Abstract.
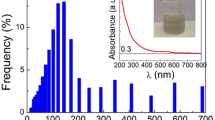
Laser-synthesized photoluminescent Si nanopowders, of interest for application in optoelectronics, have been studied by small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to characterize their size-distribution function, which correlates with emission spectra and optical performances. The SANS measurements were carried out over a wide Q-range by using the D22 instrument at ILL. The analysis of the size distributions obtained from the SANS data reveals that the microstructure of such powders includes particles as large as those observed by TEM (30–200 Å in diameter) and a distribution of tiny inhomogeneities (5–10 Å in diameter), possibly micropores, which can have relevant consequences on material performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 August 2001 / Accepted: 13 November 2001
RID="*"
ID="*"Corresponding author. (Fax: +39-6/9400-5763, E-mail: botti@efr406.frascati.enea.it)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Botti, S., Coppola, R., Gourbilleau, F. et al. SANS and TEM investigation of laser-synthesized photoluminescent Si nanoparticles . Appl Phys A 74 (Suppl 1), s1230–s1232 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390201712
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390201712