Abstract
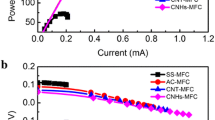
A multi-walled, carbon nanotube (MWNT)-modified graphite felt (GF) cathode was fabricated to improve the performance of sediment microbial fuel cells (SMFC). Three types of MWNT-modified GF cathodes were prepared by different electrophoretic deposition (EPD) times. Maximum power density of SMFC with MWNT-GF*** cathode at 60 min EPD was 215 ± 9.9 mW m−2. This was 1.6 times that of SMFC with a bare GF cathode. Cyclic voltammetry and the amount of biomass showed that biomass density and electrochemical activity increased as the electrophoretic deposition time extended. Therefore the electrode possesses the highest catalytic behavior toward O2 reduction reaction. This simple process of carbon nanotube modification of a cathode by EPD can serve as an effective technique to improve the performance of SMFC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boccaccini AR, Cho J, Roether JA, Thomas BJC, Minay EJ, Shaffer MSP (2006) Electrophoretic deposition of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 44:3149–3160
Bond DR, Holmes DE, Tender LM, Lovley DR (2002) Electrode-reducing microorganisms that harvest energy from marine sediments. Science 295:483–485
Cheng S, Liu H, Logan BE (2006) Power densities using different cathode catalysts (Pt and CoTMPP) and polymer binders (Nafion and PTFE) in single chamber microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 40:364–369
De Schamphelaire L, van den Bossche L, Dang HS, Höfte M, Boon N, Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2008) Microbial fuel cells generating electricity from rhizodeposits of rice plants. Environ Sci Technol 42:3053–3058
De Schamphelaire L, Boeckx P, Verstraete W (2010) Evaluation of biocathodes in freshwater and brackish sediment microbial fuel cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1675–1687
Donovan C, Dewan A, Heo D, Beyenal H (2008) Batteryless, wireless sensor powered by a sediment microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 42:8591–8596
Donovan C, Dewan A, Heo D, Lewandowski Z, Beyenal H (2013) Sediment microbial fuel cell powering a submersible ultrasonic receiver: new approach to remote monitoring. J Power Sour 233:79–85
Findlay RH, King GM, Watling L (1989) Efficacy of phospholipid analysis in determing microbial biomass in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:2888–2893
Hong SW, Kim HS, Chung TH (2010) Alteration of sediment organic matter in sediment microbial fuel cells. Environ Pollut 158:185–191
Liang P, Wang HY, Xia X, Huang X, Mo YH, Cao XX, Fan M (2011) Carbon nanotube powders as electrode modifier to enhance the activity of anodic biofilm in microbial fuel cells. Biosen Bioelectr 26:3000–3004
Logan BE, Regan JM (2006) Electricity-producing bacterial communities in microbial fuel cells. Trends Microbiol 14:512–518
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal R, Schroder U, Keller J, Freguia S, Aelterman P, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40:5181–5192
Lowy DA, Tender LM, Zeikus JG, Park DH, Lovley DR (2006) Harvesting energy from the marine sediment–water interface II. Kinetic activity of anode materials. Biosens Bioelectron 21:2058–2063
Reimers CE, Tender LM, Fertig S, Wang W (2001) Harvesting energy from the marine sediment–water interface. Environ Sci Technol 35:192–195
Reimers CE, Girguis P, Stecher HA III, Tender LM, Ryckelynck N, Whaling P (2006) Microbial fuel cell energy from an ocean cold seep. Geobiology 4:123–136
Rezaei F, Richard TL, Brennan RA, Logan BE (2007) Substrate-enhanced microbial fuel cells for improved remote power generation from sediment based systems. Environ Sci Technol 41:4053–4058
Sharma T, Mohana Reddy AL, Chandra TS, Ramaprabhu S (2008) Development of carbon nanotubes and nanofluids based microbial fuel cell. Int J Hydrog Energy 33:6749–6754
Song TS, Jiang HL (2011) Effects of sediment pretreatment on the performance of sediment microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 102:10465–10470
Song TS, Yan ZS, Zhao ZW, Jiang HL (2010) Removal of organic matter in freshwater sediment by microbial fuel cells at various external resistances. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:1489–1493
Song TS, Wang DB, Han S, Wu XY, Zhou CC (2014) Influence of biomass addition on electricity harvesting from solid phase microbial fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:1056–1062
Tender LM, Reimers CE, Stecher HA III, Holmes DE, Bond DR, Lowy DA, Pilobello K, Fertig SJ, Lovley DR (2002) Harnessing microbially generated power on the seafloor. Nat Biotechnol 20:821–825
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973) (Grant No. 2011CBA00806, 2012CB721100); the National Science Fund of China (Grant No. 51209116, 21390204); Fund from the State Key Laboratory of Materials-Oriented Chemical Engineering (ZK201312); Program for New Century Excellent Talents at the Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. NCET-11-0987); the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (RFDP) (Grant No. 20113221120007) and the Priority Academic Program from Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Dawei Zhu and De-Bin Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, D., Wang, DB., Song, Ts. et al. Effect of carbon nanotube modified cathode by electrophoretic deposition method on the performance of sediment microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol Lett 37, 101–107 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1671-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1671-6