Abstract
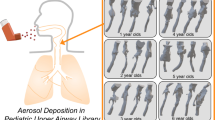
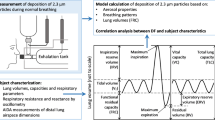
As a human grows from birth to adulthood, both airway anatomy and breathing conditions vary, altering the deposition rate and pattern of inhaled aerosols. However, deposition studies have typically focused on adult subjects, results of which may not be readily extrapolated to children. This study numerically evaluated the age-related effects on the airflow and aerosol dynamics in image-based nose–throat models of a 10-day-old newborn, a 7-month-old infant, a 5-year-old child, and a 53-year-old adult. Differences in airway physiology, breathing resistance, and aerosol filtering efficiency among the four models were quantified and compared. A high-fidelity fluid-particle transport model was employed to simulate the multi-regime airflows and particle transport within the nasal–laryngeal airways. Ultrafine particles were evaluated under breathing conditions ranging from sedentary to heavy activities. Results of this study indicate that the nasal–laryngeal airways at different ages, albeit differ significantly in morphology and dimension, do not significantly affect the total deposition fractions or maximum local deposition enhancement for ultrafine aerosols. Further, the deposition partitioning in the sub-regions of interest is different among the four models. Results of this study corroborate the use of the in vivo-based diffusion parameter (D 0.5 Q −0.28) over the replica-based parameter in correlating nasal–laryngeal depositions of ultrafine aerosols. Improved correlations have been developed for the four age groups by implementing this in vivo-based diffusion parameter as well as the Cunningham correction factor.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M. D., and O. G. Raabe. Slip correction measurements of spherical solid aerosol particles in an improved Millikan apparatus. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 4:269–286, 1985.
Asgharian, B., M. G. Ménache, and F. J. Miller. Modeling age-related particle deposition in humans. J. Aerosol Med. 17(3):213–224, 2004.
Becquemin, M. H., D. L. Swift, A. Bouchikhi, M. Roy, and A. Teillac. Particle deposition and resistance in the noses of adults and children. Eur. Respir. J. 4(6):694–702, 1991.
Bennett, W. D., and K. L. Zeman. Effect of race on fine particle deposition for oral and nasal breathing. Inhalation Toxicol. 17(12):641–648, 2005.
Bennett, W. D., K. L. Zeman, and A. M. Jarabek. Nasal contribution to breathing and fine particle deposition in children versus adults. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 71(3):227–237, 2008.
Bobak, M., and D. A. Leon. The effect of air pollution on infant mortality appears specific for respiratory causes in the postneonatal period. Epidemiology 10(6):666–670, 1999.
Brancatisano, T., P. W. Collett, and L. A. Engel. Respiratory movements of the vocal cords. J. Appl. Physiol. 54(4):1269–1276, 1983.
Bridger, G. P. Physiology of the nasal valve. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 92(6):543–553, 1970.
Bridger, G. P., and D. F. Proctor. Maximum nasal inspiratory flow and nasal resistance. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 79(3):481–488, 1970.
Cheng, Y. S. Aerosol deposition in the extrathoracic region. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 37:659–671, 2003.
Cheng, K. H., Y. S. Cheng, H. C. Yeh, R. A. Guilmette, S. Q. Simpson, S. Q. Yang, and D. L. Swift. In vivo measurements of nasal airway dimensions and ultrafine aerosol depositing in human nasal and oral airways. J. Aerosol Sci. 27:785–801, 1996.
Cheng, K. H., Y. S. Cheng, H. C. Yeh, and D. L. Swift. Deposition of ultrafine aerosols in the head airways during natural breathing and during simulated breath holding using replicate human upper airway casts. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 23(3):465–474, 1995.
Cheng, Y. S., S. M. Smith, H. C. Yeh, D. B. Kim, K. H. Cheng, and D. L. Swift. Deposition of ultrafine aerosols and thoron progeny in peplicas of nasal airways of young children. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 23(4):541–552, 1995.
Cheng, Y. S., Y. F. Su, H. C. Yeh, and D. L. Swift. Deposition of Thoron progeny in human head airways. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 18:359–375, 1993.
Cheng, Y. S., Y. Yamada, H. C. Yeh, and D. L. Swift. Diffusional deposition of ultrafine aerosols in a human nasal cast. J. Aerosol Sci. 19:741, 1988.
Cheng, Y. S., H. C. Yeh, R. A. Guilmette, S. Q. Simpson, K. H. Cheng, and D. L. Swift. Nasal deposition of ultrafine particles in human volunteers and its relationship to airway geometry. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 25(3):274–291, 1996.
Cohen Hubal, E. A., J. S. Kimbell, and P. S. Fedkiw. Incorporation of nasal-lining mass-transfer resistance into a CFD model for prediction of ozone dosimetry in the upper respiratory tract. Inhalation Toxicol. 8(9):831–857, 1996.
