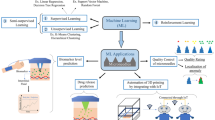
Abstract
Drop-on-demand (DOD) printing is widely used in bioprinting for tissue engineering because of little damage to cell viability and cost-effectiveness. However, satellite droplets may be generated during printing, deviating cells from the desired position and affecting printing position accuracy. Current control on cell injection in DOD printing is primarily based on trial-and-error process, which is time-consuming and inflexible. In this paper, a novel machine learning technology based on Learning-based Cell Injection Control (LCIC) approach is demonstrated for effective DOD printing control while eliminating satellite droplets automatically. The LCIC approach includes a specific computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation model of piezoelectric DOD print-head considering inverse piezoelectric effect, which is used instead of repetitive experiments to collect data, and a multilayer perceptron (MLP) network trained by simulation data based on artificial neural network algorithm, using the well-known classification performance of MLP to optimize DOD printing parameters automatically. The test accuracy of the LCIC method was 90%. With the validation of LCIC method by experiments, satellite droplets from piezoelectric DOD printing are reduced significantly, improving the printing efficiency drastically to satisfy requirements of manufacturing precision for printing complex artificial tissues. The LCIC method can be further used to optimize the structure of DOD print-head and cell behaviors.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlfeld, T., A. R. Akkineni, Y. Förster, T. Köhler, S. Knaack, M. Gelinsky, and A. Lode. Design and fabrication of complex scaffolds for bone defect healing: combined 3D plotting of a calcium phosphate cement and a growth factor-loaded hydrogel. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 45:224–236, 2017.
Barron, V., K. Merghani, G. Shaw, C. Coleman, J. Hayes, S. Ansboro, A. Manian, G. O’Malley, E. Connolly, and A. Nandakumar. Evaluation of cartilage repair by mesenchymal stem cells seeded on a PEOT/PBT scaffold in an osteochondral defect. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43:2069–2082, 2015.
Bogy, D. B., and F. Talke. Experimental and theoretical study of wave propagation phenomena in drop-on-demand ink jet devices. IBM J. Res. Dev. 28:314–321, 1984.
Brackbill, J., D. B. Kothe, and C. Zemach. A continuum method for modeling surface tension. J. Comput. Phys. 100:335–354, 1992.
Dey, R., A. Ghoshal, and B. Tudu. Electromyogram (EMG) signal categorization in parkinson’s disease tremor detection by applying MLP (Multilayer Perceptron) technique: a review. Advances in Systems, Control and Automation, Singapore: Springer, 2018, pp. 693–699.
Dhanarajan, G., M. Mandal, and R. Sen. A combined artificial neural network modeling–particle swarm optimization strategy for improved production of marine bacterial lipopeptide from food waste. Biochem. Eng. J. 84:59–65, 2014.
Dos Santos, E. B., R. Pistor, and A. P. Gerlich. Pulse profile and metal transfer in pulsed gas metal arc welding: droplet formation, detachment and velocity. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 22:627–641, 2017.
Dudhagara, D. R., R. K. Rajpara, J. K. Bhatt, H. B. Gosai, and B. P. Dave. Bioengineering for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation by Mycobacterium litorale: Statistical and artificial neural network (ANN) approach. Chemometrics Intell. Lab. Syst. 159:155–163, 2016.
Fluent, A. 14.5, theory guide. Canonsburg: Ansys Inc., 2012.
Hatami, M., and D. Ganji. Natural convection of sodium alginate (SA) non-Newtonian nanofluid flow between two vertical flat plates by analytical and numerical methods. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 2:14–22, 2014.
Kani, M. H., E. C. Chan, R. C. Young, T. Butler, R. Smith, and J. W. Paul. 3D cell culturing and possibilities for myometrial tissue engineering. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 45:1746–1757, 2017.
Kotsiantis, S. B., I. Zaharakis, and P. Pintelas. Supervised machine learning: A review of classification techniques. In: Emerging Artificial Intelligence Applications in Computer Engineering, edited by R. Mizoguchi, M. Musen, N. Zhong, J. Breuker, R. Dieng-Kuntz, N. Guarino, J. N. Kok, and J. Liu. Amsterdam: IOS Press, 2007, pp. 3–24.
