Abstract
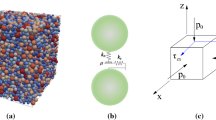
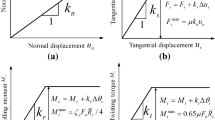
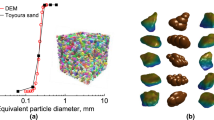
Understanding the evolution of microstructure in granular soils can provide significant insights into constitutive modeling of soil liquefaction. In this study, micromechanical perspectives of the liquefaction process are investigated using the Discrete Element simulation. It is observed that during various stages of undrained cyclic loading, the soil exhibits definitive change in the load-bearing structure, indicated by evolution of the coordination number and non-affine displacements. A new particle-void fabric, termed as “centroid distance”, is also proposed to quantify the evolution of particles and voids distribution in the granular packing. The fabric index is found to have strong correlation with cyclic mobility and post-liquefaction deformation of granular soils. Evolution of the fabric index indicates that particles and voids redistribute irreversibly before and after liquefaction. A highly anisotropic particle-void structure and loading-bearing capacity can be formed in the post liquefaction stage.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashmawy, A.K., Sukumaran, B., Hoang, V.V.: Evaluating the influence of particle shape on liquefaction behavior using discrete element modeling. Proc. 13th Int. Offshore Polar Eng. Conf. ISOPE Honol. 2, 542–549 (2003)
Bray, J., Sancio, R.: Assessment of the liquefaction susceptibility of fine-grained soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 132(9), 1165–1177 (2006)
Castro, G.: Liquefaction and cyclic mobility of saturated sands. J. Geotech. Eng. Div. ASCE 101(GT6), 551–569 (1975)
Christoffersen, J., Mehrabadi, M.M., Nemat-Nasser, S.: A micromechanical description of granular material behavior. J. Appl. Mech. 48, 339–44 (1981)
Dafalias, Y.F., Manzari, M.T.: Simple plasticity sand model accounting for fabric change effect. J. Eng. Mech. ASCE 130(6), 622–634 (2004)
Elgamal, A., Yang, Z., Parra, E., Ragheb, A.: Modeling of cyclic mobility in saturated cohesionless soils. Int. J. Plast. 19(6), 883–905 (2003)
Goldenberg, C., Tanguy, A., Barrat, J.L.: Particle displacements in the elastic deformation of amorphous materials: local fluctuations vs. non-affine field. Europhys. Lett. 80, 16003 (2007)
Gu, X., Huang, M., Qian, J.: DEM investigation on the evolution of microstructure in granular soils under shearing. Granul. Matter 16, 91–106 (2014)
Guo, N., Zhao, J.: The signature of shear-induced anisotropy in granular media. Comput. Geotech. 47, 1–15 (2013)
Idriss, I.M., Boulanger, R.W.: Semi-empirical procedures for evaluating liquefaction potential during earthquakes. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 26, 115–130 (2006)
Idriss, I.M., Boulanger, R.W.: Soil Liquefaction During Earthquakes. Earthquake Engineering Research Institute, Oakland, California (2008)
Ishihara, K.: Liquefaction and flow failure during earthquakes. Géotechnique 43(3), 351–415 (1993)
Kramer, S.L.: Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering, 1st edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey (1996)
Li, X., Li, X.S.: Micro-macro quantification of the internal structure of granular materials. J. Eng. Mech. ASCE 135(7), 641–656 (2009)
Mitchell, J., Soga, K.: Fundamentals of Soil Behavior. Wiley, New York (2005)
Ng, T.T., Dobry, R.: Numerical simulations of monotonic and cyclic loading of granular soil. J. Geotech. Eng. ASCE 120(2), 388–403 (1994)
O’Sullivan, C.: Particulate Discrete Element Modelling, A Geomechanics Perspective. Spon Press, Oxon, UK (2011)
Radjaï, F., Wolf, D.E., Jean, M., Moreau, J.J.: Bimodal character of stress transmission in granular packings. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 61–64 (1998)
Rothenburg, L., Bathurst, R.J.: Analytical study of induced anisotropy in idealized granular materials. Géotechnique 39(4), 601–614 (1989)
