Abstract
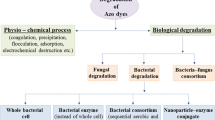
Molasses melanoidin (MM) is a major pollutant in biomethanated distillery spent wash (BMDS) due to its recalcitrant properties. The 75% colour and 71% COD of MM (1,000 ppm) were reduced with developed bacterial consortium comprising Proteus mirabilis (IITRM5; FJ581028), Bacillus sp. (IITRM7; FJ581030), Raoultella planticola (IITRM15; GU329705) and Enterobacter sakazakii (IITRM16, FJ581031) in the ratio of 4:3:2:1 within 10 days at optimized nutrient. Bacterial consortium showed manganese peroxidase and laccase activity during MM decolourisation. The dominant growth of R. planticola and E. sakazakii was noted in consortium during MM decolourisation. The comparative GC–MS analysis of extracted compounds of control and degraded samples showed that most of the compounds present in control were completely utilized by bacterial consortium along with production of some metabolites. The developed bacterial consortium could be a tool for the decolourisation and degradation of melanoidin containing BMDS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, (American Public Health Association) (2005) Standard Method for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st edn. AWWA and WEF, Washington
Arora DS, Chander M, Gill PK (2002) Involvement of lignin peroxidase, manganese peroxidase and laccase in degradation and selective ligninolysis of wheat straw. Inter Biodeterior Biodegrad 50:115–120
Bharagava RN, Chandra R (2009) Isolation and characterisation of phenolic compounds by 1HNMR and mass spectrometric analysis from sugarcane molasses post methanated distillery effluent. Indian J Environ Prot 29:873–881
Bharagava RN, Chandra R (2010) Biodegradation of the major colour containing compounds in distillery wastewater by an aerobic bacterial culture and characterization of their metabolites. Biodegradation 21:703–711
Bharagava RN, Chandra R, Singh SK (2008) Characterization of phenolic metabolites from post methanated distillery effluent (PMDE) after degradation with bacterial consortium. Indian J Environ Prot 28:1019–1027
Bharagava RN, Chandra R, Rai V (2009) Isolation and characterization of aerobic bacteria capable of the degradation of synthetic and natural melanoidins from distillery waste water. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:737–744
Boer CG, Obici L, D’Souza CGM (2006) Peralta RM Purification and some properties of Mn peroxidase from Lentinula edodes. Process Biochem 41:1203–1207
Chandra R, Abhishek A (2011) Bacteria decolorization of black liquor in axenic and mixed condition and characterization of metabolites. Biodegradation 22:603–611
Chandra R, Pandey PK (2001) Decolourisation of anaerobically treated distillery distillery wastewater. Indian J Environ Prot 2:132–134
Chandra R, Bharagava RN, Rai V (2008) Melanoidins as major colorant in sugarcane molasses based distillery effluent and its degradation. Bioresour Technol 99:4648–4660
Chopra P, Singh D, Verma V, Puniya AK (2004) Bioremediation of melanoidin containing digested spent wash from cane–molasses distillery with white rot fungus Coriolus versicolor. Indian J Microbiol 44:197–200
Gonzalez T, Terron MC, Yague S, Zapico E, Galletti GC, Gonzalez AE (2000) Pyrolysis/gas chromatography/mass spectrometry monitoring of fungal-biotreated distillery wastewater using Trametes sp. I-62 (CECT 20197). Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 14:1417–1424
Kalavathi DF, Uma L, Subramanian G (2001) Degradation and metabolization of the pigment-melanoidin in distillery effluent by marine cyanobacterium Oscillatoria boryana BDU. Enzym Microb Technol 29:246–251
Kim SB, Hayase F, Kato H (1985) Decolorization and degradation products of melanoidins on ozonolysis. Agric Biol Chem 49:785–792