Lai, J. M., C. Y. Huang, C. H. Chen, K. Linliu, and J. D. Lin. Influence of liquid hydrophobicity and nozzle passage curvature on microfluidic dynamics in a drop ejection process. J. Micromech. Microeng. 20:015033, 2010.
Li, E. Q., Q. Xu, J. Sun, J. Y. H. Fuh, Y. S. Wong, and S. T. Thoroddsen. Design and fabrication of a PET/PTFE-based piezoelectric squeeze mode drop-on-demand inkjet printhead with interchangeable nozzle. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 163:315–322, 2010.
Malda, J., J. Visser, F. P. Melchels, T. Jungst, W. E. Hennink, W. J. Dhert, J. Groll, and D. W. Hutmacher. 25th anniversary article: Engineering hydrogels for biofabrication. Adv. Mater. 25:5011–5028, 2013.
Milo, R., and R. Phillips. Cell Biology by the Numbers. Abington: Garland Science, 2015.
Moon, S., B. Y. Ryu, J. Choi, B. Jo, and R. J. Farris. The morphology and mechanical properties of sodium alginate based electrospun poly (ethylene oxide) nanofibers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 49:52–59, 2009.
Muthamizhi, K., P. Kalaichelvi, S. T. Powar, and R. Jaishree. Investigation and modelling of surface tension of power-law fluids. RSC Adv. 4:9771–9776, 2014.
Nasir, A. A., M. Y. Mashor, and H. Rosline. Classification of acute leukaemia cells using multilayer perceptron and simplified fuzzy ARTMAP neural networks. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 10:356–364, 2013.
Nishiyama, Y., M. Nakamura, C. Henmi, K. Yamaguchi, S. Mochizuki, H. Nakagawa, and K. Takiura. Development of a three-dimensional bioprinter: construction of cell supporting structures using hydrogel and state-of-the-art inkjet technology. J. Biomech. Eng. Trans. 131:35, 2009.
Riedmiller, M. Advanced supervised learning in multi-layer perceptrons—from backpropagation to adaptive learning algorithms. Comput. Stand. Interfaces. 16(3):265–278, 1994.
Ross, S. E., Z. Ouyang, S. Rajagopalan, and T. M. Bruns. Evaluation of decoding algorithms for estimating bladder pressure from dorsal root ganglia neural recordings. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 46:233–246, 2018.
Suh, Y., and G. Son. A sharp-interface level-set method for simulation of a piezoelectric inkjet process. Numer Heat Tranf. B Fundam. 55:295–312, 2009.
Tsinalis, O., P. M. Matthews, and Y. Guo. Automatic sleep stage scoring using time-frequency analysis and stacked sparse autoencoders. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 44:1587–1597, 2016.
Vatankhah, E., D. Semnani, M. P. Prabhakaran, M. Tadayon, S. Razavi, and S. Ramakrishna. Artificial neural network for modeling the elastic modulus of electrospun polycaprolactone gelatin scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 10:709–721, 2014.
Wust, S., R. Muller, and S. Hofmann. Controlled positioning of cells in biomaterials-approaches towards 3D tissue printing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2:119–154, 2011.
Xu, C., W. Chai, Y. Huang, and R. R. Markwald. Scaffold-free inkjet printing of three-dimensional zigzag cellular tubes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 109:3152–3160, 2012.
Xu, C., M. Zhang, Y. Huang, A. Ogale, J. Fu, and R. R. Markwald. Study of droplet formation process during drop-on-demand inkjetting of living cell-laden bioink. Langmuir 30:9130–9138, 2014.
Yang, Q., H. Li, M. Li, Y. Li, S. Chen, B. Bao, and Y. Song. Rayleigh instability-assisted satellite droplets elimination in inkjet printing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(47):41521, 2017.
Zhang, Y., Y. Sun, P. Phillips, G. Liu, X. Zhou, and S. Wang. A multilayer perceptron based smart pathological brain detection system by fractional Fourier entropy. J. Med. Syst. 40:173, 2016.
Acknowledgment
Jia Shi thanks the China Scholarship Council (CSC) for the financial support of a visiting program at National University of Singapore.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial or personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately have influenced their work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Smadar Cohen oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, J., Wu, B., Song, B. et al. Learning-Based Cell Injection Control for Precise Drop-on-Demand Cell Printing. Ann Biomed Eng 46, 1267–1279 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-2054-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-2054-2