Abstract
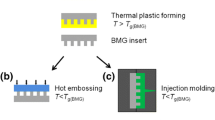
Micro components processed by injection molding still have a defect of bad precision and short life. A Zr- based metallic glass was reported for injection mold insert which can solve the problem well. The microstructure of metallic glass mold insert can be fabricated by wire electrical discharge machining-low speed (WEDM-LS), WEDM-LS has higher machining accuracy than WEDM-high speed, and X-ray diffraction curves show that the processed sample still retained better amorphous characteristic, afterward, time-temperature-transformation diagram shows metallic glass has a long service life in production. Finally, under the observe of scanning electron microscope, it is found that the products after injection molding not only completely replicates the structure on metallic glass but also have a better surface morphology. These experiments show that processing a sophisticated and durable Zr-based metallic glass mold by WEDM-LS is good for getting micro structure injection of polymers. It also provides a good mold material and machining method for injection industry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.S. Argon, Plastic deformation in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 27, 47–58 (1979)
M.F. Ashby, A.L. Greer, Metallic glasses as structural materials. Scr. Mater. 54, 321–326 (2006)
M. Avella, M.E. Errico, R. Rimedio, PVA/PTFE nanocomposites: Thermal, mechanical, and barrier properties. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 6133–6136 (2004)
M. Chen, Mechanical behavior of metallic glasses: Microscopic understanding of strength and ductility. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 38, 445–469 (2008)
M. Chiarbonello, D. Firrao, R. Gerosa, A. Ghidini, M.G. Ienco, P. Matteis, et al., Mechanical properties of large plastic-Mold steel blooms. Fracture of Nano & Engineering Materials & Structures, 433–434 (2006)
G. Duan, A. Wiest, M.L. Lind, J. Li, W.K. Rhim, W.L. Johnson, Bulk metallic glass with benchmark thermoplastic Processability. Adv. Mater. 19, 4272–4275 (2010)
J. Eckert, J. Das, S. Pauly, C. Duhamel, Mechanical properties of bulk metallic glasses and composites. Mrs Bull. 32, 635–638 (2007)
R.K. Garg, K.K. Singh, A. Sachdeva, V.S. Sharma, K. Ojha, S. Singh, Review of research work in sinking EDM and WEDM on metal matrix composite materials. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 50, 611–624 (2010)
E. Georgatis, A. Lekatou, H. Petropoulos, S. Katsamakis, A. Poulia, Development of a cast Al-MgSi-Si In Situ composite: Microstructure, heat treatment, and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 22, 729–741 (2013)
Y. Gong, Y. Sun, X. Wen, C. Wang, Q. Gao, Experimental study on surface integrity of Ti-6Al-4V machined by LS-WEDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 88, 1–11 (2016)
X. Gu, W. Hao, J. Wang, H. Kou, J. Li, Microstructure changes in Zr-based metallic glass induced by ion milling. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 39, 1693–1696 (2010)
S.F. Guo, Z.Y. Wu, L. Liu, Preparation and magnetic properties of FeCoHfMoBY bulk metallic glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 468, 54–57 (2009)
M. Heckele, W.K. Schomburg, Review on micro molding of thermoplastic polymers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, R1 (2004)
H. Hu, J. Yan, On the surface characteristics of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by microelectrical discharge machining. Appl. Surf. Sci. 355, 1306–1315 (2015)
H. Hu, J. Yan, Microstructural changes of Zr-based metallic glass during micro-electrical discharge machining and grinding by a sintered diamond tool. J. Alloys Compd. 688, 14–21 (2016)
A. Inoue, Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys ☆. Acta Mater. 48, 279–306 (2000)
W.L. Johnson, G. Kaltenboeck, M.D. Demetriou, J.P. Schramm, X. Liu, K. Samwer, et al., Beating crystallization in glass-forming metals by millisecond heating and processing. Science 332, 828–833 (2011)
M. Kunieda, C. Furudate, High precision finish cutting by dry WEDM. Ann. CIRP 50, 121–124 (2001)
J.J. Lewandowski, A.L. Greer, Temperature rise at shear bands in metallic glasses. Nat. Mater. 5, 15–18 (2006)
G. Liu, P. Gao, Z. Xue, Z. Tong, M. Zhang, Ultra-high strength mg–Li based bulk metallic glasses: Preparation and performance research. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 7156–7160 (2011)
J. Ma, X. Zhang, W.H. Wang, Metallic glass mold insert for hot embossing of polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 112(32), 024506 (2012)
S.S. Mahapatra, A. Patnaik, Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process parameters using Taguchi method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 34, 911–925 (2007)
L. Mingqi, L. Minghui, X. Guangyao, Study on the variations of form and position of the wire electrode in WEDM-HS. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 25, 929–934 (2005)
P.D. Mitcheson, P. Miao, B.H. Stark, E.M. Yeatman, A.S. Holmes, T.C. Green, MEMS electrostatic micropower generator for low frequency operation. Sensors Actuators A Phy. 115, 523–529 (2004)
Y. Saotome, K. Itoh, T. Zhang, A. Inoue, Superplastic nanoforming of Pd-based amorphous alloy. Scr. Mater. 44, 1541–1545 (2001)
J. Schroers, The superplastic forming of bulk metallic glasses. JOM 57, 35–39 (2005)
W.H. Wang, The elastic properties, elastic models and elastic perspectives of metallic glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 487–656 (2012)
D. Wang, G. Liao, J. Pan, Z. Tang, P. Peng, L. Liu, et al., Superplastic micro-forming of Zr 65 cu 17.5 Ni 10 Al 7.5 bulk metallic glass with silicon mold using hot embossing technology. J. Alloys Compd. 484, 118–122 (2009)
A. Wiest, J.S. Harmon, M.D. Demetriou, R.D. Conner, W.L. Johnson, Injection molding metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 60, 160–163 (2009)
Y.M. Yeh, G.C. Tu, T.H. Fang, Nanomechanical properties of nanocrystalline Ni–Fe mold insert. J. Alloys Compd. 372, 0–230 (2004)
S.H. Yeo, P.C. Tan, E. Aligiri, S.B. Tor, N.H. Loh, Processing of zirconium-based bulk metallic glass (BMG) using micro electrical discharge machining (micro-EDM). Mater. Manuf. Processes. 24, 1242–1248 (2009)
L. Yi, X. Wang, Y. Fan, Microfluidic chip made of COP (cyclo-olefin polymer) and comparion to PMMA (polymethylmethacrylate) microfluidic chip. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 208, 63–69 (2008)
N. Zhang, J.S. Chu, C.J. Byrne, D.J. Browne, M.D. Gilchrist, Replication of micro/nano-scale features by micro injection molding with a bulk metallic glass mold insert. J. Micromech. Microeng. 22, 065019 (2012a)
X. Zhang, J. Ma, R. Bai, Q. Li, B.L. Sun, C.Y. Shen, Polymer micro hot embossing with bulk metallic glass Mold insert. Adv. Mater. Res. 510, 639–644 (2012b)
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the NSF of China (Nos. 51871157, 51605304), the Ph.D. Start-up Fund of Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Nos. 2016A030310036, 2016A030310043), the Science and Technology Innovation Commission Shenzhen (Nos. JCYJ20170412111216258, JCYJ20160520164903055 and JCYJ20160422162907121), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shenzhen University (No. 2017034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Liang, X., Chang, C. et al. WEDM-LS processing sophisticated and durable Zr-based metallic glass mold insert for micro structure injection of polymers. Biomed Microdevices 21, 13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0366-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0366-0