Kumar P, Chandra R (2006) Decolourisation and detoxification of synthetic molasses melanoidins by individual and mixed cultures of Bacillus spp. Bioresour Technol 97:2096–2102
Kumar V, Wati L, Nigam P, Banat IM, MacMullan G, Singh D, Marchant R (1997) Microbial decolorization and bioremediation of anaerobically digested molasses spent wash wastewater by aerobic bacterial culture. Microbios 89:81–90
Manisankar P, Rani C, Vishwanathan S (2004) Effect of halides in the electrochemical treatment of distillery effluent. Chemosphere 57:961–966
Migo VP, Rosario DEJ, Matsumura M (1997) Flocculation of melanoidins induced by inorganic ions. J Ferment Bioeng 83:287–291
Minuti L, Pellegrino RM, Tesei I (2006) Simple extraction method and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in the selective ion monitoring mode for the determination of phenols in wine. J Chromatogr 1114:263–268
Miyata N, Mori T, Iwahori K, Fujita M (2000) Microbial decolorization of melanoidins containing wastewaters: combined use of activated sludge and the fungus Coriolus hirsutus. J Biosci Bioeng 89:145–150
Mohana S, Desai C, Madamwar D (2007) Biodegradation and decolourisation of anaerobically treated distillery spent wash by a novel bacterial consortium. Bioresour Technol 98:333–339
Morales FJ, Fraguas CF, Perez SJ (2005) Iron-binding ability of melanoidins from food and model systems. Food Chem 90:821–827
Ohmomo S, Aoshima I, Tozawa Y, Sakurada N, Ueda K (1985) Purification and some properties of melanoidin decolourizing enzymes, P-3 and P-4, from mycelia of Coriolus versicolor Ps4a. Agric Biol Chem 49:2047–2053
Ott L (1984) An introduction to statistical methods and data analysis, 2nd edn. PWS, Boston
Pant D, Adholeya A (2007) Biological approaches for treatment of distillery waste water: a review. Bioresour Technol 98:2321–2334
Pant D, Adholeya A (2009) Nitrogen removal from biomethanated spent wash using hydroponic treatment followed by fungal decolorization. Environ Eng Sci 26:559–565
Pena M, Gonzalez G, San N, Nieto H (1996) Color elimination from molasses wastewater by Aspergillus niger. Bioresour Technol 57:229–235
Plavsic M, Cosovic B, Lee C (2006) Copper complexing properties of melanoidins and marine humic material. Sci Total Environ 366:310–319
Raghukumar C, Mohandass C, Kamat S, Shailaja MS (2004) Simultaneous detoxification and decolorization of molasses spentwash by the immobilized white-rot fungus Flavadon flavus isolated from the marine habitat. Enzym Microb Technol 35:197–202
Rubia TDL, Linares A, Perez J, Dorado JM, Romera J, Martinez J (2002) Characterization of manganese-dependent peroxidase isoenzymes from the ligninilytic fungus Phanerochaete flavido-alba. Res Microbiol 153:547–554
Sangeeta Y, Chandra R, Rai V (2011) Characterization of potential MnP producing bacteria and its metabolic products during decolourisation of synthetic melanoidins due to biostimulatory effect of D-xylose at stationary phase. Process Biochem 86:1774–1784
Sirianuntapiboon S, Phothilangka P, Ohmomo S (2004a) Decolorization of molasses wastewater by a strain No. BP103 of acetogenic bacteria. Bioresour Technol 92:31–39
Sirianuntapiboon S, Zohsalam P, Ohmomo S (2004b) Decolorization of molasses wastewater by Citeromyces sp. WR-43-6. Process Biochem 39:917–924
Acknowledgments
The financial assistance from Council of Scientific Industrial Research, New Delhi to Ms. Sangeeta Yadav, SRF and project NWP–19 is duly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, S., Chandra, R. Biodegradation of organic compounds of molasses melanoidin (MM) from biomethanated distillery spent wash (BMDS) during the decolourisation by a potential bacterial consortium. Biodegradation 23, 609–620 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9537-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9537-x