Abstract
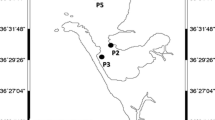
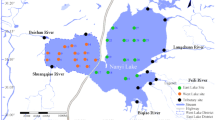
Measurement of the organic compounds found in western Taihu Lake and evaluation of the ambient severity (AS) of the water using multimedia environmental goals (MEG) was conducted. The comet assay and the antioxidant enzyme approach were used to test the potential toxicity of water samples on the microalgae Euglena gracilis. Total concentrations of 25 organic pollutants in samples from two sites were 6.700 and 14.655 μg/l, respectively, with a calculated total ambient severity (TAS) of less than 1 and therefore minimal risk to human and ecological health. Organic extracts from the samples at these two sites was found to induce dose-dependent DNA damage on microalgae cells. DNA damage together with changes in superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) activities indicated that the potential pollutant toxicity was far higher at one of the two sites than at the other site. The comet assay combined with the activities of antioxidant enzymes may be of value as a biomarker for presence of organic pollutants in drinking water sources.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adibi JJ, Perera FP, Jedrychiwski W, Camann DE, Barr D, Jacek R, Whyatt RM (2003) Prenatal exposures to phthalates among women in New York and Krakow, Poland. Environ Health Perspect 111:1719–1722. doi:10.1289/ehp.6235
Akcha F, Arzul G, Rousseau S, Bardouil M (2008) Comet assay in phytoplankton as biomarker of genotoxic effects of environmental pollution. Mar Environ Res 66:59–61. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2008.02.022
Aoyama K, Iwahori K, Miyata N (2003) Application of Euglena gracilis cells to comet assay: evaluation of DNA damage and repair. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 538:155–162. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(03)00113-X
Api AM (2001) Toxicological profile of diethyl phthalate: a vehicle for fragrance and cosmetic ingredients. Food Chem Toxicol 39:97–108
Baasel WD (1985) Economic methods for multipollutant analysis and evaluation. M Dekker, New York, pp 188–297
Bornehag CG, Sundell J, Weschler CJ, Sigsgaard T, Lundgren B, Hasselgren M, Hägerhed-Engmanl L (2004) The association between asthma and allergic symptoms in children and phthalates in house dust: a nested case–control study. Environ Health Perspect 112:1393–1397. doi:10.1289/ehp.7187
Checcucci A, Colombetti G, Ferrara R, Lenci F (1976) Action spectra for photoaccumulation of green and colorless Euglena: evidence for identification of receptor pigments. Photochem Photobiol 23:51–54. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.1976.tb06770.x
Chen YG, Chen HG, Wu YL, Li ZL, Sun LW, Qu MM, Kong ZM (2007) Toxicity evaluation of Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu, China—a drinking water source. Hydrobiologia 581:297–303. doi:10.1007/s10750-006-0498-0
Collins AR (2004) The comet assay for DNA damage and repair principles, applications, and limitations. Mol Biotechnol 26:249–261. doi:10.1385/MB:26:3:249
Collins AR, Dusinska M, Ma AG, Fleming I (1995) The comet assay modified to detect DNA-base oxidation, and repair of DNA-damage in cellular and subcellular systems. J Cell Biochem (Suppl) 347
Committee on Biological Markers of the National Research Council (1987) Biological markers in environmental health research. Environ Health Perspect 74:3–9
Cotelle S, Ferard JF (1999) Comet assay in genetic ecotoxicology: a review. Environ Mol Mutagen 34:246–255
Decaprio AP (1997) Biomarkers: coming of age for environmental health and risk assessment. Environ Sci Technol 31(7):1837–1848
DeLorenzo ME, Taylor LA, Lund SA, Pennington PL, Strozier ED, Fulton MH (2002) Toxicity and bio-concentration potential of the agricultural pesticide endosulfan in phytoplankton and zooplankton. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 42:173–181
Djomo JE, Dauta A, Ferrier V, Narbonne JF, Monkiedje A, Njine T, Garrigues P (2004) Toxic effects of some major polyaromatic hydrocarbons found in crude oil and aquatic sediments on Scenedesmus subspicatus. Water Res 38:1817–1821. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2003.10.023
Erbes M, Webler A, Obst U, Wild A (1997) Detection of primary DNA damage in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by means of modified microgel electrophoresis. Environ Mol Mutagen 30:448–458
Foltinova P, Grones J (1997) Euglena gracilis as an eukaryotic test organism for detecting mutagens and antimutagens. Mutat Res 393:1–6
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2005) Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling: a metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell 17:1866–1875. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.033589
Franqueira D, Orosa M, Torres E, Herrero C, Cid A (2000) Potential use of flow cytometry in toxicity studies with microalgae. Sci Total Environ 247:119–126
Gao JJ, Liu LH, Liu XR, Zhou HD, Huang SB, Wang ZJ (2008) Levels and spatial distribution of chlorophenols 2,4-dichloro-phenol, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, and pentachlorophenol in surface water of China. Chemosphere 71:1181–1187. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.10.018
