Abstract
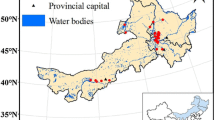
Temporal and spatial distributions of dissolved organic carbon (DOC), dissolved organic nitrogen (DON), chlorophyll-a and inorganic nitrogen were investigated in two small mountainous lakes (Lake Hongfeng and Baihua), on the Southwestern China Plateau, based on almost 2 years’ field observation. DOC concentrations ranged from 163 μM to 248 μM in Lake Hongfeng and from 143 μM to 308 μM in Lake Baihua, respectively, during the study period. DON concentrations ranged from 7 μM to 26 μM in Lake Hongfeng and from 14 μM to 47 μM in Lake Baihua. DOC showed vertical heterogeneity with higher concentrations in the epilimnion than in the hypolimnion during the stratification period. The DON concentration profiles appeared to be more variable than the DOC profiles. Apparent DON maxima occurred in the upper layer of water. In Lake Hongfeng, DOC concentration in the surface water was highest at the end of spring and early summer. DON concentration was 2–5 μM higher in May 2003 and in June 2004 than in adjacent months. DOC and chlorophyll-a concentrations were significantly correlated (r = 0.79, P < 0.05). The period of highest concentrations of DOC in Lake Hongfeng was also the season of concentrated rainfall. Algae activity and allochthonous input might result in an increase of DOC and DON concentrations together. In Lake Baihua, the maximum concentrations of DOC and DON in the surface water occurred simultaneously in May 2003 and February 2004. DOC concentrations were significantly correlated with DON (r = 0.90, P < 0.01), indicating the common sources. Allochthonous input, biological processes, stratification and mixing were the most important factors controlling the distributions and cycling of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and inorganic nitrogen in these two lakes. Inference from the corresponding vertical distributions of DOM and inorganic nitrogen indicated that DOM played potential roles in the internal loading of nitrogen and metabolism in the water body in these small lakes. The carbon/nitrogen (C/N) ratio showed a potential significance for tracing the source and biogeochemical processes of DOM in the lakes. These results are of significance in the further understanding of biogeochemical cycling and environmental effects of DOM and nitrogen in lake ecosystems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber LB, Leenheer JA, Noyes TI, Stiles EA (2001) Nature and transformation of dissolved organic matter in treatment wetlands. Environ Sci Technol 35:4805–4816
Bronk DA (2002) Dynamics of DON. In: Hansell DA, Carlson CA (eds) Biogeochemistry of marine dissolved organic matter. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 153–249
Brooks PD, O’Reilly CM, Diamond SA, Campbell DH, Knapp R, Bradford D, Corn PS, Hossack B, Tonnessen K (2005) Spatial and temporal variability in the amount and source of dissolved organic carbon: implications for ultraviolet exposure in amphibian habitats. Ecosystems 8:478–487
Butt SB, Riaz M, Iqbal MZ (2001) Simultaneous determination of nitrite and nitrate by normal phase ion-pair liquid chromatography. Talanta 55:789–797
Charles S, Hopkinson JR, Fry B, Amy LN (1997) Stoichiometry of dissolved organic matter dynamics on the continental shelf of the northeastern USA. Cont Shelf Res 17:473–489
Cowie GL, Hedges JI (1994) Biochemical indication of diagenetic alteration in natural organic matter mixtures. Nature 369:304–307
Doig LE, Liber K (2006) Influence of dissolved organic matter on nickel bioavailability and toxicity to Hyalella azteca in water-only exposures. Aquat Toxicol 76:203–216
Ertel JR, Hedges JI, Devol AH, Richey JE, Nazare Goes Ribeiro M (1986) Dissolved humic substances of the Amazon River system. Limnol Oceanogr 31:739–754
Fukushima T, Park JC, Imai A, Matsushige K (1996) Dissolved organic carbon in a eutrophic lake; dynamics, biodegradability and origin. Aquat Sci 58:139–157
Hama T, Handa N (1983) The seasonal variation of organic constituents in a eutrophic lake, Lake Suwa, Japan. Part II. Dissolved organic matter. Arch Hydrobiol 98:443–462
Herczeg A L (1988) Early diagenesis of organic matter in lake sediments: a stable C isotope study of pore waters. Chem Geol 72:199–209
Hinton MJ, Schiff SL, English MC (1997) The significance of storms for the concentration and export of dissolved organic carbon from two Precambrian Shield catchments. Biogeochemistry 36:67–88
Hopkinson C, Cifuentes L (1993) DON subgroup report. Mar Chem 41:23–36
Houser JN, Bade DL, Cole JJ, Pace ML (2003) The dual influences of dissolved organic carbon on hypolimnetic metabolism: organic substrate and photosynthetic reduction. Biogeochemistry 64:247–269
Hutchinson GE (1938) On the relation between the oxygen deficit and the productivity and typology of lakes. Int Rev Gesamten Hydrobiol 36:336–355
Imai A, Fukushima T, Matsushige K, Kim YH (2001) Fractionation and characterization of dissolved organic matter in a shallow eutrophic lake, its inflowing rivers, and other organic matter sources. Water Res 35:4019–4028
Jin XC, Tu QY (1990) Investigation criterion of eutrophication in lakes (in Chinese), 2nd edn. Chinese Environment Science Press, Beijing, pp 268–270
Kim B, Choi K, Kim C, Lee UH, Kim YH (2000) Effects of the summer monsoon on the distribution and loading of organic carbon in a deep reservoir Lake Soyang, Korea Water Res 34:3495–3504
