Abstract.
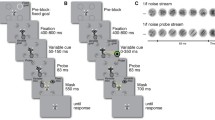
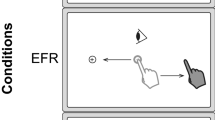
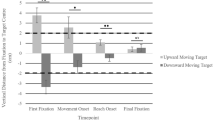
It has been suggested that the basal ganglia preferentially contribute to movements made to remembered targets, whereas the cerebellum preferentially contributes to movements based on visual cues. Thus, it is possible that eye-hand coordination may differ in these two types of movement. To examine this issue we compared the response characteristics of combined eye and hand movements made towards visual versus remembered targets. In addition, the influence of the eye movement on the hand movement was investigated by comparing the effects of visual fixation in each task. Our results demonstrated that hand movement amplitude was greater when the hand movements were produced in isolation versus in combination with an eye movement. This was true regardless of whether the movement was made to a visual or a remembered target. This suggests that the integration of eye position information into the manual motor response occurs at a common neural site for both tasks. By contrast, the timing between saccade and hand onsets and offsets differed in the two conditions. This is consistent with the idea that the timing inherent in eye-hand coordination is the result of separate processing within either the basal ganglia or cerebellar systems. Taken together, the results from this study demonstrate that certain processes underlying eye-hand coordination during movements to visual versus remembered targets share a common neural substrate whereas others function independently.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Donkelaar, P., Staub, J. Eye-hand coordination to visual versus remembered targets. Exp Brain Res 133, 414–418 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000422
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000422