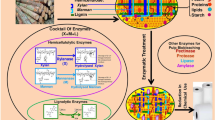
Abstract
The use of enzymes has a high potential in the pulp and paper industry to improve the economics of the paper production process and to achieve, at the same time, a reduced environmental impact. Specific enzymes contribute to reduce the amount of chemicals and energy required for the modification of fibers and helps to prevent the formation or development of biofilms. This review is aimed at presenting the latest progresses made in the application of enzymes as refining aids and biofilm control agents.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar M, Scott GM, Swaney RE, Shipley DF (2000) Biomechanical pulping a mill-scale evaluation. Resour Conserv Recycl 28:241–252
Bajpai P (1999) Application of enzymes in the pulp and paper industry. Biotechnol Prog 15:147–157
Bajpai P (2010) Solving the problems of recycled fiber processing with enzymes. Bioresour 5(2):1–15
Bhardwaj NK, Bajpai P, Bajpai PK (1996) Use of enzymes in modification of fibres for improved beatability. J Biotechnol 51(1):21–26
Blanco A (2003) Microbiology in papermaking. Recent Res Dev Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 1:187–134
Blanco A, Negro C, Gaspar I, Tijero J (1996) Slime problems in the paper and board industry. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46:203–208
Blanco A, Negro C, Díaz L, Saarimaa V, Sundberg A, Holmbom B (2009) Influence of thermostable lipase treatment of thermomechanical pulp (TMP) on extractives and paper properties. Appita J 62(2):113–117
Blanco A, Torres CE, Fuente E, Negro C (2011) New tool to monitor biofilm growth in industrial process waters. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:5766–5773
Blomstedt MM, Asikainen J, Lähdeniemi A, Ylönen T, Paltakari J, Hakala T (2010) Effect of xylanase treatment on dewatering properties of birch kraft pulp. Bioresour 5(2):1164–1177
Burmolle M, Webb JS, Rao D, Hansen LH, Sorensen SJ, Kjelleberg S (2006) Enhanced biofilm formation and increased resistance to antimicrobial agents and bacterial invasion are caused by synergistic interactions in multi-species biofilms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:3916–3923
Cadena E, Chriac AI, Pastor FI, Diaz P, Vidal T, Torres AL (2010a) Use of cellulases and recombinant cellulose binding domains for refining TCF kraft pulp. Biotechnol Prog 26(4):960–967
Cadena EM, Vidal T, Torres AL (2010b) Can the laccase mediator system affect the chemical and refining properties of the Eucalyptus pulp? Bioresour Technol 101:8199–8204
Cadena EM, Vidal T, Torres AL (2010c) Influence of the hexenuronic acid content on refining and ageing in Eucalyptus TCF pulp. Bioresour Technol 101(10):3554–3560
Camarero S, Ibarra D, Martínez A, Romero J, Gutiérrez A, del Río J (2007) Paper pulp delignification using laccase and natural mediators. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:1264–1271
Cordeiro AL, Werner C (2011) Enzymes for antifouling strategies. J Adhes Sci Technol 25:2317–2344
Dhiman SS, Sharma J, Battan B (2008) Microbial xylanases: review. Bioresour 3(4):1377–1402
Du M, Li X, Li W (2012) Modification of bleached softwood pulp with xylanase. Adv Mater Res 393–395:855–858
Ferraz A, Guerra A, Mendonza R, Masarin F, Vicentim MP, Aguiar A, Pavan PC (2008) Technological advances and mechanistic basis for fungal biopulping. Enzyme Microb Technol 43:178–185
Flemming H (2002) Mini-review. Biofouling in water systems cases, causes and countermeasures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:629–640
Gandinia A, Pasquini D (2012) The impact of cellulose fibre surface modification on some physico-chemical properties of the ensuing papers. Ind Crop Prod 35:15–21
