Abstract
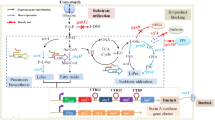
Sphingobium sp. strain SYK-6 expresses the best characterized catabolic systems for lignin-derived aromatic compounds. However, the uptake systems for these aromatics remain unknown. In this study, we identified and characterized the protocatechuate (PCA) transporter gene SLG_12880 (pcaK) in SYK-6. Sequence comparisons revealed that PcaK belongs to the aromatic acid/H+ symporter family of major facilitator superfamily transporters. Further, pcaK was highly conserved among Sphingomonadales possessing catabolic genes for vanillate and PCA. The growth of an SYK-6 pcaK mutant was significantly delayed on PCA medium and PCA uptake rate was only 8% of wild type. In addition, vanillate uptake rate was 78% of wild type, although the pcaK mutant grew as well as the wild type on vanillate. When pcaK was expressed in Sphingobium japonicum UT26S, the transformant acquired the capacity to uptake both PCA and vanillate. These results indicate that pcaK is responsible for the major proportion of PCA uptake and a minor fraction of vanillate uptake in SYK-6. The productivity of 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylate (PDC), a building block of functional polymers, was evaluated using a PDC hydrolase SYK-6 mutant harboring a pcaK plasmid. The mutant exhibited 1.27-fold greater PCA conversion and 1.24-fold greater PDC production compared to the control strain, suggesting that enhanced expression of transporter genes for lignin-derived aromatics can be used to increase the production of value-added metabolites.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe T, Masai E, Miyauchi K, Katayama Y, Fukuda M (2005) A tetrahydrofolate-dependent O-demethylase, LigM, is crucial for catabolism of vanillate and syringate in Sphingomonas paucimobilis SYK-6. J Bacteriol 187(6):2030–2037. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.187.6.2030-2037.2005
Chaudhry MT, Huang Y, Shen XH, Poetsch A, Jiang CY, Liu SJ (2007) Genome-wide investigation of aromatic acid transporters in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microbiology 153:857–865. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.2006/002501-0
Chen Z, Huang J, Wu Y, Wu W, Zhang Y, Liu D (2017) Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid from glucose and xylose. Metab Eng 39:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.11.009
Choudhary A, Purohit H, Phale PS (2017) Benzoate transport in Pseudomonas putida CSV86. FEMS Microbiol Lett 364(12). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnx118
Collier LS, Nichols NN, Neidle EL (1997) benK encodes a hydrophobic permease-like protein involved in benzoate degradation by Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1. J Bacteriol 179(18):5943–5946. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.18.5943-5946.1997
D'Argenio DA, Segura A, Coco WM, Bünz PV, Ornston LN (1999) The physiological contribution of Acinetobacter PcaK, a transport system that acts upon protocatechuate, can be masked by the overlapping specificity of VanK. J Bacteriol 181(11):3505–3515
Ditta G, Stanfield S, Corbin D, Helinski DR (1980) Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 77(12):7347–7351
Ditty JL, Harwood CS (1999) Conserved cytoplasmic loops are important for both the transport and chemotaxis functions of PcaK, a protein from Pseudomonas putida with 12 membrane-spanning regions. J Bacteriol 181(16):5068–5074
Ditty JL, Harwood CS (2002) Charged amino acids conserved in the aromatic acid/H+ symporter family of permeases are required for 4-hydroxybenzoate transport by PcaK from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol 184(5):1444–1448. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.184.5.1444-1448.2002
Hishida M, Shikinaka K, Katayama Y, Kajita S, Masai E, Nakamura M, Otsuka Y, Ohara S, Shigehara K (2009) Polyesters of 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid (PDC) as bio-based plastics exhibiting strong adhering properties. Polym J 41(4):297–302. https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.PJ2008291
Jessen-Marshall AE, Parker NJ, Brooker RJ (1997) Suppressor analysis of mutations in the loop 2-3 motif of lactose permease: evidence that glycine-64 is an important residue for conformational changes. J Bacteriol 179(8):2616–2622. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.8.2616-2622.1997
Johnson M, Zaretskaya I, Raytselis Y, Merezhuk Y, McGinnis S, Madden TL (2008) NCBI BLAST: a better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res 36(Web Server):W5–W9. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn201
Kaczmarczyk A, Vorholt JA, Francez-Charlot A (2012) Markerless gene deletion system for sphingomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(10):3774–3777. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.07347-11