Satake, M.: Fabric tensor in granular materials. In: Proceedings IUTAM Conference on Deformation and Failure of Granular Materials, Delft, pp. 63–67 (1982)
Seed, H.B., Lee, K.L.: Liquefaction of saturated sands during cyclic loading. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. ASCE 92(SM6), 105–134 (1966)
Seed, R.B., Cetin, K.O., Moss, R.E.S., et al.: Recent advances in soil liquefaction engineering: a unified and consistent framework. EERC Report 2003-06, University of California, Berkeley (2003)
Shamoto, Y., Zhang, J.M., Goto, S.: Mechanism of large post-liquefaction deformation in saturated sand. Soils Found. 37(2), 71–80 (1997)
Shire, T., O’Sullivan, C., Barreto, D., Gaudray, G.: Quantifying stress-induced anisotropy using inter-void constrictions. Géotechnique 63(1), 85–91 (2013)
Sitar N.: Slope stability in coarse sediments. In: Yong, R.N. (ed.) Special Publication on Geological Environmental and Soil Properties, ASCE, pp. 82–98 (1983)
Sitharam, T.G., Vinod, J.S., Ravishankar, B.V.: Post-liquefaction undrained monotonic behavior of sands: experiments and DEM simulations. Géotechnique 59(9), 739–749 (2009)
Šmilauer, V., Catalano, E., Chareyre, B., Dorofeenko, S., Duriez, J, Gladky, A., Kozicki, J., Modenese, C., Scholtès, L., Sibille, L., Stránský, J., Thoeni, K.: Yade documentation. In: Šmilauer V., (ed.) The Yade Project, 1st edn. http://yade-dem.org/doc/ (2010)
Thornton, C.: Numerical simulations of deviatoric shear deformation of granular media. Géotechnique 50(1), 43–53 (2000)
Vaid, Y.P., Sivathayalan, S.: Static and cyclic liquefaction potential of Fraser Delta sand in simple shear and triaxial tests. Can. Geotech. J. 33(2), 281–289 (1996)
Vaid, Y.P., Stedman, J.D., Sivathayalan, S.: Confining stress and static shear effects in cyclic liquefaction. Can. Geotech. J. 38(3), 580–591 (2001)
Wang, G., Xie, Y.: Modified bounding surface hypoplasticity model for sands under cyclic loading. J. Eng. Mech. ASCE 140(1), 91–104 (2014)
Wang, Z.L., Dafalias, Y.F., Shen, C.K.: Bounding surface hypoplasticity model for sand. J. Eng. Mech. ASCE 116(5), 983–1001 (1990)
Yang, J., Sze, H.Y.: Cyclic behaviour and resistance of saturated sand under non-symmetrical loading conditions. Géotechnique 61(1), 59–73 (2011)
Ye, J.H., Wang, G.: Seismic dynamics of offshore breakwater on liquefiable seabed foundation. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 76, 86–99 (2015)
Youd, T.L.: Packing changes and liquefaction susceptibility. J. Geotech. Eng. Div. ASCE 103(8), 918–922 (1977)
Youd, T.L., Idriss, I.M., Andrus, R.D., Ignacio, A., Gonzalo, C., Christian, J.T., Dobry, R., Finn, W.D.L., et al.: Liquefaction resistance of soils: summary report from the 1996 NCEER and 1998 NCEER/NSF workshops on evaluation of liquefaction resistance of soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. ASCE 127(10), 297–313 (2001)
Zhao, J., Guo, N.: Unique critical state characteristics in granular media considering fabric anisotropy. Géotechnique 63, 695–704 (2013)
Zienkiewicz, O.C., Chan, A.H.C., Pastor, M., Schrefler, B.A., Shiomi, T.: Computational Geomechanics: With Special Reference to Earthquake Engineering. Wiley, New York (1999)
Acknowledgments
The study was financially supported by General Research Fund Grant No. 16213615, Research Project Competition (UGC/HKUST) Grant No. RPC11EG27 and Theme-based Research Scheme Grant No. T22-603/15N from Hong Kong Research Grants Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Micro origins for macro behavior of granular matter.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Wei, J. Microstructure evolution of granular soils in cyclic mobility and post-liquefaction process. Granular Matter 18, 51 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-016-0621-5
Received:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-016-0621-5