Abstract.
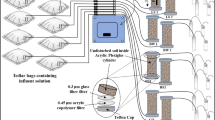
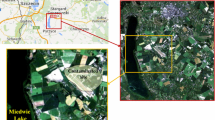
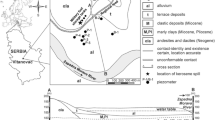
This paper deals with sorption and anaerobic biodegradation of the soluble aromatic fraction of jet fuel and how it is influenced by pore-water velocity during transport in a groundwater aquifer. The study was carried out as controlled laboratory column experiments. A binary mixture of toluene and 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene with a concentration ratio of 2:1 was used through the entire investigations. The column experiments were conducted with contaminated sediments and groundwater, taken from wells at a field research site. The columns were operated anaerobically under continuous-flow conditions at 10 °C in a temperature-controlled refrigerator. Two percent sodium azide was added to the injection solution of two of the columns to prevent biodegradation of the studied organic mixture. Chloride was used as a conservative tracer to characterize the hydrodynamic parameters such as dispersivity and porosity of the columns. The results showed that both compounds in the mixture were attenuated because of sorption and biodegradation processes in the columns. 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene was attenuated more significantly than toluene. Biodegradation of toluene was coupled mainly with the microbial reduction of ferric iron, whereas 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene, in contrast, was mostly sorbed. Their sorption and biodegradation were studied with different pore-water velocities, and a mass balance approach was applied to calculate biodegradation rates. The biodegradation rates of toluene were –0.16, –0.21, and –0.26 (unit: mM day–1) for pore-water velocities of 96, 82.4, and 54.9 (unit: cm day–1), respectively. This indicates that a decrease in the pore-water velocity significantly enhanced the biodegradation of toluene, consistent with other reports in the literature. For 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene the biodegradation rates were –0.05, –0.13 (unit: mM day–1) for pore-water velocities of 96 and 82.4 (unit: cm day–1), respectively. The biodegradation rate of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene did not increase at the lowest pore water velocity as expected. This might be a result of substrate competition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Aagaard, P. & Breedveld, G.D. Sorption and anaerobic biodegradation of soluble aromatic compounds during groundwater transport. 1. Laboratory column experiments. Env Geol 41, 922–932 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-001-0470-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-001-0470-2