Abstract
Seepage through dikes under steady-state conditions is a classical problem in geotechnics. Several analytical solutions exist for estimating seepage through 2D dikes. In practice, many dikes have a limited length in the third dimension. This is particularly true for water flow through a waste rock barricade to hold backfill slurry in underground stopes. Three-dimensional solutions are necessary to evaluate seepage through 3D trapezoidal dikes. In this study, existing 2D solutions developed for estimating seepage through 2D dikes under steady-state conditions are presented and generalized for 3D dikes. The validity of these 3D generalized solutions is tested by numerical modeling with FLAC3D. Results show that the 3D solution based on a generalization of the Dupuit solution predicts seepage variation as a function of upstream hydraulic head well, but fails to describe seepage variation as a function of downstream hydraulic head. Further analyses reveal that the Dupuit model involves assumptions by which the flow path can be underestimated and the mean flow cross-section from the bottom to the top surface of the downstream water tends to be overestimated. The 3D generalized Dupuit solution was therefore modified by adding two calibration coefficients, one for the flow path length and another for the mean flow cross-section. The two calibration coefficients were then obtained by calibration against a few 3D numerical results. The validity of the proposed and calibrated analytical solution was then tested against additional numerical results. Finally, both the numerical model and the proposed calibrated analytical solutions were validated by laboratory test results.
Zusammenfassung
Die stationäre Dammdurchströmung ist ein klassisches Problem der Geotechnik. Zur Abschätzung der Dammdurchströmung existieren ver-schiedene zweidimensionale analytische Lösungsverfahren. In der Praxis haben viele Deiche eine begrenzte Länge in der 3. Dimension. Dies gilt insbesondere für die Wasser¬strömung durch eine Schüttsteinbarrikade zum Rückhalt von Versatz¬schlämmen in Stollen. Zur Bewertung der Versickerung durch trapezförmige Deiche sind dreidimensionale Lösungsverfahren notwendig. Diese Arbeit stellt bestehende 2D-Lösungsverfahren vor, die zur Abschätzung der stationären Dammdurchströmung entwickelt wurden und verallgemeinert sie für dreidimensionale Anwendung bei längeren Dämmen. Die Gültigkeit dieser 3D-Lösungen wurde durch die numerische Modellierung mit FLAC3D getestet. Die Ergebnisse zeigen, dass die dreidimensionale Lösung, die auf einer Verallgemeinerung der Dupuit¬lösung basiert, die Sickerwassermenge als Funktion des oberstromigen hydraulischen Potentials gut vorhersagt, aber die Sickerwassermenge als Funk¬tion der unterstromigen hydraulischen Potentials schlecht abbildet. Weiter¬führende Anlaysen zeigen, dass das Dupuitmodell Annahmen enthält, durch die der Fließweg unterschätzt und der mittlere Fließquer¬schnitt vom Unter- zum Oberwasser tenden¬ziell überschätzt werden. Die verallge-meinerte 3D-Dupuitlösung wird durch zwei zusätzliche Kalibrier-koeffizienten modifiziert. Ein Koeffizient repräsentiert die Fließstrecke und der andere den mittleren Fließquerschnitt. Die beiden Koeffizienten werden durch die Kalibrierung nume¬rischer 3D-Modelle ermittelt. Die Gültigkeit der vorgeschlagenen und kalibrierten analytischen Lösung wird anhand weiterer numerischer Modellierungen getestet. Schließlich werden sowohl das numerische Modell als auch die vorgeschlagenen kalibrierten analytischen Lösungen durch Labortests validiert.
Resumen
La infiltración a través de diques en condiciones estables es un problema clásico en geotecnia. Existen varias soluciones analíticas para estimar la infiltración a través de diques 2D. En la práctica, muchos diques tienen una longitud limitada en la tercera dimensión. Esto es especialmente cierto en el caso del flujo de agua a través de una barricada de roca estéril para retener el lodo de relleno en las excavaciones subterráneas. Las soluciones tridimensionales son necesarias para evaluar la infiltración a través de diques trapezoidales 3D. En este trabajo, se presentan las soluciones 2D existentes desarrolladas para estimar la infiltración a través de diques 2D en condiciones de estado estacionario y se generalizan para los diques 3D. La validez de estas soluciones generalizadas en 3D se comprueba mediante modelización numérica con FLAC3D. Los resultados muestran que la solución 3D basada en una generalización de la solución Dupuit predice bien la variación de la infiltración en función de la altura hidráulica aguas arriba, pero no describe la variación de la infiltración en función de la altura hidráulica aguas abajo. Otros análisis revelan que el modelo de Dupuit implica suposiciones por las que la trayectoria del flujo puede ser subestimada y la sección transversal media del flujo desde el fondo hasta la superficie superior del agua aguas abajo tiende a ser sobreestimada. Debido a ello, la solución 3D generalizada de Dupuit es modificada añadiendo dos coeficientes de calibración, uno para la longitud de la trayectoria del flujo y otro para la sección transversal del flujo medio. Los dos coeficientes de calibración se obtienen entonces mediante la calibración con algunos resultados numéricos en 3D. La validez de la solución analítica propuesta y calibrada se comprueba con resultados numéricos adicionales. Por último, tanto el modelo numérico como las soluciones analíticas calibradas propuestas se validan mediante resultados de pruebas de laboratorio.
摘要
摘要: 通过堤坝的稳态渗流是土力学中的一个经典问题。相应的计算穿过二维堤坝的渗流解析解也已经有几个了。而在实际中, 坝体在第三个方向的长度总是有限的。在地下采空区用废石堆建的用于保持充填泥浆的的堤坝(挡墙)尤为如此。因此, 拥有适用于估算三维坝体渗流的三维解析解是非常有必要的。本文对已有的穿过二维堤坝的二维稳态渗流解先做了简单的介绍, 然后对其进行了三维推广。被推广而得到的三维解析解的有效性通过和FLAC3D数值模拟结果进行了比较和检验。比较和检验的结果表明, 基于Dupuit解析解推广而来的三维解能很好地预测渗流随上游压力水头的变化情况, 但无法描述渗流随下游压力水头的变化。进一步分析表明, Dupuit模型包含的一些假设会让渗流的路径被低估, 而让靠近下游从底部到顶部的平均过水断面被高估。为解决这个问题, 基于Dupuit模型推广而来的三维解需要两个校正系数, 一个校正渗流路径长度, 另一个校正平均过水断面。两个校正参数的数值先通过与几个三维数值模拟结果相比较而获得并固定下来, 作为我们所提出来的三维渗流解析解。其有效性则通过和新的数值模拟结果相比较, 以得到进一步地验证。最后, 我们所用的数值模型和我们所提出的三维渗流解析解都通过和室内实验结果相比较而得到了验证。