Kamimura N, Masai E (2014) The protocatechuate 4,5-cleavage pathway: overview and new findings. In: Nojiri H, Tsuda M, Fukuda M, Kamagata Y (eds) Biodegradative bacteria: how bacteria degrade, survive, adapt, and evolve. Springer Japan, Tokyo, pp 207–226
Kamimura N, Takahashi K, Mori K, Araki T, Fujita M, Higuchi Y, Masai E (2017) Bacterial catabolism of lignin-derived aromatics: new findings in a recent decade. Environ Microbiol Rep 9(6):679–705. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12597
Kasai D, Kamimura N, Tani K, Umeda S, Abe T, Fukuda M, Masai E (2012) Characterization of FerC, a MarR-type transcriptional regulator, involved in transcriptional regulation of the ferulate catabolic operon in Sphingobium sp. strain SYK-6. FEMS Microbiol Lett 332(1):68–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02576.x
Kashket ER (1985) The proton motive force in bacteria: a critical assessment of methods. Annu Rev Microbiol 39:219–242. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001251
Katayama Y, Nishikawa S, Nakamura M, Yano K, Yamasaki M, Morohoshi N, Haraguchi T (1987) Cloning and expression of Pseudomonas paucimobilis SYK-6 genes involved in the degradation of vanillate and protocatechuate in P. putida. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 33(1):77–79
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305(3):567–580. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Ledger T, Aceituno F, González B (2009) 3-Chlorobenzoate is taken up by a chromosomally encoded transport system in Cupriavidus necator JMP134. Microbiology 155:2757–2765. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.029207-0
Leveau JHJ, Zehnder AJB, van der Meer JR (1998) The tfdK gene product facilitates uptake of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate by Ralstonia eutropha JMP134(pJP4). J Bacteriol 180(8):2237–2243
Masai E, Katayama Y, Fukuda M (2007) Genetic and biochemical investigations on bacterial catabolic pathways for lignin-derived aromatic compounds. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.60437
Masai E, Momose K, Hara H, Nishikawa S, Katayama Y, Fukuda M (2000) Genetic and biochemical characterization of 4-carboxy-2-hydroxymuconate-6-semialdehyde dehydrogenase and its role in the protocatechuate 4,5-cleavage pathway in Sphingomonas paucimobilis SYK-6. J Bacteriol 182(23):6651–6658. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.182.23.6651-6658.2000
Masai E, Sasaki M, Minakawa Y, Abe T, Sonoki T, Miyauchi K, Katayama Y, Fukuda M (2004) A novel tetrahydrofolate-dependent O-demethylase gene is essential for growth of Sphingomonas paucimobilis SYK-6 with syringate. J Bacteriol 186(9):2757–2765. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.9.2757-2765.2004
Masai E, Shinohara S, Hara H, Nishikawa S, Katayama Y, Fukuda M (1999) Genetic and biochemical characterization of a 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid hydrolase involved in the protocatechuate 4,5-cleavage pathway of Sphingomonas paucimobilis SYK-6. J Bacteriol 181(1):55–62
Merkens H, Beckers G, Wirtz A, Burkovski A (2005) Vanillate metabolism in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Curr Microbiol 51(1):59–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-005-4531-8
Michinobu T, Bito M, Yamada Y, Tanimura M, Katayama Y, Masai E, Nakamura M, Otsuka Y, Ohara S, Shigehara K (2009) Fusible, elastic, and biodegradable polyesters of 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid (PDC). Polym J 41(12):1111–1116. https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.PJ2009045R
Nagata Y, Ohtsubo Y, Endo R, Ichikawa N, Ankai A, Oguchi A, Fukui S, Fujita N, Tsuda M (2010) Complete genome sequence of the representative g-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium Sphingobium japonicum UT26. J Bacteriol 192(21):5852–5853. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00961-10
Nichols NN, Harwood CS (1997) PcaK, a high-affinity permease for the aromatic compounds 4-hydroxybenzoate and protocatechuate from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol 179(16):5056–5061. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.16.5056-5061.1997
Noda Y, Nishikawa S, Shiozuka K, Kadokura H, Nakajima H, Yoda K, Katayama Y, Morohoshi N, Haraguchi T, Yamasaki M (1990) Molecular cloning of the protocatechuate 4,5-dioxygenase genes of Pseudomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 172(5):2704–2709. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.172.5.2704-2709.1990
Nogales J, Canales Á, Jiménez-Barbero J, Serra B, Pingarrón JM, García JL, Díaz E (2011) Unravelling the gallic acid degradation pathway in bacteria: the gal cluster from Pseudomonas putida. Mol Microbiol 79(2):359–374. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07448.x
