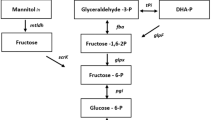
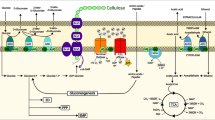
Abstract
Metabolic flux analysis was used to reveal the metabolic distributions in Gluconacetobacter xylinus (CGMCC no. 2955) cultured on different carbon sources. Compared with other sources, glucose, fructose, and glycerol could achieve much higher bacterial cellulose (BC) yields from G. xylinus (CGMCC no. 2955). The glycerol led to the highest BC production with a metabolic yield of 14.7 g/mol C, which was approximately 1.69-fold and 2.38-fold greater than that produced using fructose and glucose medium, respectively. The highest BC productivity from G. xylinus CGMCC 2955 was 5.97 g BC/L (dry weight) when using glycerol as the sole carbon source. Metabolic flux analysis for the central carbon metabolism revealed that about 47.96 % of glycerol was transformed into BC, while only 19.05 % of glucose and 24.78 % of fructose were transformed into BC. Instead, when glucose was used as the sole carbon source, 40.03 % of glucose was turned into the by-product gluconic acid. Compared with BC from glucose and fructose, BC from the glycerol medium showed the highest tensile strength at 83.5 MPa, with thinner fibers and lower porosity. As a main byproduct of biodiesel production, glycerol holds great potential to produce BC with superior mechanical and microstructural characteristics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodin A, Backdahl H, Fink H, Gustafsson L, Risberg B, Gatenholm P (2006) Influence of cultivation conditions on mechanical and morphological properties of bacterial cellulose tubes. Biotechnol Bioeng 97:425–434
Braud HS (2007) Thermal characterization of bacterial cellulose-phosphate composite membranes. J Therm Anal Calorim 87:815–818
Cannon RE, Anderson SM (1991) Biogenesis of bacterial cellulose. Crit Rev Microbiol 17:435–447
Ha JH, Shah N, Ul-Islam M, Khan T, Park JK (2011) Bacterial cellulose production from a single sugar α-linked glucuronic acid-based oligosaccharide. Process Biochem 46:1717–1723
Heo MS, Son HJ (2002) Development of an optimized simple chemically defined medium for bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter sp. A9 in shaking cultures. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 36:41–45
Huang D, Wen JP, Wang GY, Yu GH, Jia XQ, Chen YL (2012) In silico aided metabolic engineering of Streptomyces roseosporus for daptomycin yield improvement. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:637–649
Li YJ, Tian CJ, Tian H, Zhang JL, He X, Ping WX, Lei H (2012) Improvement of bacterial cellulose production by manipulating the metabolic pathways in which ethanol and sodium citrate involved. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1479–1487
Jung HI, Jeong JH, Lee OM, Park GT, Kim KK, Park HC, Lee SM, Kim YG, Kim HG, Son HJ (2010) Influence of glycerol on production and structural–physical properties of cellulose from Acetobacter sp. V6 cultured in shake flasks. Bioresour Technol 101:3602–3608
Keshk S, Sameshima K (2006) The utilization of sugar cane molasses with/without the presence of lignosulfonate for the production of bacterial cellulose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:291–296
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink HP, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:3358–3393
Klemm D, Schumann D, Kramer F, Hessler N, Hornung M, Schmauder H, Marsch S (2006) Nanocelluloses as innovative polymers in research and application. Adv Polym Sci 205:49–96
Ma K, Zhao HX, Zhang C, Lu Y, Xing XH (2012) Impairment of NADH dehydrogenase for increased hydrogen production and its effect on metabolic flux redistribution in wild strain and mutants of Enterobacter aerogenes. Int J Hydrogen Energy. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene. 2012.08.017
Matsuoka M, Tsuchida T, Matsushita K, Adachi O, Yoshinaga F (1996) A synthetic medium for bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter xylinum subsp. sucrofermentans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 100:575–579
Mikkelsen D, Flanagan BM, Dykes GA, Gidley MJ (2009) Influence of different carbon sources on bacterial cellulose production by Gluconacetobacter xylinus strain ATCC 53524. J Appl Microbiol 107:576–583
Naritomi T, Kouda T, Yano H, Yoshinaga F (1998) Effect of lactate on bacterial cellulose production from fructose in continuous culture. J Ferm Bioeng 85:89–95
Nguyen VY, Flanagan B, Gidley MJ, Dykes GA (2008) Characterization of cellulose production by a Gluconacetobacter xylinus strain from kombucha. Curr Microbiol 57:449–453
Oh SY, Yoo DI, Shin Y, Kim HC (2005) Crystalline structure analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide by means of X-ray diffraction and FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydr Res 340:2376–2391
Oikawa T, Nakai J, Tsukagawa Y, Soda K (1997) A novel type of d-mannitol dehydrogenase from Acetobacter xylinum occurrence purification and basic properties. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:1778–1782
Park ST, Kim E, Kim YM (2006) Overproduction of cellulose in Acetobacter xylinum KCCM 10100 defective in GDP-mannosyltransferase. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:961–964