Gil N, Gil C, Amaral ME, Costa AP, Duarte AP (2009) Use of enzymes to improve the refining of a bleached Eucalyptus globulus kraft pulp. Biochem Eng J 46:89–95
Haki GD, Rakshit SK (2003) Developments in industrially important thermostable enzymes: a review. Bioresour Technol 89:17–34
Hart PW, Waite DM, Thibault L, Tomashek J, Rousseau ME, Hill C, Sabourin MJ (2009) Selective enzyme impregnation of chips to reduce specific refining energy in alkaline peroxide mechanical pulping. Holzforschung 63:418–423
Huang J, Lu Y, Weng J, Wu Z (2010) Improvement of refining of secondary fiber from old carton by cellulose pretreatment. East China Pulp Paper Ind 2010-05. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZZSH.0.2010-05-033
Huang J, Lu Y, Weng J, Wu Z (2011) Improving refining effect of old carton secondary fibers by amylase. Paper Chemicals. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZZHX.0.2011-01-013
Ibarra D, Monte MC, Blanco A, Martínez AT, Martínez MJ (2011) Enzymatic deinking of secondary fibers: cellulases/hemicellulases versus laccase-mediator system. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s10295-011-0991
Jefferson K (2004) What drives bacteria to produce a biofilm? FEMS Microbiol Lett 236:163–173
Jurasek L, Paice MG (1988) Biological treatments of pulps. Biomass 15(2):103–108
Karmakar M, Ray RR (2011) Current trend in research and application of microbial cellulases. J Microbiol 6(1):41–53
Kaur A, Mahajan R, Singh A, Garg G, Sharma J (2010) Application of cellulase-free xylano-pectinolytic enzymes from the same bacterial isolate in biobleaching of kraft pulp. Bioresour Technol 101:9150–9155
Kazymov D (2010) Biochemical modification of thermomechanical pulp fibers. Master’s Degree Program in Chemical and Process Engineering. Lappeenranta University of Technology
Kenealy WR, Jeffries TW (2003) Enzyme processes for pulp and paper: a review of recent developments. Am Chem Soc ACS Symp Ser 845:210–239
Kerekes RJ (1990) Characterization of pulp refiners by a C-factor. Nordic Pulp Paper Res J 1:3–8
Ko CH, Tsai CH, Lin PH, Chang KC, Tu J, Wang YN, Yang CY (2010) Characterization and pulp refining activity of a Paenibacillus campinasensis cellulase expressed in Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 101:7882–7888
Ko CH, Chen FJ, Lee JJ, Tzou DLM (2011) Effects of fiber physical and chemical characteristics on the interaction between endoglucanase and eucalypt fibers. Cellulose 18:1043–1054
Kolari M (2003) Attachment mechanisms and properties of bacterial biofilms on non-living surfaces. Ph.D. thesis. University of Helsinki
Kristensen JB, Meyer RL, Laursen BS, Shipovskov S, Besenbacher F, Poulsen CH (2008) Antifouling enzymes and the biochemistry of marine settlement. Biotechnol Adv 26:471–481
Kuhad RC, Gupta R, Singh A (2011) Microbial cellulases and their industrial applications. Enzyme Res. doi:10.4061/2011/280696
Lecourt M, Meyer V, Sigoillot JC, Petit-Conil M (2010a) Energy reduction of refining by cellulases. Holzforschung 64:441–446
Lecourt M, Sigoillot JC, Petit-Conil M (2010b) Cellulase-assisted refining of chemical pulps: impact of enzymatic charge and refining intensity on energy consumption and pulp quality. Process Biochem 45:1274–1278
Lecourt M, Soranzo A, Petit-Conil M (2011) Refining of Pinus radiata and Eucalyptus kraft pulps assisted with commercial laccase mediator systems. O Papel 72(8):57–61
Li K, Lei X, Lu L, Camm C (2010) Surface characterization and surface modification of mechanical pulp fibres. Pulp Paper Canada 111(1):28–33
Li B, Li H, Zha Q, Bandekar R, Alsaggaf A, Ni Y (2011) Review: effects of wood quality and refining process on TMP pulp and paper quality. Bioresour 6(3):3569–3584
