Abstract
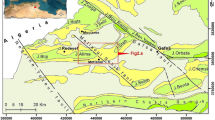
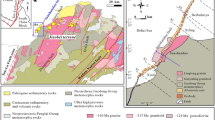
Earth fissures in Jiangsu Province, China have caused serious damages to properties, farmlands, and infrastructures and adversely affected the local or regional economic development. Under the geological and environmental background in Jiangsu Province, this paper presents the earth fissures caused by excessive groundwater withdrawal and coupled by distinctive geological structures such as Ancient Yellow River Fault in Xuzhou karst area, and Ancient Yangtze River Course and bedrock hills in Suzhou, Wuxi, and Changzhou area. Although all the earth fissures are triggered by groundwater exploitation, the characteristics are strongly affected by the specific geological and hydrogeological settings. In particular, in the water-thirsty Xuzhou city, the cone of depression caused by groundwater extraction enlarged nearly 20 times and the piezometric head of groundwater declined 17 m over a decade. As groundwater is extracted from the shallowly buried karst strata in the Ancient Yellow River Fault zone, the development of earth fissures is highly associated with the development of karstic cavities and sinkholes and their distribution is controlled by the Ancient Yellow River Fault with all the 17 sinkholes on the fault. On the other hand, in the rapidly developing Southern Jiangsu Province, groundwater is mainly pumped from the second confined aquifer in the Quaternary, which is distributed neither homogeneously nor isotropically. The second confined aquifer comprises more than 50 m thick sand over the Ancient Yangtze River Course, but this layer may completely miss on the riverbank and bedrock hills. With a typical drawdown rate of 4–6 m per annum, the piezometric head of groundwater in the second confined aquifer has declined 76 m at Maocunyuan since 1970s and 40 m at Changjing since mid-1980s, and a large land subsidence, e.g., 1,100 mm at Maocunyuan, is triggered. Coupled with the dramatic change of the bedrock topography that was revealed through traditional geological drilling and modern seismic reflection methods, the geological-structure-controlled differential settlement and earth fissures are phenomenal in this area.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asfaw LM (1998) Environmental hazard from fissures in the Main Ethiopian Rift. J Afr Earth Sci 27(3/4):481–490
Ayalew L, Yamagishi H, Reik G (2004) Ground cracks in Ethiopian Rift Valley: facts and uncertainties. Eng Geol 75:309–324
Beckwith GH, Slemmons DB, Weeks RE (1991) Use of low-sun angle photography for identification of subsidence-induced earth fissures. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Land Subsidence, IAHS Press, Houston, Wallingford,
Billi A, Valle A, Brilli M, Faccenna C, Funiciello R (2007) Fracture-controlled fluid circulation and dissolutional weathering in sinkhole-prone carbonate rock from central Italy. J Struct Geol 29:385–395
Chen CX, Pei SP, Jiao JJ (2003) Land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in Suzhou city, China. Hydrogeol J 11:275–287
Contaldo GJ, Mueller JE (1991) Earth fissures and land subsidence of the Mimbres Basin, Southwestern NM, USA In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Land Subsidence, IAHS Press, Houston, Wallingford (12–17 May 1991)
Corwin EJ, Alhadeff SC, Oggel SP, Shlemon RJ (1991) Earth fissures, urbanization and litigation: a case study from the Temecula, Southwestern Riverside County, CA. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Land Subsidence, IAHS Press, Houston, Wallingford (12–17 May 1991)
Eeckhaut MVD, Poesen J, Dusar M, Martens V, Duchateau P (2007) Sinkhole formation above underground limestone quarries: a case study in South Limburg (Belgium). Geomorphology 91:19–37
Gao Z, Zhu Q, Ji Y, Chen X (1997) The research on the distribution feature, genetic type and countermeasure about ground fissure events. Chin J Seismol 1:1–10
Goodings DJ, Abdulla WA (2002) Stability charts for predicting sinkholes in weakly cemented sand over karst limestone. Eng Geol 65:179–184
Haneberg WC, Reynolds CB, Reynolds IB (1991) Geophysical characterization of soil deformation associated with earth fissures near San Marcial Deming, NM. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Land Subsidence, IAHS Press, Houston, Wallingford (12–17 May 1991)
Holzer TL, Pampeyan EH (1981) Earth fissures and localized subsidence. Water Resour Res 17(1):223–227
