Abstract
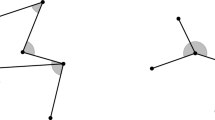
We introduce a new structure for a set of points in the plane and an angle \(\alpha \), which is similar in flavor to a bounded-degree MST. We name this structure \(\alpha \)-MST. Let P be a set of points in the plane and let \(0 < \alpha \le 2\pi \) be an angle. An \(\alpha \)-ST of P is a spanning tree of the complete Euclidean graph induced by P, with the additional property that for each point \(p \in P\), the smallest angle around p containing all the edges adjacent to p is at most \(\alpha \). An \(\alpha \)-MST of P is then an \(\alpha \)-ST of P of minimum weight, where the weight of an \(\alpha \)-ST is the sum of the lengths of its edges. For \(\alpha < \pi /3\), an \(\alpha \)-ST does not always exist, and, for \(\alpha \ge \pi /3\), it always exists (Ackerman et al. in Comput Geom Theory Appl 46(3):213–218, 2013; Aichholzer et al. in Comput Geom Theory Appl 46(1):17–28, 2013; Carmi et al. in Comput Geom Theory Appl 44(9):477–485, 2011). In this paper, we study the problem of computing an \(\alpha \)-MST for several common values of \(\alpha \). Motivated by wireless networks, we formulate the problem in terms of directional antennas. With each point \(p \in P\), we associate a wedge \({\textsc {w}_{p}}\) of angle \(\alpha \) and apex p. The goal is to assign an orientation and a radius \(r_p\) to each wedge \({\textsc {w}_{p}}\), such that the resulting graph is connected and its MST is an \(\alpha \)-MST (we draw an edge between p and q if \(p \in {\textsc {w}_{q}}\), \(q \in {\textsc {w}_{p}}\), and \(|pq| \le r_p, r_q\)). We prove that the problem of computing an \(\alpha \)-MST is NP-hard, at least for \(\alpha =\pi \) and \(\alpha =2\pi /3\), and present constant-factor approximation algorithms for \(\alpha = \pi /2, 2\pi /3, \pi \). One of our major results is a surprising theorem for \(\alpha = 2\pi /3\), which, besides being interesting from a geometric point of view, has important applications. For example, the theorem guarantees that given any set P of 3n points in the plane and any partitioning of the points into n triplets, one can orient the wedges of each triplet independently, such that the graph induced by P is connected. We apply the theorem to the antenna conversion problem and to the orientation and power assignment problem.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman, E., Gelander, T., Pinchasi, R.: Ice-creams and wedge graphs. Comput. Geom.: Theory Appl. 46(3), 213–218 (2013)
Aichholzer, O., Hackl, T., Hoffmann, M., Huemer, C., Pór, A., Santos, F., Speckmann, B., Vogtenhuber, B.: Maximizing maximal angles for plane straight-line graphs. Comput. Geom.: Theory Appl. 46(1), 17–28 (2013)
Arkin, E.M., Fekete, S.P., Islam, K., Meijer, H., Mitchell, J.S.B., Rodríguez, Y.N., Polishchuk, V., Rappaport, D., Xiao, H.: Not being (super) thin or solid is hard: a study of grid Hamiltonicity. Comput. Geom.: Theory Appl. 42(6–7), 582–605 (2009)
Arora, S.: Polynomial time approximation schemes for Euclidean traveling salesman and other geometric problems. J. ACM 45(5), 753–782 (1998)
Aschner, R., Katz, M.J.: Bounded-angle spanning tree: modeling networks with angular constraints. In: Proceeding of the 41st International Colloquium on Automata, Languages, and Programming (ICALP), pp. 387–398 (2014)
Aschner, R., Katz, M.J., Morgenstern, G.: Symmetric connectivity with directional antennas. Comput. Geom.: Theory Appl. 46(9), 1017–1026 (2013)
Bárány, I., Pór, A., Valtr, P.: Paths with no small angles. SIAM J. Discret. Math. 23(4), 1655–1666 (2009)
Bose, P., Carmi, P., Damian, M., Flatland, R., Katz, M.J., Maheshwari, A.: Switching to directional antennas with constant increase in radius and hop distance. Algorithmica 69(2), 397–409 (2014)