Greenberg AE, Clesceri LS, Eaton AD (1992) Standard method for examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn, vol 8. APHA AWWA and WPCF, Washington, DC, pp 26–27
Gregory EM, Fridovich I (1973) Oxygen toxicity and the superoxide dismutase. J Bacteriol 114:1193–1197
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (2007) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 4th edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Hartter DR (1985) The use and importance of nitroaromatic chemicals in the chemical industry. In: Rickert DE (ed) Toxicity of nitroaromatic compounds. Hemisphere Publishing Corp, Washington, DC, pp 1–14
Jeffrey SW, Humphrey GF (1975) New spectrophotometric equation for determining chlorophyll a, b, c 1 and c 2. Biochem Physiol Pflanz 167:194–204
Jin XC, Hu XZ (2003) A comprehensive plan for treating the major polluted regions of Lake Taihu, China. Lakes Reserv Res Manag 8:217–230. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1770.2003.00220.x
Katsoyiannis A, Samara C (2005) Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the conventional activated sludge treatment process: fate and mass balance. Environ Res 97:245–257. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2004.09.001
Kavlock R, Boekelheide K, Chapin R, Cunningham M, Faustman E, Foster P (2002) NTP Center for the Evaluation of Risks to Human Reproduction: phthalates expert panel report on the reproductive and developmental toxicity of butyl benzyl phthalate. Reprod Toxicol 16:453–487
Keith LH, Telliard WA (1979) Priority pollutants: I—a perspective view. Environ Sci Technol 13:416–423
Li HS (2000) Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment. Higher Education Press, Beijing, pp 134–137
Lopes PA, Pinheiro T, Santos MC, Mathias ML, Collares-Pereira MJ, Viegas-Crespo AM (2001) Response of antioxidant enzymes in freshwater fish populations (Leuciscus alburnoides complex) to inorganic pollutants exposure. Sci Total Environ 280:153–163
Maskaoui K, Zhou JL, Hong HS, Zhang ZL (2002) Contamination by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Jiulong River Estuary and Western Xiamen Sea, China. Environ Pollut 118:109–122
Mayer P, Cuhel R, Nyholm N (1997) A simple in vitro fluorescence method for biomass measurements in algal growth inhibition tests. Water Res 31:2525–2531
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase: an enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
MEPPRC (2002) Standard methods for water and wastewater monitoring and analysis, 4th edn. Ministry of Environmental Protection of China, Beijing
Minier C, Abarnou A, Jaouen-Madoulet A, Guellec AML, Tutundiian R, Bocquene G, Leboulenger F (2006) A pollution-monitoring pilot study involving contaminant and biomarker measurements in the Seine Estuary, France, using zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha). Environ Toxicol Chem 25:112–119
Mitter R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Rickert DE, Butterworth BE, Popp JA, Krahn DF (1984) Dinitrotoluene: acute toxicity, oncogenicity, genotoxicity, and metabolism. Crit Rev Toxicol 13:217–234
Sosak-Swiderska B, Tyrawska D, Maslikowska B (1998) Microalgal ecotoxicity test with 3,4-dichloroaniline. Chemosphere 37:2975–2982. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00338-5
Strickland JD, Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull Fish Res Board Can 167:201–203
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(2000)35:3<206::AID-EM8>3.0.CO;2-J
Watanabe M, Suzuki T (2002) Involvement of reactive oxygen stress in cadmium-induced cellular damage in Euglena gracilis. Comp Biochem Physiol C 131:491–500. doi:10.1016/S1532-0456(02)00036-4
WHO (2008) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 3rd edn. WHO, Geneva
Wu YL, Chen HG, Li ZL, Sun LW, Qu MM, Li M, Kong ZM (2008) Genotoxicity evaluation of drinking water sources in human peripheral blood lymphocytes using the comet assay. J Environ Sci 20:487–491. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62084-7
Yuan SY, Liu C, Liao CS, Chang BV (2002) Occurrence and microbial degradation of phthalate esters in Taiwan river sediments. Chemosphere 49:1295–1299. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00495-2
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2008CB418003), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31072217), National Major Project of Science & Technology Ministry of China (No. 2008ZX07101-004, 2008ZX07526-003) and State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology (KF2009-19). Great thanks go to Professor Nils Ekelund, Mid Sweden University, Sundsvall, Sweden for the gift of microalga.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Shi, X., Cui, Y. et al. Organic pollutants and ambient severity for the drinking water source of western Taihu Lake. Ecotoxicology 20, 959–967 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0681-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0681-6