Abstract
TiO2-coated surfaces are increasingly studied for their ability to inactivate microorganisms. The activity of glass coated with thin films of TiO2, CuO and hybrid CuO/TiO2 prepared by atmospheric Chemical Vapour Deposition (Ap-CVD) and TiO2 prepared by a sol–gel process was investigated using the inactivation of bacteriophage T4 as a model for inactivation of viruses. The chemical oxidising activity was also determined by measuring stearic acid oxidation. The results showed that the rate of inactivation of bacteriophage T4 increased with increasing chemical oxidising activity with the maximum rate obtained on highly active sol–gel preparations. However, these were delicate and easily damaged unlike the Ap-CVD coatings. Inactivation rates were highest on CuO and CuO/TiO2 which had the lowest chemical oxidising activities. The inactivation of T4 was higher than that of Escherichia coli on low activity surfaces. The combination of photocatalysis and toxicity of copper acted synergistically to inactivate bacteriophage T4 and retained some self-cleaning activity. The presence of phosphate ions slowed inactivation but NaCl had no effect. The results show that TiO2/CuO coated surfaces are highly antiviral and may have applications in the food and healthcare industries.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari SA, Sattar SA, Springthorpe S, Wells GA, Tostowaryk W (1988) Rotavirus survival on human hands and transfer to animate and non-porous inanimate surfaces. J Clin Microbiol 26:1513–1518
Ansari SA, Springthorpe S, Sattar SA, Rivard S, Rahman M (1991) Potential role of hands in the spread of respiratory viral infections: studies with human parainfluenza virus 3 and rhinovirus 14. J Clin Microbiol 29:2115–2119
Araña J, Herrera Melián JA, Doña Rodriguez JM, González Diaz O, Viera A, Pérez Peña J, Marrero Sosa PM, Espino Jiménez V (2002) TiO2-photocatalysis as a tertiary treatment of naturally treated wastewater. Catal Today 76:279–289
Armon R, Laot N, Narkis N, Neeman I (1998) Photocatalytic inactivation of different bacteria and bacteriophages in drinking water at different TiO2 concentration with or without exposure to O2. J Adv Oxid Technol 3:145–150
Aubry E, Ghazzal MN, Demange V, Chaoui N, Robert D, Billard A (2007) Poisoning prevention of TiO2 photocatalyst coatings sputtered on soda-lime glass by intercalation of SiNx diffusion barriers. Surf Coat Technol 201:7706–7712
Belhacova L, Krysa J, Geryk J, Jirkovsky J (1999) Inactivation of microorganisms in a flow through photoreactor with an immobilised TiO2 layer. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 74:149–154
Blake DM, Maness P-C, Huang Z, Wolfrum EJ, Jacoby WA, Huang J (1999) Application of the photocatalytic chemistry of titanium dioxide to disinfection and the killing of cancer cells. Sep Purif Methods 28:1–50
Cho M, Chung H, Choi W, Yoon J (2005) Different inactivation behaviours of ms-2 phage and Escherichia coli in TiO2 photocatalytic disinfection. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:270–275
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37 –38 (07 July 1972); DOI https://doi.org/10.1038/238037a0
Gogniat G, Thyssen M, Denis M, Pulgarin C, Dukan S (2006) The bactericidal effect of TiO2 photocatalysis involves adsorption onto catalyst and the loss of membrane integrity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 258(1):18–24
Gratia A (1936) Des relations numeriques entre bacteries lysogenes et particules de bacteriophage. Ann Inst Pasteur 57:652–676
Hashimoto K, Irie H, Fujishima A (2005) TiO2 photocatalysis: a historical overview and future prospects. Jpn J Appl Phys 44:8269–8285
Horie Y, Taya M, Tone S (1998a) Effect of cell adsorption on photosterilization of Escherichia coli over titanium-dioxide-activated charcoal granules. J Chem Eng Jpn 31:922–929
Horie Y, Taya M, Tone S (1998b) Evaluation of photocatalytic sterilisation rates of Escherichia coli in titanium dioxide slurry irradiated with various light sources. J Chem Eng Jpn 31:577–584
Jung S-C, Kim B-J, Imaishi N, Cho Y-I (2005) Characterisation of a TiO2 photocatalyst film deposited by CVD and its photocatalytic activity. Chem Vap Depos 11:137–141
Kakita Y, Kashige N, Miake F, Watanabe K (1997) Photocatalysis-dependent inactivation of Lactobacillus phage PL-1 by a ceramics preparation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:1947–1948
Kakita Y, Obuchi E, Nakano K, Murata K, Kuriowa A, Miake F, Watanabe K (2000) Photocatalytic inactivation of Lactobacillus PL-1 phages by a thin film of titania. Biocontrol Sci 5:73–79
Kashige N, Kakita Y, Nakashima Y, Miake F, Watanabe K (2001) Mechanism of the photocatalytic inactivation of Lactobacillus casei phage PL-1 by titania thin film. Curr Microbiol 42:184–189
Kikuchi Y, Sunada K, Iyoda T, Hashimoto K, Fujishima A (1997) Photocatalytic bactericidal effect of TiO2 thin films: dynamic view of the active oxygen species responsible for the effect. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 106:51–56