Calinescu, G.: Min-power strong connectivity. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Approximation Algorithms for Combinatorial Optimization Problems, pp. 67–80 (2010)
Calinescu, G., Mandoiu, I.I., Zelikovsky, A.: Symmetric connectivity with minimum power consumption in radio networks. In: Proceedings of the 2nd IFIP International Conference on Theoretical Computer Science, pp. 119–130 (2002)
Caragiannis, I., Kaklamanis, C., Kranakis, E., Krizanc, D., Wiese, A.: Communication in wireless networks with directional antennas. In: 20th ACM Symposium on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures, pp. 344–351 (2008)
Carmi, P., Katz, M.J., Lotker, Z., Rosén, A.: Connectivity guarantees for wireless networks with directional antennas. Comput. Geom.: Theory Appl. 44(9), 477–485 (2011)
Chan, T.M.: Euclidean bounded-degree spanning tree ratios. Discret. Comput. Geom. 32(2), 177–194 (2004)
Clementi, A.E.F., Penna, P., Silvestri, R.: Hardness results for the power range assignment problem in packet radio networks. In: 2nd International Workshop on Approximation Algorithms for Combinatorial Optimization Problems, pp. 197–208 (1999)
Dobrev, S., Eftekhari, M., MacQuarrie, F., Manuch, J., Morales-Ponce, O., Narayanan, L., Opatrny, J., Stacho, L.: Connectivity with directional antennas in the symmetric communication model. In: Mexican Conference on Discrete Mathematics and Computational Geometry (2013)
Dumitrescu, A., Pach, J., Tóth, G.: Drawing Hamiltonian cycles with no large angles. Electron. J. Comb. 19(2), P31 (2012)
Efrat, A., Itai, A., Katz, M.J.: Geometry helps in bottleneck matching and related problems. Algorithmica 31(1), 1–28 (2001)
Fekete, S.P., Woeginger, G.J.: Angle-restricted tours in the plane. Comput. Geom.: Theory Appl. 8, 195–218 (1997)
Itai, A., Papadimitriou, C.H., Szwarcfiter, J.L.: Hamilton paths in grid graphs. SIAM J. Comput. 11(4), 676–686 (1982)
Jothi, R., Raghavachari, B.: Degree-bounded minimum spanning trees. Discret. Appl. Math. 157(5), 960–970 (2009)
Khuller, S., Raghavachari, B., Young, N.E.: Low-degree spanning trees of small weight. SIAM J. Comput. 25(2), 355–368 (1996)
Kirousis, L.M., Kranakis, E., Krizanc, D., Pelc, A.: Power consumption in packet radio networks. Theor. Comput. Sci. 243, 289–305 (2000)
Kranakis, E., Krizanc, D., Morales, O.: Maintaining connectivity in sensor networks using directional antennae. In: Nikoletseas, S., Rolim, J.D.P. (Eds.) Theoretical Aspects of Distributed Computing in Sensor Networks, Chapter 3. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Mitchell, J.S.B.: Guillotine subdivisions approximate polygonal subdivisions: a simple polynomial-time approximation scheme for geometric TSP, k-MST, and related problems. SIAM J. Comput. 28(4), 1298–1309 (1999)
van Nijnatten, F.: Range Assignment with Directional Antennas. Master’s Thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven (2008)
Papadimitriou, C.H., Vazirani, U.V.: On two geometric problems related to the travelling salesman problem. J. Algorithms 5(2), 231–246 (1984)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A preliminary version of this paper appears in the Proceedings of ICALP’14 [5]. Work by R. Aschner was partially supported by the Lynn and William Frankel Center for Computer Sciences. Work by M. Katz was partially supported by Grant 1045/10 from the Israel Science Foundation. Work by M. Katz and R. Aschner was partially supported by Grant 2010074 from the United States—Israel Binational Science Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aschner, R., Katz, M.J. Bounded-Angle Spanning Tree: Modeling Networks with Angular Constraints. Algorithmica 77, 349–373 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00453-015-0076-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00453-015-0076-9