Kim C, Nishimura Y, Nagata T (2006) Role of dissolved organic matter in hypolimnetic mineralization of carbon and nitrogen in a large, monomictic lake. Limnol Oceanogr 51:70–78
Koroleff F (1983) Determination of ammonia. In: Grasshoff K, Ehrhardt M, Kremling K (eds) Methods of seawater analysis, 2nd edn. Verlag Chemie, Florida, pp 150–157
Lehmann MF, Bernasconi SM, McKenzie JA (2004) Seasonal variation of the δ13C and δ15N of particulate and dissolved carbon and nitrogen in Lake Lugano: constraints on biogeochemical cycling in a eutrophic lake. Limnol Oceanogr 49:415–429
Lobbes JM, Fitznar HP, Kattner G (2000) Biogeochemical characteristics of dissolved and particulate organic matter in Russian rivers entering the Arctic Ocean. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:2973–2983
Mague TH, Friberg E, Hudges DJ, Morris I (1980) Extracellular release of carbon by marine phyto-plankton; a physiological approach. Limnol Oceanogr 25:262–279
Mash H, Westerhoff PK, Baker LA, Nieman RA, Nguyen ML (2004) Dissolved organic matter in Arizona reservoirs: assessment of carbonaceous sources. Org Geochem 35:831–843
Mostofa KMG, Yoshioka T, Konohira E, Tanoue E, Hayakawa K, Takahashi M (2005) Three-dimensional fluorescence as a tool for investigating the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in the Lake Biwa watershed. Limnology 6:101–115
Nakashima S, Yamada Y, Tada K (2007) Characterization of the water quality of dam lakes on Shikoku Island, Japan. Limnology 8:1–22
Norrman B, Zweifel UL, Hopkinson CS Jr, Fry B (1995) Production and utilization of dissolved organic carbon during an experimental diatom bloom. Limnol Oceanogr 40:898–907
Ogawa H, Fukuda R, Koike I (1999) Vertical distributions of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in the Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Res I 46:1809–1826
Ohlenbusch G, Kumke MU, Frimmel FH (2000) Sorption of phenols to dissolved organic matter investigated by solid phase microextraction. Sci Total Environ 253:63–74
Palmstrom NS, Carlson RE, Cooke DG (1988) Potential links between eutrophication and the formation of carcinogens in drinking waters. Lake Res Manage 4:1–15
Parks SJ, Barker LA (1997) Sources and transport of organic carbon in an Arizona river-reservoir system. Water Res 31:1751–1759
Ritchie JD, Perdue EM (2003) Proton-binding study of standard and reference fulvic acids, humic acids, and natural organic matter. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:85–96
Schindler DW, Curtis PJ, Bayley SE, Parker BR, Beaty KG, Stainton MP (1997) Climate-induced changes in the dissolved organic carbon budgets of boreal lakes. Biogeochemistry 36:9–28
State Environmental Protection Agency (SEPA) of China (2002) Monitor and analysis method of water and wastewater. Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Sugiyama Y, Anegawa A, Kumagai T, Harita Y, Hori T, Sugiyama M (2004) Distribution of dissolved organic carbon in lakes of different trophic types. Limnology 5:165–176
Tanoue E, Midorikawa T (1995) Detection, characterization and dynamics of dissolved organic ligands in oceanic waters. In: Sakai H, Nozaki Y (eds) Biogeochemical processes and ocean flux in the western pacific. Terra Scientific Publishing, Tokyo, pp 201–224
Thomas JD (1997) The role of dissolved organic matter, particularly free amino acids and humic substances, in freshwater ecosystems. Freshw Biol 38:1–36
Wetzel RG (1972) The role of carbon in hard-water marl lakes. In: Likens GE (ed) Nutrients and eutrophication: the limiting-nutrient controversy. Special symposium. Am Soc Limnol Oceanogr 1:84–97
Wu FC, Tanoue E (2001) Isolation and partial characterization of dissolved copper-complexing ligands in streamwaters. Environ Sci Technol 35:3646–3652
Wu F, Qing H, Wan G (2001) Regeneration of N, P and Si near the sediment/water interface of lakes from Southwestern China Plateau. Water Res 35:1334–1337
Xiao HY, Liu CQ, Li SL, Wang SL (2002) Nitrogen biogeochemical cycles in lakes with strong hydraulic power during summer stratification: a case study of Hongfeng Lake in Guizhou Province, Southwest China (in Chinese). Geochimica 31:571–576
Yoshioka T, Ueda S, Khodzher T, Bashenkhaeva N, Korovyakova I, Sorokovikova L, Gorbunova L (2002) Distribution of dissolved organic carbon in Lake Baikal and its watershed. Limnology 3:159–168
Zhang W (1999) Environmental characteristics and eutrophication of Lake Hongfeng and Baihua (in Chinese). Guizhou Science and Technology Press, China, pp 57–137
Acknowledgments
This research was jointly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (40525011, 40632011, 40703022) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (kzcx2-yw-102). We would like to thank Dr. K.M.G. Mostofa for his helpful comments on the earlier version of this manuscript. We are grateful to two anonymous reviewers for their insightful and helpful comments and suggestions. The experiments complied with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Wu, F., Liu, C. et al. Temporal and spatial distributions of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in two small lakes on the Southwestern China Plateau. Limnology 9, 163–171 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-008-0241-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-008-0241-9