Abstract
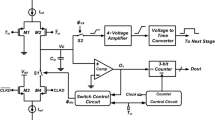
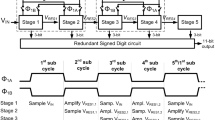
A new power reduction technique for analog-to-digital converters is proposed in this paper. A novel current-mode algorithm which uses time to perform analog-to-digital conversion has been described and a 12 bit 100-ksample/s time-based pipeline analog to digital converter has been designed and simulated in standard 90-nm CMOS technology based on introduced structure. Employed circuit techniques include a continues-time comparator, bottom plate sampling, digital correction and a state machine. A time based-mechanism has been used for subtraction and amplification. Simulation results show that the pipelined ADC achieves a peak signal-to-noise-and-distortion ratio of 69.8 dB, a peak spurious-free dynamic range of 75 dB, a total harmonic distortion of 73 dB, and a peak integral nonlinearity of 0.85 least significant bits. The total power dissipation is 90 μW from a 3-V supply.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chae, M., Liu, W., Yang, Z., Chen, T., Kim, J., Sivaprakasam, M., & Yuce, M. (2008). A 128-channel 6 mW wireless neural recording IC with on-the-fly spike sorting and UWB transmitter. In IEEE international solid-state circuits conference.
Harrison, R. R., Watkins, P. T., Kier, R. J., Lovejoy, R. O., Black, D. J., Greger, B., et al. (2007). A low-power integrated circuit for a wireless 100-electrode neural recording system. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42(1), 123–133.
Farshchi, S., Markovic, D., Pamarti, S., Razavi, B., & Judy, J. W. (2007). Towards neuromote: A single-chip, 100-channel, neural-signal acquisition, processing, and telemetry device. In 29th IEEE engineering in medicine and biology conference.
Olsson, R. H., III, & Wise, K. D. (2005). A three-dimensional neural recording microsystem with implantable data compression circuitry. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40(12), 2796–2804.
Zarifi, M. H., Frounchi, J., Farshchi, S., & Judy, J. W. (2008). A low-power, low-noise neural-signal amplifier circuit in 90-nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE engineering in medicine and biology conference.
Rostami, A., Zarifi, M. H., KuzeKanani, Z. D., & Sobhi, J. (2007). A 12 bit, 80 Msamples/s, pipeline analog to digital converter. In Proceeding of 5th international conference on electrical and electronics engineering, Bursa, Turkey.
Grace, C. R., Hurst, P. J., & Lewis, S. H. (2005). A 12-bit, 80-Msample/s pipeline analog to digital converter with bootstrapped digital calibration. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40(5), 1038–1046.
Scott, M. D., Boser, B. E., & Pister, K. S. J. (2003). An ultra low-energy ADC for smart dust. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(7), 1123–1129.
Uyttenhove, K., & Steyaert, M. S. J. (2003). A 1.8-V 6-bit 1.3-GHz flash ADC in 0.25-μm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(7), 1115–1122.
Li, Y., & Sanchez-Sinencio, E. (2003). A wide input bandwidth 7-bit 300-Msample/s folding and current-mode interpolating ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(8), 1405–1410.
Gupta, S. K., & Fong, V. (2002). A 64-MHz clock-rate Σ∆ ADC with 88-dB SNDR and -105-dB IM3 distortion at a 1.5-MHz signal frequency. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37(12), 1653–1661.
Abo, A. M. (1999). Design for reliability of low-voltage, switched-capacitor circuits, Ph.D. dissertation, Dept. Elect. Eng. Comput. Sci., Berkeley, California, spring.
Cline, D. W., & Gray, P. R. (1996). A power optimized 13-b 5 Msamples/s pipelined analog-to-digital converter in 1.2 μm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 31(3), 294–303.
Lo, T. Y., & Hung, C. C. (2007). A wide tuning range Gm–C continuous-time analog filter. IEEE Transactions on Circuit and Systems—I: Regular Papers, 54(4), 713–722.
Yang, H. Y., & Sarpeshkar, R. (2005). A time-based energy-efficient analog-to-digital converter. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40(8), 1590–1601.
Yao, L., Steyaert, M., & Sansen, W. (2004). A 1-V 88-dB 20-kHz Σ∆ modulator in 90-nm CMOS. Digital Technique Papers ISSCC, 12, 80–514.
Sauerbrey, J., Schmitt-Landsiedel, D., & Thewes, R. (2003). A 0.5-V 1-W successive approximation ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(7), 1261–1265.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarifi, M.H., Frounchi, J., Farshchi, S. et al. A novel time-based low-power pipeline analog to digital converter. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 62, 281–289 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-009-9346-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-009-9346-2