Abstract
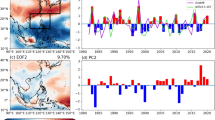
Based on the data analyses by using NCEP/ NCAR reanalysis data and other data (OLR, precipita-tion and temperature), it is shown that the tropospheric circulation and climate in East Asia and the northwestern Pacific region have the evident quasi-biennial oscillation (TBO) feature. It is also shown that anomalous East Asian winter monsoon can impact the atmospheric circulation and climate variations in the following summer, particularly in East Asian region; there is clear interaction between anomalous East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO cycle. The continuous strong (weak) East Asian winter monsoon can ex-cite El Niño (La Niña) through the air-sea interaction, the El Niño (La Niña) event can lead the East Asian winter monsoon to be weak (strong) through the teleconnections or remote responses. The strong or weak winter monsoon and ENSO cycle are linked each other. It can be suggested that interaction between anoma-lous East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO cycle is a fundamental origin of the TBO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augell, J. K., and J. Korshover, 1968: Additional evidence for quasi-biennial variations in tropospheric paramenters. Mon. Wea. Rev., 96, 778–784.
Chan, J. C. L., 1995: Tropical cyclone activity in the western North Pacific in relation to the stratospheric quasi-bi- ennial oscillation. Mon. Wea. Rev., 123, 2567–2571.
Chen Jun, and Sun Shuqing, 1999: Eastern Asian winter monsoon anomaly and variation of global circulation, Part I: A comparison study on strong and weak winter monsoon. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 23, 101–111.
Eisner, J. B.,A. B. Kara, and M. A. Owens, 1999: Fluctuations in North Atlantic hurricane frequency. J. Climate, 12, 407–437.
Gray, W. M., 1984: Atlantic seasonal hurricane frequency, Part I: El Niño and 30 mb quasi-biennial oscillation in-fluences. Mon. Wea. Rev., 112, 1649–1668.
Gray, W. M., J. D. Sheaffer, and J. A. Knaff, 1992: Influence of the stratospheric QBO on ENSO variability., J. Me- teor. Soc. Japan, 70(5), 1–21.
Holton, J. R., and R. S. Lindzen, 1972: An updated theory for the quasi-biennial cycle of the tropical stratosphere. J. Atmas. Sci., 29, 1076–1080.
Huang Jiayou, 1988: The spatial and temporal analysis of the representations of the quasi-biennial oscillation in pre- cipitation over China. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 12, 323–330.
Ji Liren, Sun Shuqing, K. Arpe, and L. Bengtsson, 1997: Model study on the interannual variability of Asian winter monsoon and its influence. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 14, 1–22.
Kawamura, R. 1988: Quasi-biennial oscillation modes appearing in the tropical sea water temperature and 700 mb zonal wind. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 66, 955–965.
Lau, K. M., and P. J. Sheu, 1988: Annual cycle, equasi-biennial oscillation, and southern oscillation in global precip-itation. J. Geophys. Res., 93, 10975–10988.
Lau, K. M., and S. Yang, 1996: The Asian monsoon and predictability of the tropical ocean-atmosphere system. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 122, 945–957.
Li Chongyin, and Long Zhenxia, 1992: Quasi-biennial oscillation and its influence on general atmospheric circula- tion and climate in East Asia. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 16, 70–79.
Li Chongyin, and Long Zhenxia, 1997: Relationship between subtropical high activities over the western Pacific and quasi-biennial oscillation in the stratosphere. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 21, 343–352.
Li Chongyin, 1989: The frequent activities of stronger aerotrough in East Asia in wintertime and the occurrence of the El Niño event. Scientia Sinica (Series B), 32, 976–985.
Li Chongyin, 1990: Interaction between anomalous winter monsoon in East Asia and El Niño events. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences., 7, 36–46.
Li Chongyin, 1996: A further study on interaction between anomalous winter monsoon in East Asia and El Niño. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 10, 309–320.
Lindzin, R. S., and J. R. Holton, 1968: A theory of the quasi-biennial oscillation. J. Atmos. Sci., 25, 1095–1107.
Meehl, G. A., 1997: The south Asian monsoon and the tropospheric biennial oscillation. J. Climate, 10, 1921–1943.
Mukherjee, B. K., K. Indira, R. S. Reddy, and Et Al., 1985: Quasi-biennial oscillation in stratospheric zonal wind and Indian summer monsoon. Mon. W eu. Rev., 113, 1421–1424.
Mu Mingquan, and Li Chongyin, 1999: ENSO signals in interannual variability of East Asian winter monsoon, Part I: Observed data analyses. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 23, 139–149.
Rasmusson, E. M., X. Wang, and C. F. Ropelewski, 1990: The biennial component of ENSO variability. J. Mar. Sys., 1,71–96.
Reed, R. J., and D. G. Rogers, 1962: The circulation of the tropical stratosphere during the years 1954-1960. J. Atmos. Sci., 19, 127–135.
Reed, R. J., 1961: Evidence of the downward-propagating wind reversal in the equatorial stratosphere. J. Geophys, Res., 66, 813–818.
Ropelewski, C. F., M. S. Halpert, and X. Wang, 1992: Observed tropospheric biennial variability and its relationship to the southern oscillation. J. Climate, 5, 594–614.
Shen, S., and K. M. Lau, 1995: Biennial oscillation associated with the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical sea surface temperatures. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 73, 105–124.
Sun Bomin, and Sun Shuqing, 1994: The analysis on the features of the atmospheric circulation in preceding winter for the summer drought and flooding in the Yangtze and Huaihe River valley. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 11, 79–90.
Tomita, T., and T. Yasunari, 1996: Role of the northeast winter monsoon on the biennial oscillation of the ENSO/ monsoon system. J. Meteoro. Soc. Japan, 74, 399–413.
Tucker, G. B., and J. M. Hopwood, 1968: The 26-month zonal wind oscillation in the lower stratosphere of the Southern Hemisphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 25, 293–298.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by National Key Basic Science Program in China (G1998040900) and NSFC (49823002).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chongyin, L., Shuqing, S. & Mingquan, M. Origin of the Tbo-Interaction between anomalous east-Asian winter monsoon and enso cycle. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 18, 554–566 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-001-0044-y
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-001-0044-y