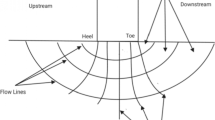
adapted from Harr 1962)

adapted from Harr 1962)










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubertin M, Mbonimpa M, Bussière B, Chapuis RP (2003) A model to predict the water retention curve from basic geotechnical properties. Can Geotech J 40(6):1104–1122. https://doi.org/10.1139/t03-054
Bowles JE (1984) Physical and geotechnical properties of soils, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Casagrande L (1932) Naeherungsmethoden zur bestimmung von art und menge der sickerung durch geschuettete dämme (approximate methods to determine the seepage through spillway dikes). Institute of Technology, Vienna (in German)
Chapuis RP (1990) Sand–bentonite liners: field control methods. Can Geotech J 27:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1139/T10-035
Chapuis RP (2011) Steady state groundwater seepage in sloping unconfined aquifers. Bull Eng Geol Environ 70:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0282-2
Chapuis RP, Aubertin M (2001) A simplified method to estimate saturated and unsaturated seepage through dikes under steady-state conditions. Can Geotech J 38(6):1321–1328. https://doi.org/10.1139/t01-068
Chapuis RP, Chenaf D, Bussière B, Aubertin M, Crespo R (2001) A user’s approach to assess numerical codes for saturated and unsaturated seepage conditions. Can Geotech J 38(5):1113–1126. https://doi.org/10.1139/t01-055
Chen Q, Zhang LM (2006) Three-dimensional analysis of water infiltration into the Gouhou rockfill dam using saturated unsaturated seepage theory. Can Geotech J 43(5):449–461. https://doi.org/10.1139/t06-011
Crespo R (1994) Modélisation des écoulements à travers les ouvrages de retenue et de confinement des résidus miniers par un logiciel d’éléments finis. MScA thesis, École Polytechnique de Montréal, Montréal
Darcy H (1856) Les fontaines publiques de la ville de Dijon. Dalmont, Paris
Dupuit J (1863) Études théoriques et pratiques sur le mouvement des eaux dans les canaux découverts et à travers les terrains perméables, 2nd edn. Dunod, Paris
Harr ME (1962) Groundwater and seepage. McGraw-Hill, New York
Itasca Consulting Group, Inc (2017) FLAC3D—fast Lagrangian analysis of continua in three-dimensions, Ver. 6.0. Minneapolis
Iterson FKTV (1917) Eenige theoretische beschouwingen over kwel, De Ingenieur
Li L (2013) A simple solution to assess pore-water pressure in barricades made of waste rock. CIM J 4(1):53–60
Li L, Aubertin M (2011) Limit equilibrium analysis for the design of backfilled stope barricades made of waste rock. Can Geotech J 48(11):1713–1728. https://doi.org/10.1139/t11-063
Li L, Ouellet S, Aubertin M (2009) A method to evaluate the size of backfilled stope barricades made of waste rock. Proc, 62nd Canadian geotechnical conf and 10th joint CGS/IAH-CNC Groundwater specialty conf. Canadian Geotechnical Soc, Richmond, pp 497–503
Pavlovsky NN (1931) Seepage through earth dikes. Instit. Gidrotekhniki i Melioratsii, Leningrad
Richards KS, Reddy KR (2007) Critical appraisal of piping phenomena in earth dams. Bull Eng Geol Environ 66(4):381–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-007-0095-0
Schaffernak F (1917) Über die Standicherheit durchlaessiger geschuetteter Dämme. Allge, Eauzeitung
Yang PY, Brochu-Baekelmans M, Li L, Aubertin M (2014) An improved solution for sizing barricades made of waste rock to retain cemented paste backfill. Proc, 67th Canadian geotech conf, Regina, Canada
Yang PY, Li L, Aubertin M, Brochu-Baekelmans M, Ouellet S (2017) Stability analyses of waste rock barricades designed to retain paste backfill. Int J Geomech 17(3):04016079. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000740
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC 402318), Fonds de Recherche du Québec - Nature et Technologies (FRQNT 2015-MI-191676), and the partners of the Research Institute on Mines and Environment (RIME UQAT - Polytechnique; http://rime-irme.ca). The anonymous reviewers are gratefully acknowledged for their critical questions and constructive comments, which helped the authors significantly improve the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, Y., Li, L. & Chapuis, R.P. Analytical, Numerical and Experimental Studies on Steady-State Seepage Through 3D Rockfill Trapezoidal Dikes. Mine Water Environ 40, 931–942 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-021-00798-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-021-00798-8