Hu JP, Wu SL (1998) Geohydrologic environment issues in Suzhou-Changzhou-Wuxi urban group. Chin J Hydrogeol Eng Geol 4:5–7
Hyatt JA, Jacobs PM (1996) Distribution and morphology of sinkholes triggered by flooding following Tropical Storm Alberto at Albany, Georgia, USA. Geomorphology 17:305–316
Keaton JR, Shlemon RJ (1991) Fort Hancock earth fissure system, Hudspeth County, Texas: uncertainties and implications. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Land Subsidence, IAHS Press, Houston, Wallingford
Kyriiacou E (1990) Ground cracks in Aradhippouvillage in Cyprus. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Congress International Association of Engineering Geology. A A Balkema, Rotterdam, Amsterdam 6–10 August 1990
Lee CF, Zhang JM, Zhang YX (1996) Evolution and origin of the ground fissures in Xian, China. Eng Geol 43:45–55
Li GY, Zhou WF (1999) Sinkholes in karst mining areas in China and some methods of prevention. Eng Geol 52:45–50
Li Y, Yang J, Hu X (2000) Origin of ground fissures in the Shanxi Graben system, Northern China. Eng Geol 55:267–275
Li X, Wang SJ, Liu TY, Ma FS (2004) Engineering geology, ground surface movement and fissures induced by underground mining in the Jinchuan Nickel Mine. Eng geol 76:93–107
Liu Y, Chen Z, Zhao Z (1990) Engineering geological characters of Xian ground fissures and the disaster analyses. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Congress International Association of Engineering Geology. A A Balkema, Amsterdam, Rotterdam, 6–10 August 1990
Lolcama JL, Cohen HA, Tonkin MJ (2002) Deep karst conduits, flooding, and sinkholes: lessons for aggregates industry. Eng Geol 65:151–157
Prestininzi A, Romeo R (2000) Earthquake-induced ground failures in Italy. Eng Geol 58:387–397
Qi S, Wu F, Yan F, Lan H (2004) Mechanism of deep cracks in the left bank slope of Jinping first stage hydropower station. Eng Geol 73:129–144
Rojas E, Arzate J, Arroyo M (2002) A method to predict the group fissuring and faulting caused by regional groundwater decline. Eng Geol 65:245–260
Salvati R, Sasowsky ID (2002) Development of collapse sinkholes in areas of groundwater discharge. J Hydrol 264:1–11
Sarkar I (2004) The role of the 1999 Chamoli earthquake in the formation of ground cracks. J Asian Earth Sci 22:529–538
Schumann HH, Cripe LS, Laney RL (1986) Land subsidence and earth fissures caused by groundwater depletion in southern AZ, USA. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Internation Symposium on Land Subsidence, IAHS Press, Venice, Wallingford, 19–25 March 1986
Wang Z (1998) Sustainable development suffering overexploitation of groundwater—land subsidence and its conflicting in Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou area, Jiangsu Province. Chin J Geoll Hazard Control 9(2):18–26
Wang GY, You G, Shi B, Xu YL (2008) Investigation on the Nanjing Gypsum Mine Flooding. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Geotechnical Engineering for Disaster Mitigation and Rehabilitation, Nanjing, China, 30 May–2 June 2008
Whiteley RJ (2005) Gravity mapping and seismic imaging of large tunnel routes in Sydney Australia. In: Butler DK (ed) Near surface geophysics. Society of Exploration Geophysics, Tulsa, pp 503–512
Whiteley RJ (2006) Seismic imaging of unstable ground. In: Proceedings of the ASCE 2006, Melbourne, 2–6 July 2006
Yu J, Wang XM, Su XS, Yu Q (2004) The mechanism analysis on ground fissure disaster formation in Suzhou–Wuxi–Changzhou area. J Jilin Univ (Earth Sci Edn) 34(2):236–241
Yuan H, Yang SH, Andrus RD, Jung CH (2004) Liquefaction-induced ground failure: a study of the Chi–Chi earthquake cases. Eng Geol 71(1–2):141–155
Zhang Y, Xue YQ, Wu JC, Ye SJ, Wei ZX, Li QF, Yu J (2007a) Characteristics of aquifer system deformation in the Southern Yangtze Delta, China. Eng Geol 90:160–173
Zhang Y, Xue YQ, Wu JC, Yu J, Wei ZX, Li QF (2007b) Land subsidence and earth fissures due to groundwater withdrawal in the Southern Yangtze Delta, China. Environ Geol. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-1028-8
Zhu Q, Gao Z, Guo J (1993) Earth fissures and their genesis analysis in Dongting, Wuxi. Chin J Seismol 3:31–35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G.Y., You, G., Shi, B. et al. Earth fissures triggered by groundwater withdrawal and coupled by geological structures in Jiangsu Province, China. Environ Geol 57, 1047–1054 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1390-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1390-1