Kiwi J, Nadtochenko V (2005) Evidence for the mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of the bacterial wall membrane at the TiO2 interface by ATR-FTIR and laser kinetic spectroscopy. Langmuir 21:4631–4641
Koizumi Y, Taya M (2002) Photocatalytic inactivation rate of phage ms2 in titanium dioxide suspensions containing various ionic species. Biotechnol Lett 24:459–462
Kuhn KP, Chaberny IF, Massholder K, Stickler M, Benz VW, Sonntag H-G, Erdinger L (2003) Disinfection of surfaces by photocatalytic oxidation with titanium dioxide and UVA light. Chemosphere 53:71–77
Laot N, Narkis N, Neeman I, Vilanovic D, Armon R (1999) TiO2 Photocatalytic Inactivation of Selected microorganisms under various conditions: sunlight, intermittent and variable irradiation intensity, CdS augmentation and entrapment of TiO2 into sol gel. J Adv Oxid Technol 4:97
Lee S, Nishida K, Otaki M, Ohgaki S (1997) Photocatalytic inactivation of phage Qβ by immobilized titanium dioxide mediated photocatalyst. Water Sci Technol 35:101–106
Matsunaga T, Tomada R, Nakajima T, Wake H, (1985) Photoelectrochemical sterilization of microbial cells by semiconductor powders. FEMS Microbiol Lett 29:211–214
Mills A, Le Hunte S (1997) An overview of semiconductor photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 108:1–35
Mills A, Elliott N, Hill G, Fallis D, Durrant JR, Willis RL (2003a) Preparation and characterisation of novel thick sol–gel titania film photocatalysts. Photochem Photobiol Sci 2:591–596
Mills A, Hill G, Bhopal S, Parkin IP, O’Neill SA (2003b) Thick titanium dioxide films for semiconductor photocatalysis. Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 160:185–194
Otaki M, Hirata T, Oghaki S (2000) Aqueous microorganisms inactivation by photocatalytic reaction. Water Sci Technol 42:103–108
Sagripanti J-L (1992) Metal based formulations with high microbicidal activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3157–3162
Sagripanti J-L, Lightfoote MM (1996) Cupric and ferric ions inactivate HIV. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 12:333–336
Sagripanti J-L, Routson LB, Lytle CD (1993) Virus inactivation by copper or iron ions alone and in the presence of peroxide. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:4374–4376
Sagripanti J-L, Routson LB, Bonifacino AC, Lytle CD (1997) Mechanism of copper-mediated inactivation of herpes simplex virus. Antimicrob Agent Chemother 41:812–817
Sjogren JC, Sierka RA (1994) Inactivation of phage MS2 by iron-aided titanium dioxide photocatalysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:344–347
Sunada K, Watanabe T, Hashimoto K (2003) Bactericidal activity of copper-deposited TiO2 thin film under weak UV light illumination. Environ Sci Technol 37:4785–4789
Watts RJ, Kong S, Orr M, Miller GC, Henry BE (1995) Photocatalytic inactivation of coliform bacteria and viruses in secondary wastewater effluent. Water Res 29:95–100
Widdowson M-A, Glass R, Monroe S, Beard S, Bateman JW, Lurie P, Johnson C (2005) Probable transmission of norovirus on an airplane. JAMA 15:1859–1860
Yates HM, Nolan MG, Sheel DW, Pemble MEJ (2006) The role of nitrogen doping on the development of visible light-induced photocatalytic activity in thin TiO2 films grown on glass by chemical vapour deposition. Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 179:213
Yates HM, Brook LA, Ditta IB, Evans P, Foster HA, Sheel DW, Steele A (2008) Photo-induced self cleaning and biocidal behaviour of titania and copper oxide multilayers. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A. DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2007.12.023
Yu JC, Ho W, Lin J, Yip H, Wong PK (2003) Photocatalytic activity, antibacterial effect, and photoinduced hydrophilicity of TiO2 films coated on a stainless steel substrate. Environ Sci Technol 37:296–301
Acknowledgements
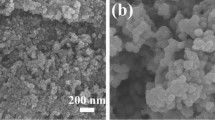
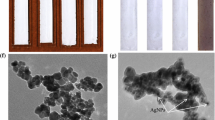
This work was supported by an EEC grant GRD1-2001-40791 “Advanced materials and manufacturing technologies for photocatalytically active surfaces”. We are grateful to Mr. Alan Robinson and Dr Mark Nolan for stearic acid oxidation data and to Professor Andrew Mills, University of Strathclyde for providing the sol–gel coated samples and M. Faulkner from University of Manchester Materials Science Centre for the scanning electron microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ditta, I.B., Steele, A., Liptrot, C. et al. Photocatalytic antimicrobial activity of thin surface films of TiO2, CuO and TiO2/CuO dual layers on Escherichia coli and bacteriophage T4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79, 127–133 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1411-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1411-8