Abstract.
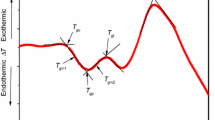
The glass-transition (Tg) and crystallisation (Tx) temperatures of glassy GexSeyIn12 (7≤x≤28) have been determined from differential scanning calorimetry measurements. The variations of Tg and Tx with composition have been specified. It has been found that Tg reaches a maximum at 614 K for the composition Ge23.33 Se64.67 In12 while Tx passes through a minimum at 740 K for the same composition. The values of the cohesive energies of the studied compositions have also been estimated using the chemical bond approach method. It is found that the composition Ge23.33Se64.67In12 possesses the maximum cohesive energy. These results are explained in terms of the structure of Ge-Se-In glasses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 March 2001 / Accepted: 29 March 2001 / Published online: 23 May 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saffarini, G. The effect of compositional variations on the glass-transition and crystallisation temperatures in Ge-Se-In glasses . Appl Phys A 74, 283–285 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390100894
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390100894