Abstract
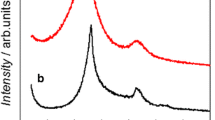
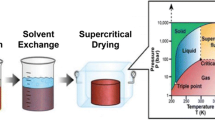
Binderless carbon nanotubes aerogel (CNAG) composites represent a new class of high-performing electrodes for energy storage applications such as electrochemical double layer capacitors. The composites developed here differ significantly from these previously prepared with dispersion processes. The CNAG material was prepared by a molding procedure that is the synthesis by a chemical vapor deposition method to grow carbon nanotubes directly onto a microfibrous carbon paper substrate. Then the carbon aerogel is synthesized on the carbon nanotubes. The key feature of the method is eliminating the need of controlling the carbon nanotube concentration, which permits optimized dispersion processes to reinforce the aerogel's networks. The CNAG electrode delivered very high specific capacitances of 524 F g−1 in KOH electrolyte and 280 F g−1 in H2SO4 electrolyte. Furthermore, this better integration of carbon nanotubes in the matrix of carbon aerogel improved its resistance to the attack by the electrolyte and conferred an excellent cycle life over 5,000 cycles of charge–discharge in both electrolytes.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burke A (2000) J Power Sources 91:37
Aricò AS, Bruce P, Scrosati B, Tarascon J-M, Schalkwijk WV (2005) Nat Matters 5:366
Pekala RW, Farmer JC, Alviso CT, Tran TD, Mayer ST, Miller JM, Dunn B (1998) J Non-Cryst Solids 225:74
Gouérec P, Talbi H, Miousse D, Tran-Van F, Dao LH, Lee KH (2001) J Electrochem Soc 148:A94
Wei Y-Z, Fang B, Iwasa S, Kumagai M (2005) J Power Sources 141:386
Wang J, Zhang SQ, Guo YZ, Shen J, Attia SM, Zhou B, Zheng GZ, Gui YS (2001) J Electrochem Soc 148:D75
Talbi H, Just P-E, Dao LH (2003) J Appl Electrochem 33:465
Li W, Pröbstle H, Fricke J (2003) J Non-Cryst Solids 325:1
Long JW, Dening BM, McEvoy TM, Rolison DR (2004) J Non-Cryst Solids 350:97
Hwang SW, Hyun S-H (2004) J Non-Cryst Solids 347:238
Kim H-J, Kim J-H, Kim W-I, Suh DJ (2005) Korean J Chem Eng 22:740
Bordjiba T, Mohamedi M, Dao LH (2007) Nanotechnology 18:035202
Bordjiba T, Mohamedi M, Dao LH, Aïssa B, El Khakani MA (2007) Chem Phys Lett 441:88
Bordjiba T, Mohamedi M, Dao LH (2007) J Power Sources 172:991
Bordjiba T, Mohamedi M, Dao LH (2008) Electrochem Soc Trans 6:183
Bordjiba T, Mohamedi M, Dao LH (2008) J Electrochem Soc 155:A115
Bordjiba T, Mohamedi M, Dao LH (2008) Adv Mater 20:815
Aïssa B, Hamoudi Z, Takahashi H, Tohji K, Mohamedi M, El Khakani MA (2009) Electrochem Commun 11:862
Frackowiak E, Béguin F (2001) Carbon 39:937
Kinoshita K (1988) Carbon-electrochemical and physicochemical properties. Wiley, New York
Shao Y, Yin G, Zhang J, Gao Y (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:5853
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Natural Sciences Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the Fonds Québécois pour la Recherche en Nature et Technologie (FQRNT), NanoQuébec, and the Centre Québécois pour les Matériaux Fonctionnels (CQMF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bordjiba, T., Mohamedi, M. Molding versus dispersion: effect of the preparation procedure on the capacitive and cycle life of carbon nanotubes aerogel composites. J Solid State Electrochem 15, 765–771 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1155-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1155-0