López D, Vlamakis H, Kolter R (2010) Biofilms. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2(7). doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a000398
Luo Q, Li XP, Liu Y (2011) Effects of cellulose modification on fiber surface and quality of masson pine mechanical pulp. Adv Mater Res 291:3405–3408
Maciel MJM, Silva AC, Ribeiro HCT (2010) Industrial and biotechnological applications of ligninolytic enzymes of the Basidiomycota: a review. Electron J Biotechnol 13. ISSN: 0717-3458
Maijala P, Kleen M, Westin C, Poppius-Levlin K, Herranen K, Lehto JH, Reponen P, Maentausta O, Mettala A, Hatakka A (2008) Biomechanical pulping of softwood with enzymes and white-rot fungus Physisporinus rivulosus. Enzyme Microb Technol 43:169–177
Maloney TC, Paulapuro H (1999) The formation of pores in cell wall. J Pulp Paper Sci 25:430–436
Menon V, Rao M (2012) Trends in bioconversion of lignocellulose: biofuels, platform chemicals & biorefinery concept. Progr Energ Combust Sci 38 (4):522–550
Michalopoulos DL, Gosh D, Murdoch B (2005) Enhancement of wood pulps by cellulase treatment. In: Proceedings of the 2005 TAPPI Engineering, Pulping & Environmental Conference: August 28–31. Philadelphia, PA, USA, TAPPI Press, Session 43, 7 pp, CD proceeding. TAPPI Pulping Conference Oslo, Norway
Molobela IP, Cloete TE, Beukes M (2010) Protease and amylase enzymes for biofilm removal and degradation of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens bacteria. Afr J Microbiol Res 4(14):1515–1524
O’Toole G, Kaplan HB, Kolter R (2000) Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu Rev Microbiol 54:49–79
Oulahal N, Martial-Gros A, Bonneau M, Blum LJ (2007) Removal of meat biofilms from surfaces by ultrasounds combined with enzymes and/or a chelating agent. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 8:192–196
Ponce T, Perez O (2002) Celulasas y xilanasas en la industria. Avance Perspective 21:273–277
Poorna CA, Prema P (2007) Production of cellulase free endoxylanase from novel alkalophilic thermotolerant Bacillus pumilus by solid state fermentation and its application in waste paper recycling. Bioresour Technol 98:485–490
Quinde A (1994) Enzymes in the pulp and paper industry: a review. quindeconsulting.ca/documents/enzymes. Accessed August 02, 2010
Rantanen J, Hiltunen E, Nieminen K, Kerekes R, and Paulapuro H (2011) Construction of a single bar refiner. Tappi J July: 45–51
Rashmi S, Nishi B (2010) Enzymatic treatment of secondary fibres for improving drainage: an overview. Ippta J 23(2):121–126
Ribas L, da Silva J, Jardim C, Oliveira R, Colodette J (2011) Effect of ultrasound and xylanase treatment on the physical–mechanical properties of bleached Eucalyptus kraft pulp. Nat Resour 2:125–129
Richards M, Cloete E (2010) Biofilm removal using nanozymes. In: T. Eugene Cloete, M de Kwaadsteniet, M Botes, JM López-Romero (eds) Nanotechnology in water treatment applications. Caister Academic, Norfolk. ISBN: 978-1-904455-66-0
Riva S (2006) Laccases: blue enzymes for green chemistry. Trends Biotechnol 24(5):219–226
Sabourin MJ, Hart PW (2010) Enhanced fiber quality of black spruce (Picea mariana) thermomechanical pulp fiber through selective enzyme application. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:5945–5951
Savitha S, Sadhasivam S, Swaminathan K (2009) Modification of paper properties by the pretreatment of wastepaper pulp with Graphium putredinis, Trichoderma harzianum and fusant xylanases. Bioresour Technol 100:883–889
Senior DJ, Mayers PR, Miller D, Sutcliffe R, Tan L, Saddler JN (1988) Selective solubilisation of xylan in pulp using a purified xylanase from Trichoderma harzianum. Biotechnol Lett 10(12):907–912