Crawford, D. J. Identifying critical human subpopulations by age groups: radioactivity and the lung. Phys. Med. Biol. 27:539–552, 1982.
Diot, P., L. B. Palmer, A. Smaldone, J. Decelie-Germana, R. Grimson, and G. C. Smaldone. RhDNase I aerosol deposition and related factors in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 156(5):1662–1668, 1997.
Everard, M. L. Inhalation therapy for infants. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 55(7):869–878, 2003.
Faustman, E. M., S. M. Silbernagel, R. A. Fenske, T. M. Burbacher, and R. A. Ponce. Mechanisms underlying children’s susceptibility to environmental toxicants. Environ. Health Perspect. 108:13–21, 2000.
Fleming, S., M. Thompson, R. Stevens, C. Heneghan, A. Plüddemann, I. Maconochie, L. Tarassenko, and D. Mant. Normal ranges of heart rate and respiratory rate in children from birth to 18 years of age: a systematic review of observational studies. Lancet 377(9770):1011–1018, 2011.
Fodil, R., L. Brugel-Ribere, C. Croce, G. Sbirlea-Apiou, C. Larger, J. F. Papon, C. Delclaux, A. Coste, D. Isabey, and B. Louis. Inspiratory flow in the nose: a model coupling flow and vasoerectile tissue distensibility. J. Appl. Physiol. 98(1):288–295, 2005.
Gagliardi, L., F. Rusconi, M. Castagneto, G. L. N. Porta, S. Razon, and A. Pellegatta. Respiratory rate and body mass in the first three years of life. Arch. Dis. Child. 76(2):151–154, 1997.
Garcia, G. J. M., E. W. Tewksbury, B. A. Wong, and J. S. Kimbell. Interindividual variability in nasal filtration as a function of nasal cavity geometry. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 22(2):139–155, 2009.
Ghalati, P. F., E. Keshavarzian, O. Abouali, A. Faramarzi, J. Y. Tu, and A. Shakibafard. Numerical analysis of micro- and nano-particle deposition in a realistic human upper airway. Comput. Biol. Med. 42(1):39–49, 2012.
Ginsberg, G., B. Foos, R. B. Dzubow, and M. Firestone. Options for incorporating children’s inhaled dose into human health risk assessment. Inhalation Toxicol. 22(8):627–647, 2010.
Ginsberg, G. L., B. P. Foos, and M. P. Firestone. Review and analysis of inhalation dosimetry methods for application to children’s risk assessment. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 68(8):573–615, 2005.
Golshahi, L., W. H. Finlay, J. S. Olfert, R. B. Thompson, and M. L. Noga. Deposition of inhaled ultrafine aerosols in replicas of nasal airways of infants. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 44(9):741–752, 2010.
Gradon, L., and C. P. Yu. Diffusional particle deposition in the human nose and mouth. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 11:213–220, 1989.
Grgic, B., W. H. Finlay, P. K. P. Burnell, and A. F. Heenan. In vitro intersubject and intrasubject deposition measurements in realistic mouth-throat geometries. J. Aerosol Sci. 35(8):1025–1040, 2004.
Guilmette, R. A., Y. S. Cheng, H. C. Yeh, and D. L. Swift. Deposition of 0.005–12 micrometer monodisperse particles in a computer-milled, MRI-based nasal airway replica. Inhalation Toxicology 6(Suppl. 1):395–399, 1994.
Haussermann, S., A. G. Bailey, M. R. Bailey, G. Etherington, and M. Youngman. The influence of breathing patterns on particle deposition in a nasal replicate cast. J. Aerosol Sci. 33(6):923–933, 2002.
Inthavong, K., H. Wen, Z. F. Tian, and J. Y. Tu. Numerical study of fibre deposition in a human nasal cavity. J. Aerosol Sci. 39(3):253–265, 2008.
Inthavong, K., K. Zhang, and J. Y. Tu. Numerical modelling of nanoparticle deposition in the nasal cavity and the tracheobronchial airway. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 14(7):633–643, 2011.
Janssens, H. M., J. C. de Jongste, W. J. Fokkens, S. G. Robben, K. Wouters, and H. A. Tiddens. The Sophia Anatomical Infant Nose-Throat (Saint) model: a valuable tool to study aerosol deposition in infants. J. Aerosol Med. 14(4):433–441, 2001.
Kelly, J. T., B. Asgharian, J. S. Kimbell, and B. Wong. Particle deposition in human nasal airway replicas manufactured by different methods. Part I: inertial regime particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 38:1063–1071, 2004.
Kelly, J. T., B. Asgharian, J. S. Kimbell, and B. Wong. Particle deposition in human nasal airway replicas manufactured by different methods. Part II: ultrafine particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 38:1072–1079, 2004.