Otsuka Y, Nakamura M, Shigehara K, Sugimura K, Masai E, Ohara S, Katayama Y (2006) Efficient production of 2-pyrone 4,6-dicarboxylic acid as a novel polymer-based material from protocatechuate by microbial function. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71(5):608–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0203-7
Pao SS, Paulsen IT, Saier MH Jr (1998) Major facilitator superfamily. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62(1):1–34
Pernstich C, Senior L, MacInnes KA, Forsaith M, Curnow P (2014) Expression, purification and reconstitution of the 4-hydroxybenzoate transporter PcaK from Acinetobacter sp. ADP1. Protein Expr Purif 101:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2014.05.011
Qi F, Zou L, Jiang X, Cai S, Zhang M, Zhao X, Huang J (2017) Integration of heterologous 4-hydroxybenzoic acid transport proteins in Rhodobacter sphaeroides for enhancement of coenzyme Q10 production. RSC Adv 7(28):17346–17352. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA02346D
Qian Y, Otsuka Y, Sonoki T, Mukhopadhyay B, Nakamura M, Masai E, Katayama Y, Okamura-Abe Y, Jellison J, Goodell B (2016) Engineered microbial production of 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid from lignin residues for use as an industrial platform chemical. Bioresources 11(3):6097–6109
Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A (2000) EMBOSS: the European molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet 16(6):276–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9525(00)02024-2
Salis HM, Mirsky EA, Voigt CA (2009) Automated design of synthetic ribosome binding sites to precisely control protein expression. Nat Biotechnol 27(10):946–950. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1568
Shigehara K, Okamura N, Matsumoto M, Seki C, Katayama Y, Nishikawa S (1998) Synthesis of polyamides with 2H-pyran-2-one-4,6-dicarboxylic acid(PDC) nuclei. Polym Prepr Jpn 47(2):316
Wang SH, Xu Y, Liu SJ, Zhou NY (2011) Conserved residues in the aromatic acid/H+ symporter family are important for benzoate uptake by NCgl2325 in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65(3):527–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.02.004
Wu W, Liu F, Singh S (2018) Toward engineering E. coli with an autoregulatory system for lignin valorization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(12):2970–2975. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1720129115
Xu Y, Chen B, Chao H, Zhou NY (2013) mhpT encodes an active transporter involved in 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionate catabolism by Escherichia coli K-12. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(20):6362–6368. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02110-13
Xu Y, Gao X, Wang SH, Liu H, Williams PA, Zhou NY (2012a) MhbT is a specific transporter for 3-hydroxybenzoate uptake by gram-negative bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(17):6113–6120. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01511-12
Xu Y, Wang SH, Chao HJ, Liu SJ, Zhou NY (2012b) Biochemical and molecular characterization of the gentisate transporter GenK in Corynebacterium glutamicum. PLoS One 7(7):e38701. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038701
Yamaguchi A, Someya Y, Sawai T (1992) Metal-tetracycline/H+ antiporter of Escherichia coli encoded by transposon Tn10. The role of a conserved sequence motif, GXXXXRXGRR, in a putative cytoplasmic loop between helices 2 and 3. J Biol Chem 267(27):19155–19162
Zhang H, Pereira B, Li Z, Stephanopoulos G (2015) Engineering Escherichia coli coculture systems for the production of biochemical products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(27):8266–8271. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1506781112
Acknowledgements
We thank Yuji Nagata (Tohoku University) for providing S. japonicum UT26S. We also thank Kodai Maekawa for assistance with the construction of SME002-3. We are grateful to Yoshihiro Katayama (Nihon University) for insightful discussions and support.
Funding
This work was supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI (15H04473) and a research grant from the Institute for Fermentation, Osaka.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 2542 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, K., Kamimura, N. & Masai, E. Identification of the protocatechuate transporter gene in Sphingobium sp. strain SYK-6 and effects of overexpression on production of a value-added metabolite. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 4807–4816 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8988-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8988-3