Ross P, Mayer R, Benziman M (1991) Cellulose biosynthesis and function in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 55:35–58
Ruka DR, Simon GP, Dean GM (2012) Altering the growth conditions of Gluconacetobacter xylinus to maximize the yield of bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 89:613–622
Saenge C, Cheirsilp B, Suksaroge TT, Bourtoom T (2011) Potential use of oleaginous red yeast Rhodotcorula glutinis for the bioconversion of crude glycerol from biodiesel plant to lipids and carotenoids. Process Biochem 46:210–218
Schaub J, Mauch K, Reuss M (2008) Metabolic flux analysis in Escherichia coli by integrating isotopic dynamic and isotopic stationary 13C labeling data. Biotechnol Bioeng 99:1170–1185
Schramm M, Gromet Z, Hestrin S (1957) Role of hexose phosphate in synthesis of cellulose by Acetobacter xylinum. Nature 179:28–29
Segal L, Creely J, Martin A, Conrad C (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794
Shezad O, Khan S, Khan T, Park JK (2010) Physicochemical and mechanical characterization of bacterial cellulose produced with an excellent productivity in static conditions using a simple fed-batch cultivation strategy. Carbohydr Polym 82:173–180
Shigematsu T, Takamine K, Kitazato M, Morita T, Naritomi T, Morimura S, Kida K (2005) Cellulose production from glucose using a glucose dehydrogenase gene (gdh)-deficient mutant of Gluconacetobacter xylinus and its use for bioconversion of sweet potato pulp. J Biosci Bioeng 99:415–422
Sturcová A, His I, Apperley DC, Sugiyama J, Jarvis MC (2004) Structural details of crystalline cellulose from higher plants. Biomacromolecules 5:1333–1339
Svensson A, Nicklasson E, Harrah T, Panilaitis B, Kaplan DL, Brittberg M, Gatenholm P (2005) Bacterial cellulose as a potential scaffold for tissue engineering of cartilage. Biomaterials 26:419–431
Tamahkar E, Babac C, Kutsl T, Piskin E, Denizli A (2010) Bacterial cellulose nanofibers for albumin depletion from human serum. Process Biochem 45:1713–1719
Tang WH, Jia SR, Jia YY, Yang HJ (2010) The influence of fermentation conditions and post-treatment methods on porosity of bacterial cellulose membrane. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:125–131
Toda K, Asakura T, Fukaya M, Entani E, Kawamrua Y (1997) Cellulose production by acetic acid-resistant Acetobacter xylinum. J Ferment Bioeng 84:228–231
Tonouchi N, Sugiyama M, Yokozeki K (2003) Coenzyme specificity of enzymes in the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway of Gluconobacter oxydans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:2648–2651
UI-Islam M, Khan T, Park JK (2012) Nanoreinforced bacterial cellulose–montmorillonite composites for biomedical applications. Carbohyd Polym 89:1189–1197
Vandamme EJ, De Baets S, Vanbaelen A, Joris K, De Wulf P (1998) Improved production of bacterial cellulose and its application potential. Polym Degrad Stab 59:93–99
Velasco-Bedran H, Lopez-Isunza F (2007) The unified metabolism of Gluconacetobacter entanii in continuous and batch processes. Proc Biochem 42:1180–1190
Wan YZ, Hong L, Jia SR, Huang Y, Zhu Y, Wang YL, Jiang HL (2006) Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite-bacterial cellulose nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 66:1825–1832
Weinhouse H, Benziman M (1976) Phosphorylation of glycerol and dihydroxyacetone in Acetobacter xylinum and its possible regulatory role. J Bacteriol 127:747–754
Yunoki S, Osada Y, Kono H, Takai M (2004) Role of ethanol in improvement of bacterial cellulose production: analysis using 13C-labeled carbon sources. Food Sci Technol Res 10:307–313
Zeng XB, Small DP, Wan WK (2011) Statistical optimization of culture conditions for bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter xylinum BPR 2001 from maple syrup. Carbohydr Polym 86:1558–1564
Zhong C, Cao XY, Li BZ, Yuan YJ (2009a) Biofuels in China: past, present and future. Biofuels Bioprod Bioref 3:247–270
Zhong C, Lau MW, Balan V, Dale BE, Yuan YJ (2009b) Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation from AFEX-treated rice straw. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:667–676
Zhu HX, Jia SR, Wan T, Jia YY, Yang HJ, Li J, Yan L, Zhong C (2011) Biosynthesis of spherical Fe3O4/bacterial cellulose nanocomposites as adsorbents for heavy metal ions. Carbohydr Polym 86:1558–1564
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (project no. 21106105, project no. 20976133), the Foundation of Tianjin Educational Committee (no. 20100602), and Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (no. IRT1166). We also gratefully acknowledge Rebecca G. Ong for her assistance in editing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors Cheng Zhong and Gui-Cai Zhang contributed equally to this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, C., Zhang, GC., Liu, M. et al. Metabolic flux analysis of Gluconacetobacter xylinus for bacterial cellulose production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 6189–6199 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4908-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4908-8