Abstract.
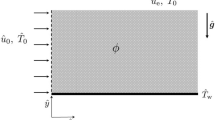
In this paper the steady free convection boundary-layer along a semi-infinite, slightly inclined (both positive and negative) to the horizontal plate embedded in a porous medium with the flow generated by Newtonian heating has been investigated. The asymptotic solution near the leading edge and the full numerical solution along the whole plate domain have been obtained numerically, whilst the asymptotic solution far downstream along the plate has been obtained analytically. For a positive inclination the full numerical solution is in agreement with the asymptotic solutions. However, for a negatively inclined plate, only the small asymptotic solution near the leading edge of the plate can be predicted giving an insight that the model for a negatively inclined plate, whilst mathematically interesting, is not physically realistic.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ingham DB; Merkin JH; Pop I (1985) Natural convection from a semi-infinite flat plate inclined at a small angle to the horizontal in a saturated porous medium. Acta Mechanica 57: 185–202
Rees DAS; Riley DS (1985) Free convection above a near horizontal semi-infinite heated surface embedded in a saturated porous medium. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 28: 183–190
Kumari M; Pop I; Nath G (1990) Natural convection in porous media above a near horizontal uniform heat flux surface. Warme – und Stoffubertr 25: 155–159
Pop I; Na T-Y (1996) Free convection on an arbitrarily inclined plate in a porous medium. Heat and Mass Transfer 32: 55–59
Weidman PD; Amberg MF (1996) Similarity solutions for steady laminar convection along heated plates with variable oblique suction: Newtonian and Darcian fluid flow. Q J Mech Appl Math 49: 373–403
Hossain MA; Pop I; Vafai K (1999) Combined heat and mass transfer in free convection above a near horizontal surface in a porous medium. Hybrid Methods in Engng 1: 87–102
Minto BJ; Ingham DB; Pop I (1998) Free convection driven by an exotermic reaction on a vertical surface embedded in porous media. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 41: 11–23
Mahmood T; Merkin JH (1998) The convective boundary-layer flow on a reacting surface in a porous medium. Transport in Porous Media 32: 285–298
Merkin JH; Mahmood T (1999) Convective flows on reactive surfaces in porous media. Transport in Porous Media 33: 279–293
Merkin JH; Pop I (2000) Free convection near a stagnation point in a porous medium resulting from an oscillatory wall temperature. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 43: 611–621
Merkin JH (1994) Natural-convection boundary-layer flow on a vertical surface with Newtonian heating. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 15: 392–398
Lesnic D; Ingham DB; Pop I (1999) Free convection boundary-layer flow along a vertical surface in a porous medium with Newtonian heating. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 42: 2621–2627
Lesnic D; Ingham DB; Pop I (2000) Free convection from a horizontal surface in a porous medium with Newtonian heating. J Porous Media 3: 227–235
Vaszi AZ; Ingham DB; Lesnic D; Munslow D; Pop I (2001) Conjugate free convection from a slightly inclined wall embedded in a porous medium. ZAMM 81: 465–479
Sparrow EM; Gregg JL (1958) Similar solutions for free convection from a non-isothermal vertical plate. Trans ASME 80: 379–386
Stewartson K (1957) On asymptotic expansions in the theory of boundary layers. J Math Phys 36: 173–191
Mahajan RL; Gebhart B (1978) Higher order approximations to natural convection flow over a uniform flux vertical surface. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 21: 549–556
Hunt R; Wilks G (1981) Continuous transformation computation of boundary layer equations between similarity regimes. J Comput Phys 40: 478–490
Merkin JH (1976) Free convection boundary layer on an isothermal horizontal cylinder. In ASME-AIChE Nat Heat Transfer Conf. Paper No. 76-HT-16 St.Louis, USA
Storr C (1999) Free convection darcian boundary layer flow originating from horizontal and inclined semi-infinite plates in a porous medium with Newtonian heating. MSc Thesis, CFD Centre, University of Leeds
Acknowledgements.
I. Pop gratefully acknowledges the support of this work by Alexander von Humboldt fellowship while he visited the Brandenburg Technical University of Cottbus, Germany. He also wishes to thank Prof. Dr. -Ing. Cristoph Egbers, Head of the Department of Aerodynamics and Fluid Mechanics of this University, for his kind hospitality. Both D.B.Ingham and I.Pop would like to thank the UK Royal Society for supporting some of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lesnic, D., Ingham, D.B., Pop, I. et al. Free convection boundary-layer flow above a nearly horizontal surface in a porous medium with newtonian heating. Heat and Mass Transfer 40, 665–672 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-003-0435-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-003-0435-y