Kesavanathan, J., R. Bascom, and D. L. Swift. The effect of nasal passage characteristics on particle deposition. J. Aerosol Med. 11(1):27–39, 1998.
Kimbell, J. S., J. H. Overton, R. P. Subramaniam, P. M. Schlosser, K. T. Morgan, R. B. Conolly, and F. J. Miller. Dosimetry modeling of inhaled formaldehyde: binning nasal flux predictions for quantitative risk assessment. Toxicol. Sci. 64(1):111–121, 2001.
Kundoor, V., and R. N. Dalby. Effect of formulation- and administration-related variables on deposition pattern of nasal spray pumps evaluated using a nasal cast. Pharm. Res. 28(8):1895–1904, 2011.
Liu, Y., E. A. Matida, J. Gu, and M. R. Johnson. Numerical simulation of aerosol deposition in a 3-D human nasal cavity using RANS, RANS/EIM, and LES. J. Aerosol Sci. 38:683–700, 2007.
Longest, P. W., and J. Xi. Effectiveness of direct Lagrangian tracking models for simulating nanoparticle deposition in the upper airways. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 41(4):380–397, 2007.
Longest, P. W., and J. X. Xi. Condensational growth may contribute to the enhanced deposition of cigarette smoke particles in the upper respiratory tract. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 42(8):579–602, 2008.
Martonen, T. B., and Z. Zhang. Deposition of sulfate acid aerosols in the developing human lung. Inhalation Toxicol. 5(1):165–187, 1993.
Martonen, T. B., Z. Q. Zhang, G. Yue, and C. J. Musante. Fine particle deposition within human nasal airways. Inhalation Toxicol. 15(4):283–303, 2003.
Matida, E. A., W. H. Finlay, and L. B. Grgic. Improved numerical simulation of aerosol deposition in an idealized mouth-throat. J. Aerosol Sci. 35:1–19, 2004.
Moghadas, H., O. Abouali, A. Faramarzi, and G. Ahmadi. Numerical investigation of septal deviation effect on deposition of nano/microparticles in human nasal passage. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 177(1):9–18, 2011.
Moller, W., G. K. Saba, K. Haussinger, S. Becker, M. Keller, and U. Schuschnig. Nasally inhaled pulsating aerosols: lung, sinus and nose deposition. Rhinology 49(3):286–291, 2011.
Morgan, K. T., and T. M. Monticello. Airflow, gas deposition, and lesion distribution in the nasal passages. Environ. Health Perspect. 85:209–218, 1990.
Mortola, J. P. Breathing pattern in newborns. J. Appl. Physiol. 56(6):1533–1540, 1984.
Nasr, H., G. Ahmadi, and J. B. McLaughlin. A DNS study of effects of particle–particle collisions and two-way coupling on particle deposition and phasic fluctuations. J. Fluid Mech. 640:507–536, 2009.
Okuyama, K., Y. Kousaka, and K. Hayashi. Change in size distribution of ultrafine aerosol particles undergoing Brownian coagulation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 101(1):98–109, 1984.
Oldham, M. J., R. C. Mannix, and R. F. Phalen. Deposition of monodisperse particles in hollow models representing adult and child-size tracheobroncial airways. Health Phys. 72(6):827–833, 1997.
Persak, S. C., S. Sin, J. M. McDonough, R. Arens, and D. M. Wootton. Noninvasive estimation of pharyngeal airway resistance and compliance in children based on volume-gated dynamic MRI and computational fluid dynamics. J. Appl. Physiol. 111(6):1819–1827, 2011.
Phalen, R. F., R. G. Cuddihy, R. G. Fisher, O. R. Moss, R. B. Schlesinger, D. L. Swift, and H. C. Yeh. Main features of the proposed NCRP respiratory tract dosimetry model. Radiat. Prot. Dosimetry 38:179–184, 1991.
Phalen, R. F., M. J. Oldham, C. B. Beaucage, T. T. Crocker, and J. D. Mortensen. Postnatal enlargement of human tracheobronchial airways and implications for particle deposition. Anat. Rec. 212:368–380, 1985.
Pickering, D. N., and C. S. Beardsmore. Nasal flow limitation in children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 27(1):32–36, 1999.
Rasmussen, T. R., A. Andersen, and O. F. Pedersen. Particle deposition in the nose related to nasal cavity geometry. Rhinology 38(3):102–107, 2000.
Rusconi, F., M. Castagneto, N. Porta, L. Gagliardi, G. Leo, A. Pellegatta, S. Razon, and M. Braga. Reference values for respiratory rate in the first 3 years of life. Pediatrics 94(3):350–355, 1994.
Scherer, P. W., K. Keyhani, and M. M. Mozell. Nasal dosimetry modeling for humans. Inhalation Toxicol. 6:85–97, 1994.
