Abstract
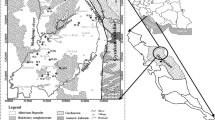
This paper deals with the drinking water quality of the Ganga-Kali sub-basin which occupies 1300 km2 over parts of Aligarh and Etah districts. Water samples were collected from shallow and deep aquifers and were analyzed for major ions and trace elements. The analytical data were interpreted according to published guidelines. Chemical analysis shows that the groundwater in the basin is alkali bicarbonate type. Trace element studies of water from the shallow aquifer show that the concentration of toxic metals Fe, Mn, Cd, Pb, and Cr+6 are above permissible limits which may present a health hazard. The water from the deep aquifer is comparatively free from contamination. The aquifers are subject to contamination due to sewage effluents and excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 December 1998 · Accepted: 2 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umar, R., Sami Ahmad, M. Groundwater quality in parts of Central Ganga Basin, India. Environmental Geology 39, 673–678 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050480
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050480