Simoes M, Simoes L, Vieira M (2010) A review of current and emergent biofilm control strategies. Food Sci Technol 43:573–583
Singh D, Chen S (2008) The white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium conditions for the production of lignin degrading enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:399–417
Singh P, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Rupani PF, Peng LC (2010) Biopulping of lignocellulosic material using different fungal species: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 9:141–151
Skals PB, Krabek A, Nielsen PH, Wenzel H (2008) Environmental assessment of enzyme assisted processing in pulp and paper industry. Int J LCA 13(2):124–132
Stoodley P, Sauer K, Davies DG, Costerton JW (2002) Review. Biofilms as complex differentiated communities. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:187–209
Torres CE, Gibello A, Nande M, Martin M, Blanco A (2008) Fluorescent in situ hybridization and flow cytometry as tools to evaluate the treatments for the control of slime-forming enterobacteria in paper mills. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 8:889–897
Torres CE, Lenon G, Craperi D, Wilting R, Blanco A (2011) Enzymatic treatment for preventing biofilm formation in the paper industry. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92(1):95–103
Valchev IV, Bikov PY (2011) Pulp dewatering and refining efficiency improvement by cellulose treatment. COST Action E54 “Characterisation of the fine structure and properties of papermaking fibres using new technologies”. ISBN: 978-91-576-9007-4. 91-95
Van Houdt R, Michielis C (2005) Role of bacterial cell surface structures in Escherichia coli biofilm formation. Res Microbiol 156:626–633
Verhoef R, Waard P, Schols HA, Siika-aho M, Voragen AGJ (2003) Methylobacterium sp. isolated from a Finnish paper machine produces highly pyruvated galactan exopolysaccharide. Carbohydr Res 338:1851–1859
Verhoef R, Schols HA, Blanco A, Siika-aho M, Ratto M, Buchert J, Lenon G, Voragen AGJ (2005) Sugar composition and FT-IR analysis of exopolysaccharides produced by microbial isolates from paper mill biofilm deposits. Biotechnol Bioeng 91(1):91–105
Wang J, Zhang WW, Liu JN, Cao YL, Bai XT, Gong YS, Cen PI, Yang MM (2010) An alkali-tolerant xylanase produced by the newly isolated alkaliphilic Bacillus pumilus from paper mill effluent. Mol Biol Rep 37:3297–3302
Watnick P, Kolter R (2000) Biofilm, city of microbes. J Bacteriol 182(10):2675–2679
Waung DW (2010) Optimizing enzymatic preparations of mechanical pulp through the characterization of new laccases and non-productive interactions between enzymes and lignin. Ph.D. thesis University of Toronto
Widsten P, Kandelbauer A (2008) Laccase applications in the forest products industry: a review. Enzyme Microb Technol 42:293–307
Yang G, Mu Y, Chen J, Zhang F (2010) Effects of enzyme-treatment on beatability of mixed poplar P-RC APMP. Chem Ind Forest Prod. doi: CNKI:SUN:LCHX.0.2010-05-012
Yang G, Lucia LA, Cehn J, Cao X, Liu Y (2011) Effects of enzyme pretreatment on the beatability of fast-growing poplar AMP pulp. Bioresour 6(3):2568–2580
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to express their appreciation to Community of Madrid for funding the project PROLIPAPEL II (S-2009/AMB-1480).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres, C.E., Negro, C., Fuente, E. et al. Enzymatic approaches in paper industry for pulp refining and biofilm control. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96, 327–344 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4345-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4345-0