical gas inhomogeneity with particle image velocimetry. Shock Waves 21, 225–231 (2011)
Haehn N., Ranjan D., Weber C., Oakley J., Anderson M., Bonazza R.: Experimental investigation of a twice-shocked spherical density inhomogeneity. Phys. Scr. T 142, 014067 (2010)
Gharib M., Rambod E., Shariff K.: A universal time scale for vortex ring formation. J. Fluid Mech. 360, 121–140 (1998)
Shusser M., Gharib M.: Energy and velocity of a forming vortex ring. Phys. Fluids 12, 618–621 (2000)
Zabusky N.J., Zeng S.M.: Shock cavity implosion morphologies and vortical projectile generation in axisymmetric shock–spherical fast/slow bubble interactions. J. Fluid Mech. 362, 327–346 (1998)
Ranjan D., Oakley J., Bonazza R.: Shock–bubble interactions. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 43, 117–140 (2011)
Ranjan D., Niederhaus J., Oakley J., Anderson M., Bonazza R., Greenough J.: Shock–bubble interactions: features of divergent shock-refraction geometry observed in experiments and simulations. Phys. Fluids 20, 036101 (2008)
Ranjan D., Niederhaus J., Oakley J., Anderson M., Bonazza R., Greenough J.: Experimental and numerical investigation of shock-induced distortion of a spherical gas inhomogeneity. Phys. Scr. T 132, 014020 (2008)
Cohen R.D.: Shattering of a liquid drop due to impact. Proc. R Soc. Lond. A 435, 483–503 (1991)
Widnall S.E., Bliss D.B., Tsai C.Y.: The instability of short waves on a vortex ring. J. Fluid Mech. 66, 35–47 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Seiler.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haehn, N., Weber, C., Oakley, J. et al. Experimental study of the shock–bubble interaction with reshock. Shock Waves 22, 47–56 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-011-0345-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-011-0345-8