Schroeter, J. D., G. J. M. Garcia, and J. S. Kimbell. Effects of surface smoothness on inertial particle deposition in human nasal models. J. Aerosol Sci. 42(1):52–63, 2011.
Schroeter, J. D., C. J. Musante, D. M. Hwang, R. Burton, R. Guilmette, and T. B. Martonen. Hygroscopic growth and deposition of inhaled secondary cigarette smoke in human nasal pathways. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 34(1):137–143, 2001.
Shi, H., C. Kleinstreuer, and Z. Zhang. Laminar airflow and nanoparticle or vapor deposition in a human nasal cavity model. J. Biomech. Eng. 128:697–706, 2006.
Shi, H., C. Kleinstreuer, and Z. Zhang. Modeling of inertial particle transport and deposition in human nasal cavities with wall roughness. J. Aerosol Sci. 38:398–419, 2007.
Storey-Bishoff, J., M. Noga, and W. H. Finlay. Deposition of micrometer-sized aerosol particles in infant nasal airway replicas. J. Aerosol Sci. 39(12):1055–1065, 2008.
Subramaniam, R. P., R. B. Richardson, K. T. Morgan, J. S. Kimbell, and R. A. Guilmette. Computational fluid dynamics simulations of inspiratory airflow in the human nose and nasopharynx. Inhalation Toxicol. 10(2):91–120, 1998.
Swift, D. L., N. Montassier, P. K. Hopke, K. Karpenhayes, Y. S. Cheng, Y. F. Su, H. C. Yeh, and J. C. Strong. Inspiratory deposition of ultrafine particles in human nasal replicate cast. J. Aerosol Sci. 23(1):65–72, 1992.
Swift, D. L., and J. C. Strong. Nasal deposition of ultrafine 218Po aerosols in human subjects. J. Aerosol Sci. 27(7):1125–1132, 1996.
Tian, L., G. Ahmadi, Z. C. Wang, and P. K. Hopke. Transport and deposition of ellipsoidal fibers in low Reynolds number flows. J. Aerosol Sci. 45:1–18, 2012.
Wang, S. M., K. Inthavong, J. Wen, J. Y. Tu, and C. L. Xue. Comparison of micron- and nanoparticle deposition patterns in a realistic human nasal cavity. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 166(3):142–151, 2009.
Wheatley, J. R., T. C. Amis, and L. A. Engel. Nasal and oral airway pressure-flow relationships. J. Appl. Physiol. 71(6):2317–2324, 1991.
Xi, J., and P. W. Longest. Transport and deposition of micro-aerosols in realistic and simplified models of the oral airway. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 35(4):560–581, 2007.
Xi, J., and P. W. Longest. Numerical predictions of submicrometer aerosol deposition in the nasal cavity using a novel drift flux approach. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51(23–24):5562–5577, 2008.
Xi, J., and P. W. Longest. Characterization of submicrometer aerosol deposition in extrathoracic airways during nasal exhalation. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 43(8):808–827, 2009.
Xi, J., P. W. Longest, and T. B. Martonen. Effects of the laryngeal jet on nano- and microparticle transport and deposition in an approximate model of the upper tracheobronchial airways. J. Appl. Physiol. 104(6):1761–1777, 2008.
Xi, J., X. Si, J. W. Kim, and A. Berlinski. Simulation of airflow and aerosol deposition in the nasal cavity of a 5-year-old child. J. Aerosol Sci. 42(3):156–173, 2011.
Yamada, Y., Y. S. Cheng, H. C. Yeh, and D. L. Swift. Inspiratory and expiratory deposition of ultrafine particles in a human nasal cast. Inhalation Toxicol. 1:1–11, 1988.
Yu, G., Z. Zhang, and R. Lessmann. Fluid flow and particle diffusion in the human upper respiratory system. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 28:146, 1998.
Zamankhan, P., G. Ahmadi, Z. Wang, P. K. Hopke, Y. S. Cheng, W. C. Su, and D. Leonard. Airflow and deposition of nano-particles in a human nasal cavity. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 40:463–476, 2006.
Zhang, Z., and C. Kleinstreuer. Computational analysis of airflow and nanoparticle deposition in a combined nasal-oral-tracheobronchial airway model. J. Aerosol Sci. 42(3):174–194, 2011.
Zhao, K., P. W. Scherer, S. A. Hajiloo, and P. Dalton. Effects of anatomy on human nasal air flow and odorant transport patterns: implications for olfaction. Chem. Senses 29(5):365–379, 2004.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Kenneth R. Lutchen oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, J., Berlinski, A., Zhou, Y. et al. Breathing Resistance and Ultrafine Particle Deposition in Nasal–Laryngeal Airways of a Newborn, an Infant, a Child, and an Adult. Ann Biomed Eng 40, 2579–2595 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0603-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0603-7